Intro
Identify Type 2 Diabetes symptoms, including insulin resistance, high blood sugar, and weight loss. Learn to recognize warning signs, manage blood glucose, and prevent complications with lifestyle changes and medical treatment for effective diabetes management.
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way the body processes blood sugar, also known as glucose. It is a major health concern worldwide, and its prevalence is increasing rapidly. The symptoms of type 2 diabetes can be subtle and may develop gradually over time, making it essential to be aware of the warning signs to seek medical attention early. In this article, we will delve into the importance of recognizing type 2 diabetes symptoms, the risks associated with the condition, and the ways to manage and prevent it.
The importance of recognizing type 2 diabetes symptoms cannot be overstated. If left untreated, type 2 diabetes can lead to serious health complications, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. Moreover, type 2 diabetes can also increase the risk of developing other health conditions, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and certain types of cancer. Therefore, it is crucial to be aware of the symptoms of type 2 diabetes and to seek medical attention if any of these symptoms are experienced.
Type 2 diabetes is a complex condition that is influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. While some people may be more susceptible to developing type 2 diabetes due to their genetic makeup, there are many lifestyle changes that can be made to reduce the risk of developing the condition. For example, maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and eating a balanced diet can all help to prevent type 2 diabetes. Additionally, avoiding sugary drinks, limiting saturated and trans fats, and getting enough sleep can also help to reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Type 2 Diabetes Symptoms and Signs

The symptoms of type 2 diabetes can vary from person to person, but common signs include increased thirst and hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, slow healing of cuts and wounds, and frequent infections. Additionally, people with type 2 diabetes may experience numbness or tingling in their hands and feet, and some may also experience erectile dysfunction or vaginal dryness. It is essential to seek medical attention if any of these symptoms are experienced, as early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent long-term health complications.
Common Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
Some of the most common symptoms of type 2 diabetes include: * Increased thirst and hunger * Fatigue * Blurred vision * Slow healing of cuts and wounds * Frequent infections * Numbness or tingling in the hands and feet * Erectile dysfunction or vaginal dryness It is essential to note that some people with type 2 diabetes may not experience any symptoms at all, which is why regular health check-ups are crucial for early diagnosis and treatment.Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes

There are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes. These include:
- Age: People over the age of 45 are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes
- Family history: Having a family history of type 2 diabetes can increase the risk of developing the condition
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes
- Physical inactivity: Leading a sedentary lifestyle can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, such as African Americans, Hispanics, and American Indians, are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes
- History of gestational diabetes: Women who have had gestational diabetes during pregnancy are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes later in life
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): Women with PCOS are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes
Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Managing type 2 diabetes requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle changes, medication, and regular health check-ups. Some of the ways to manage type 2 diabetes include: * Eating a healthy and balanced diet * Engaging in regular physical activity * Losing weight if necessary * Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly * Taking medication as prescribed by a doctor * Getting enough sleep and managing stressType 2 Diabetes Treatment Options
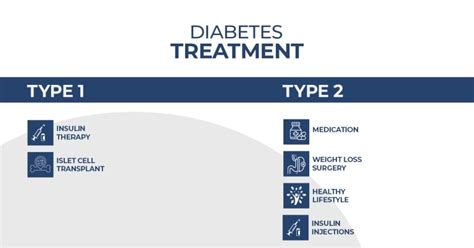
There are several treatment options available for type 2 diabetes, including:
- Metformin: A medication that helps to lower blood sugar levels
- Sulfonylureas: Medications that stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin
- Meglitinides: Medications that stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin
- Thiazolidinediones: Medications that help to improve insulin sensitivity
- GLP-1 receptor agonists: Medications that help to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce glucose production in the liver
- SGLT2 inhibitors: Medications that help to reduce glucose production in the liver and improve insulin sensitivity
Preventing Type 2 Diabetes
Preventing type 2 diabetes requires a long-term commitment to healthy lifestyle habits. Some of the ways to prevent type 2 diabetes include: * Eating a healthy and balanced diet * Engaging in regular physical activity * Maintaining a healthy weight * Avoiding sugary drinks and limiting saturated and trans fats * Getting enough sleep and managing stress * Not smoking and limiting alcohol consumptionType 2 Diabetes Complications
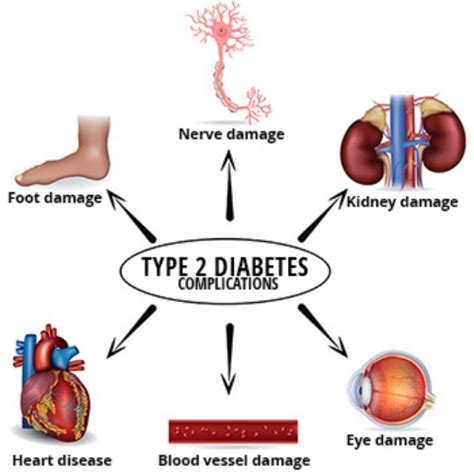
If left untreated, type 2 diabetes can lead to serious health complications, including:
- Heart disease: High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels and nerves, increasing the risk of heart disease
- Kidney damage: High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys, leading to kidney failure
- Nerve damage: High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves, leading to numbness, tingling, and pain
- Blindness: High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to blindness
- Amputations: High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves and blood vessels, leading to amputations
Living with Type 2 Diabetes
Living with type 2 diabetes requires a long-term commitment to healthy lifestyle habits and regular health check-ups. Some of the ways to manage type 2 diabetes include: * Working with a healthcare team to develop a treatment plan * Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly * Taking medication as prescribed by a doctor * Eating a healthy and balanced diet * Engaging in regular physical activity * Getting enough sleep and managing stressType 2 Diabetes and Mental Health
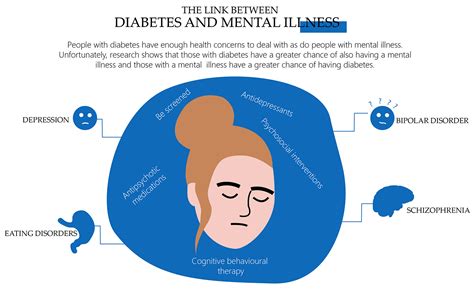
Type 2 diabetes can have a significant impact on mental health, including:
- Depression: People with type 2 diabetes are more likely to experience depression
- Anxiety: People with type 2 diabetes are more likely to experience anxiety
- Eating disorders: People with type 2 diabetes are more likely to experience eating disorders
- Sleep disorders: People with type 2 diabetes are more likely to experience sleep disorders
Support for Type 2 Diabetes
There are many resources available to support people with type 2 diabetes, including: * Support groups: Joining a support group can provide a sense of community and connection with others who are living with type 2 diabetes * Online resources: There are many online resources available to provide information and support for people with type 2 diabetes * Healthcare teams: Working with a healthcare team can provide access to medical care and support * Mental health professionals: Working with a mental health professional can provide support for mental health concernsConclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, type 2 diabetes is a serious health condition that requires a comprehensive approach to management and prevention. By understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options, people can take control of their health and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. If you are experiencing any symptoms of type 2 diabetes, it is essential to seek medical attention early to prevent long-term health complications.
We invite you to share your experiences and thoughts on type 2 diabetes in the comments section below. Your input can help others who are living with the condition, and your stories can inspire and motivate others to take control of their health. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with others who may be at risk of developing type 2 diabetes, as education and awareness are key to prevention and management.
What are the symptoms of type 2 diabetes?
+The symptoms of type 2 diabetes include increased thirst and hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, slow healing of cuts and wounds, and frequent infections.
How can I prevent type 2 diabetes?
+Preventing type 2 diabetes requires a long-term commitment to healthy lifestyle habits, including eating a healthy and balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding sugary drinks and limiting saturated and trans fats.
What are the treatment options for type 2 diabetes?
+The treatment options for type 2 diabetes include metformin, sulfonylureas, meglitinides, thiazolidinediones, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and SGLT2 inhibitors.
