Intro
Identify 5 Type A Flu Symptoms, including fever, cough, and fatigue, and learn about influenza treatment, prevention, and vaccination to manage flu season, avian flu, and swine flu outbreaks effectively.
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is a highly contagious respiratory illness caused by the influenza virus. It can affect anyone, regardless of age or health status, and its symptoms can range from mild to severe. Among the various types of influenza, Type A flu is one of the most common and can cause significant discomfort and health complications. Understanding the symptoms of Type A flu is crucial for early detection, treatment, and prevention of its spread. This article will delve into the specifics of Type A flu symptoms, discussing their importance, the mechanisms behind the flu, and providing practical advice on management and prevention.
The importance of recognizing Type A flu symptoms cannot be overstated. Early identification of the flu can lead to timely medical intervention, which is critical for preventing the progression of the disease and reducing the risk of complications, especially in vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and individuals with underlying health conditions. Furthermore, understanding the symptoms helps in taking appropriate measures to prevent the spread of the virus, thereby protecting not just the individual but the community at large.
Type A flu symptoms are similar to those of other flu types but can sometimes be more severe. They typically include fever, cough, sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, muscle or body aches, headaches, fatigue, and some people may experience vomiting and diarrhea, though this is more common in children than adults. These symptoms can appear suddenly and may vary in severity from person to person. Recognizing these symptoms is the first step in managing the flu effectively and preventing potential complications.
Type A Flu Overview
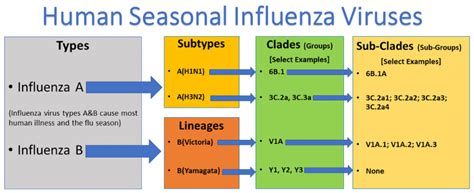
Symptoms of Type A Flu
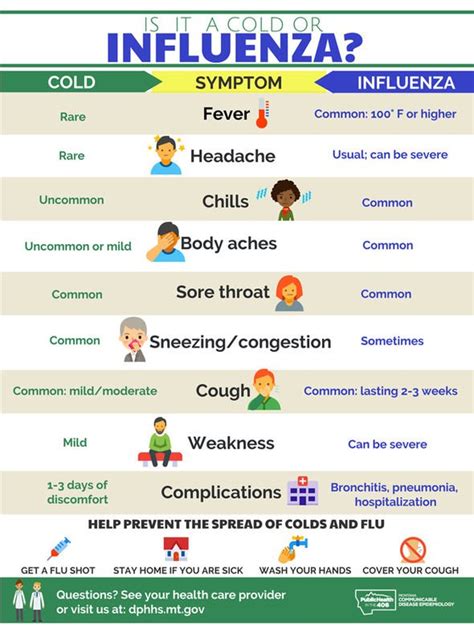
Respiratory Symptoms
Respiratory symptoms are often the most noticeable signs of Type A flu. They can include: - Cough: This can range from a mild, dry cough to a more severe, productive cough. - Sore Throat: Inflammation of the throat can cause pain and discomfort, especially when swallowing. - Runny or Stuffy Nose: The flu can cause nasal congestion and discharge, which can be clear, yellow, or green in color.Systemic Symptoms
Systemic symptoms affect the body as a whole and can include: - Fever: A high body temperature, usually above 100.4°F (38°C), is a common symptom of Type A flu. - Muscle or Body Aches: Pain and stiffness in the muscles, back, and arms can occur due to the body's inflammatory response. - Headaches: Severe headaches are common, possibly due to fever and the body's response to the virus. - Fatigue: Feeling extremely tired or weak is a hallmark symptom of the flu, making it difficult to perform daily activities.Management and Prevention of Type A Flu
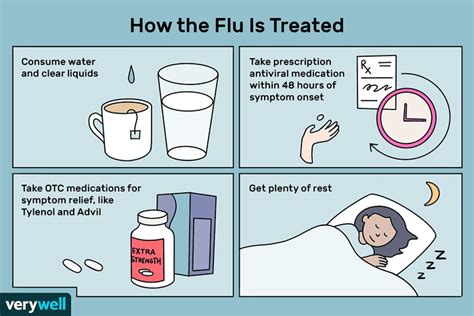
Prevention is key in controlling the spread of Type A flu. The annual flu vaccine is the most effective way to prevent the flu and its complications. Practicing good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing with soap and water, covering the mouth and nose with a tissue when coughing or sneezing, and avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick, can also significantly reduce the risk of infection.
Complications of Type A Flu

Vulnerable Populations
Certain groups of people are at an increased risk of developing severe illness from Type A flu, including: - Older adults (65 years and older) - Young children (under 5 years, especially those under 2) - Pregnant women - People with certain chronic health conditions (like heart disease, lung disease, diabetes) - People with weakened immune systems (such as those with HIV/AIDS, taking immunosuppressive drugs)Diagnosis of Type A Flu
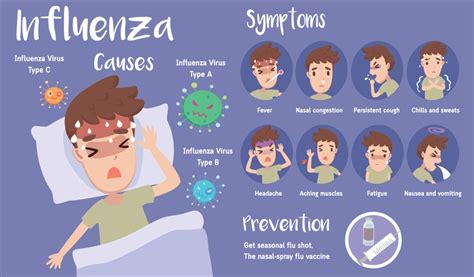
Treatment Options for Type A Flu
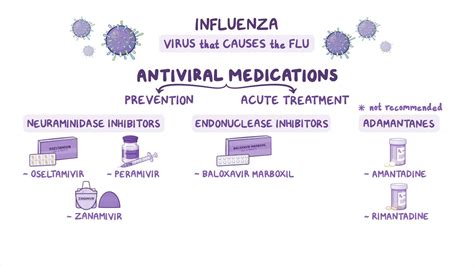
Future Directions in Type A Flu Research

Conclusion and Final Thoughts

What are the most common symptoms of Type A flu?
+The most common symptoms include fever, cough, sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, muscle or body aches, headaches, and fatigue.
How is Type A flu diagnosed?
+Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms and may be confirmed with rapid influenza diagnostic tests (RIDTs) or other flu tests.
What are the best ways to prevent Type A flu?
+The best ways to prevent Type A flu include getting the annual flu vaccine, practicing good hygiene such as frequent handwashing, and avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick.
Who is at high risk of complications from Type A flu?
+Individuals at high risk include older adults, young children, pregnant women, and people with certain chronic health conditions or weakened immune systems.
How is Type A flu treated?
+Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms with rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications, and may include antiviral drugs for individuals at high risk of complications or those who are hospitalized.
We hope this comprehensive guide to Type A flu symptoms, management, and prevention has been informative and helpful. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with managing the flu, please don't hesitate to comment below. Sharing this article with others can also help spread awareness and promote public health. Together, we can work towards reducing the impact of Type A flu and creating healthier communities.
