Intro
Learn about the Tubes Tied Procedure, a permanent birth control method, also known as tubal ligation, involving female sterilization and fallopian tube blocking for contraception.
The decision to undergo a tubal ligation, commonly known as getting one's "tubes tied," is a significant and personal choice that many women consider at some point in their lives. This surgical procedure is designed to provide a permanent form of birth control, preventing pregnancy by blocking the fallopian tubes, which are the pathways through which an egg travels from the ovaries to the uterus. Understanding the procedure, its benefits, potential risks, and what to expect can help individuals make informed decisions about their reproductive health.
For many, the appeal of tubal ligation lies in its effectiveness and permanence. It is a one-time procedure that eliminates the need for daily, weekly, or monthly birth control methods, offering a sense of freedom and reliability. However, it's crucial to approach this decision with careful consideration, as it is intended to be irreversible. The permanence of tubal ligation is a key factor that distinguishes it from other birth control methods and should be a central point of contemplation for those considering the procedure.
The importance of understanding the tubal ligation procedure extends beyond the individual, as it impacts family planning and overall well-being. It's a topic that warrants thorough exploration, including the mechanics of the procedure, recovery times, potential complications, and the emotional aspects of choosing a permanent form of birth control. As such, delving into the specifics of tubal ligation can empower individuals to make decisions that align with their health goals, personal values, and family aspirations.
What is Tubal Ligation?
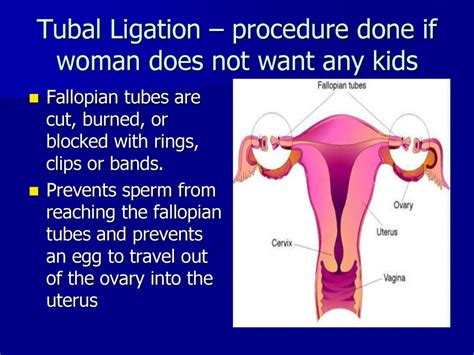
Types of Tubal Ligation
There are several methods used for tubal ligation, each with its own technique for blocking the fallopian tubes. These include: - **Bipolar Coagulation:** This involves using electrical current to cauterize a portion of the fallopian tube, leading to scarring and closure. - **Silicone Ring or Clip:** A small silicone ring or clip is applied to a loop of the fallopian tube, which cuts off blood supply to the section of the tube within the ring or clip, causing it to wither and close off. - **Tubal Ligation with Sutures or Clips:** This method involves tying off the tubes with sutures or applying small clips to block them.Benefits of Tubal Ligation
Risks and Complications
While tubal ligation is generally considered safe, as with any surgical procedure, there are risks and potential complications to be aware of. These can include: - **Infection:** As with any surgery, there is a risk of infection. - **Bleeding or Hematoma:** Excessive bleeding or the formation of a hematoma (a collection of blood outside of blood vessels) at the surgical site. - **Adhesions:** The formation of scar tissue (adhesions) in the pelvic area, which can cause bowel obstruction or chronic pain. - **Ectopic Pregnancy:** Although rare, if a pregnancy were to occur after tubal ligation, it is more likely to be ectopic, where the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, often in a fallopian tube.Recovery and Aftercare

Emotional Considerations
The decision to undergo tubal ligation is not only a physical one but also an emotional and psychological choice. It's a permanent form of birth control, which means it's intended to be a lifelong decision. Therefore, individuals should consider their current and future family planning goals, personal feelings about pregnancy and parenthood, and the potential for regret. Counseling and discussions with a healthcare provider or a therapist can provide valuable insights and support during this decision-making process.Alternatives to Tubal Ligation
Reversal of Tubal Ligation
While tubal ligation is considered a permanent form of birth control, it is sometimes possible to reverse the procedure. However, the success of reversal surgery (tubal reversal) depends on various factors, including the method used for the original tubal ligation, the length of the remaining fallopian tube, and the age of the woman. Tubal reversal is a more complex and costly procedure compared to the initial tubal ligation and may not guarantee the ability to conceive.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts, questions, or experiences regarding tubal ligation in the comments below. Your input can help create a supportive community and provide valuable insights for those navigating their reproductive health options.
What is the success rate of tubal ligation?
+Tubal ligation is highly effective, with a failure rate of less than 1%. However, the success rate can depend on the method used and individual factors.
Can tubal ligation be reversed?
+Yes, tubal ligation can sometimes be reversed through a procedure known as tubal reversal. However, the success of the reversal depends on several factors, including the original method of tubal ligation and the woman's age.
Are there any risks associated with tubal ligation?
+Like any surgical procedure, tubal ligation carries risks such as infection, bleeding, and the formation of adhesions. Additionally, if pregnancy occurs after tubal ligation, it is more likely to be ectopic.
