Intro
Discover effective walking pneumonia treatment options, including antibiotics, home remedies, and symptom relief methods, to manage mild pneumonia and prevent complications, promoting speedy recovery and overall respiratory health.
Walking pneumonia, also known as atypical pneumonia, is a mild form of pneumonia that can be caused by various bacteria, viruses, or other microorganisms. It is called "walking" pneumonia because its symptoms are often mild enough that one can still be walking around rather than being bedridden. Despite its mild nature, walking pneumonia can still cause significant discomfort and disruption to daily life. Understanding the treatment options for walking pneumonia is essential for managing its symptoms and preventing complications.
The importance of seeking medical attention for walking pneumonia cannot be overstated. While the condition may seem mild, it can progress to more severe forms of pneumonia if left untreated. Moreover, some individuals, such as the elderly, young children, and those with compromised immune systems, are at a higher risk of developing severe pneumonia. Thus, recognizing the signs and symptoms of walking pneumonia and exploring the available treatment options are crucial steps in managing the condition effectively.
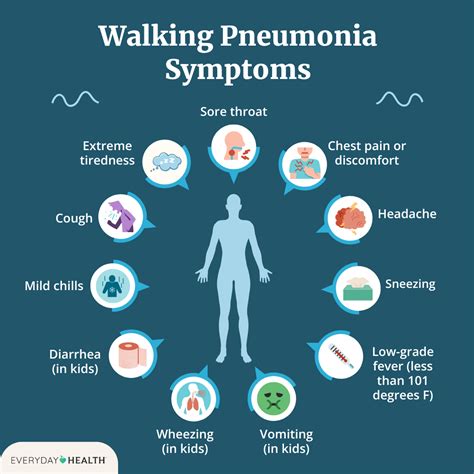
Walking pneumonia can be caused by a variety of pathogens, including Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Chlamydophila pneumoniae, and Legionella pneumophila. The symptoms of walking pneumonia may include cough, fever, headache, and fatigue, among others. Given the range of potential causes and symptoms, treatment for walking pneumonia must be tailored to the individual's specific needs. This may involve a combination of medications, lifestyle modifications, and supportive care to help manage symptoms and support the body's natural healing processes.
Understanding Walking Pneumonia
To develop an effective treatment plan for walking pneumonia, it is essential to understand the underlying cause of the infection. Diagnostic tests, such as chest X-rays and blood tests, may be ordered to confirm the presence of pneumonia and to identify the causative agent. Once the cause is determined, treatment can be targeted to address the specific pathogen involved. For instance, if the pneumonia is caused by bacteria, antibiotics may be prescribed. On the other hand, if the cause is viral, treatment will focus on relieving symptoms and supporting the body's immune response.
Causes of Walking Pneumonia
The causes of walking pneumonia are diverse, ranging from bacterial infections to viral and other microbial causes. Mycoplasma pneumoniae is one of the most common causes of walking pneumonia, particularly in school-aged children and young adults. This bacterium lacks a cell wall, which makes it resistant to certain types of antibiotics, such as penicillin. Other causes include Chlamydophila pneumoniae, Legionella pneumophila, and influenza virus, among others. Understanding the specific cause of walking pneumonia is critical for selecting the most effective treatment approach.Treatment Options for Walking Pneumonia
The treatment of walking pneumonia depends on the causative agent and the severity of symptoms. For bacterial causes, antibiotics are typically prescribed. Macrolides, such as azithromycin and clarithromycin, and fluoroquinolones are commonly used to treat walking pneumonia caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae and other bacteria. It is essential to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication, to ensure that the infection is fully cleared.
For viral causes of walking pneumonia, treatment is focused on relieving symptoms and supporting the body's immune response. This may include over-the-counter medications to reduce fever and relieve cough and headache, as well as plenty of rest and hydration. In some cases, antiviral medications may be prescribed if the pneumonia is caused by influenza virus.
Antibiotic Treatment
Antibiotics are a crucial component of treatment for bacterial walking pneumonia. The choice of antibiotic depends on the suspected or confirmed cause of the pneumonia, as well as the individual's medical history and potential allergies. Macrolides are often the first-line treatment due to their effectiveness against common causes of walking pneumonia, such as Mycoplasma pneumoniae. However, resistance to antibiotics is a growing concern, and in some cases, alternative antibiotics may be necessary.Lifestyle Modifications and Supportive Care

In addition to medication, lifestyle modifications and supportive care play a vital role in managing walking pneumonia. Getting plenty of rest is essential to help the body recover from the infection. Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids, such as water, clear broths, and electrolyte-rich beverages, can help thin out mucus and promote recovery. A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can provide the necessary nutrients to support the immune system.
Managing Symptoms
Managing symptoms is a key aspect of treating walking pneumonia. Over-the-counter medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help reduce fever and relieve headache and body aches. Cough suppressants may be used to relieve cough, although it is essential to note that coughing helps clear mucus from the lungs, and suppressing it completely may not be beneficial. Using a humidifier can add moisture to the air, which may help relieve cough and sore throat.Prevention of Walking Pneumonia

Preventing walking pneumonia involves taking steps to reduce the risk of infection. Practicing good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing, especially during cold and flu season, can help prevent the spread of viral and bacterial infections. Avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick, not sharing personal items, and keeping surfaces clean can also reduce the risk of transmission.
Vaccinations
Vaccinations are an effective way to prevent certain types of pneumonia. The pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) and the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV) are recommended for certain age groups and individuals with high-risk conditions to protect against Streptococcus pneumoniae, a common cause of pneumonia. The influenza vaccine is also crucial in preventing flu-related pneumonia.Complications of Walking Pneumonia

While walking pneumonia is generally mild, it can lead to complications, especially in high-risk individuals. These complications may include respiratory failure, which requires hospitalization and support with oxygen therapy or mechanical ventilation. Other potential complications include bacteremia (bacteria in the bloodstream), meningitis (inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord), and sepsis, a life-threatening response to infection.
High-Risk Groups
Certain groups are at a higher risk of developing severe pneumonia or complications from walking pneumonia. These include older adults, young children, and individuals with weakened immune systems due to chronic illnesses, such as diabetes, heart disease, or HIV/AIDS. Smokers and those with underlying lung diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), are also at increased risk.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, walking pneumonia is a treatable condition that requires prompt medical attention to prevent complications and ensure effective management. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to recover from walking pneumonia and prevent future occurrences. It is essential to follow the prescribed treatment plan, practice good hygiene, and maintain a healthy lifestyle to support immune function and overall well-being.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with walking pneumonia in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information. Together, we can promote awareness and understanding of walking pneumonia and its treatment options.
What are the common symptoms of walking pneumonia?
+The common symptoms of walking pneumonia include cough, fever, headache, fatigue, and sore throat. In some cases, individuals may also experience muscle aches, chills, and loss of appetite.
How is walking pneumonia diagnosed?
+Walking pneumonia is diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests such as chest X-rays and blood tests. These tests help confirm the presence of pneumonia and identify the causative agent.
Can walking pneumonia be prevented?
+Yes, walking pneumonia can be prevented by practicing good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing, avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick, and getting vaccinated against certain types of pneumonia. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can also help support immune function and reduce the risk of infection.
