Intro
Discover types of cardiomyopathy, including dilated, hypertrophic, and restrictive cardiomyopathy, and learn about their symptoms, causes, and treatments for heart failure and arrhythmias.
Cardiomyopathy is a group of diseases that affect the heart muscle, leading to heart failure and other complications. It is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, accounting for approximately 10% of all heart failure cases. The importance of understanding cardiomyopathy cannot be overstated, as it can help individuals take preventive measures and seek early treatment. In this article, we will delve into the different types of cardiomyopathy, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Cardiomyopathy can be classified into several types, each with distinct characteristics and effects on the heart. The most common types of cardiomyopathy are dilated cardiomyopathy, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, restrictive cardiomyopathy, arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy, and left ventricular non-compaction cardiomyopathy. Each type of cardiomyopathy has its unique set of symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, making it essential to understand the differences between them.
The prevalence of cardiomyopathy varies depending on the type, with some forms being more common than others. For instance, dilated cardiomyopathy is the most common type, accounting for approximately 50% of all cardiomyopathy cases. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, on the other hand, is a significant cause of sudden cardiac death in young athletes. Understanding the different types of cardiomyopathy and their characteristics is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies and improving patient outcomes.
Types Of Cardiomyopathy
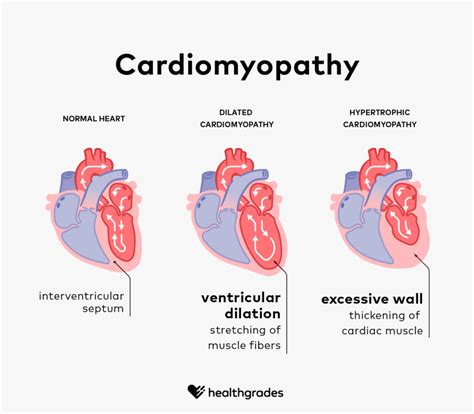
There are several types of cardiomyopathy, each with distinct characteristics and effects on the heart. The main types of cardiomyopathy are:
- Dilated cardiomyopathy: This is the most common type of cardiomyopathy, accounting for approximately 50% of all cases. It is characterized by an enlargement of the heart, which leads to a reduction in the heart's ability to pump blood effectively.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: This type of cardiomyopathy is characterized by a thickening of the heart muscle, which can lead to obstruction of blood flow and increased risk of sudden cardiac death.
- Restrictive cardiomyopathy: This type of cardiomyopathy is characterized by a stiffening of the heart muscle, which makes it difficult for the heart to fill with blood.
- Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy: This type of cardiomyopathy is characterized by a replacement of the heart muscle with fatty tissue, leading to abnormal heart rhythms and increased risk of sudden cardiac death.
- Left ventricular non-compaction cardiomyopathy: This type of cardiomyopathy is characterized by a thickening of the heart muscle, which leads to a reduction in the heart's ability to pump blood effectively.
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
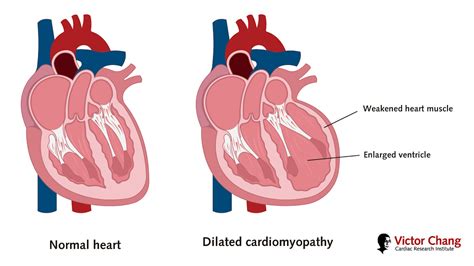
Dilated cardiomyopathy is the most common type of cardiomyopathy, accounting for approximately 50% of all cases. It is characterized by an enlargement of the heart, which leads to a reduction in the heart's ability to pump blood effectively. The symptoms of dilated cardiomyopathy include:
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Swelling in the legs and feet
- Palpitations
- Chest pain
The causes of dilated cardiomyopathy include:
- Genetics
- Viral infections
- Toxic substances
- Nutritional deficiencies
- Coronary artery disease
Treatment options for dilated cardiomyopathy include:
- Medications to improve heart function and reduce symptoms
- Implantable devices such as pacemakers and defibrillators
- Heart transplantation in severe cases
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
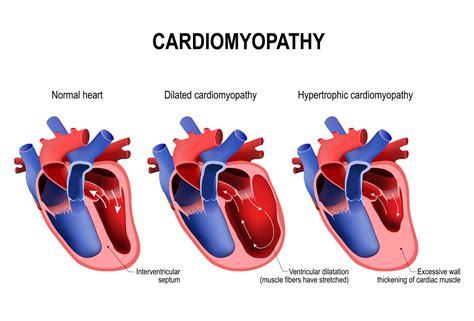
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a significant cause of sudden cardiac death in young athletes. It is characterized by a thickening of the heart muscle, which can lead to obstruction of blood flow and increased risk of sudden cardiac death. The symptoms of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy include:
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Palpitations
- Dizziness
The causes of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy include:
- Genetics
- Hypertension
- Coronary artery disease
- Obesity
Treatment options for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy include:
- Medications to reduce symptoms and improve heart function
- Implantable devices such as pacemakers and defibrillators
- Surgical procedures to remove excess heart muscle tissue
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
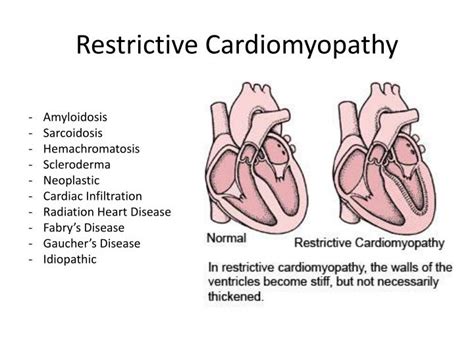
Restrictive cardiomyopathy is characterized by a stiffening of the heart muscle, which makes it difficult for the heart to fill with blood. The symptoms of restrictive cardiomyopathy include:
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Swelling in the legs and feet
- Palpitations
- Chest pain
The causes of restrictive cardiomyopathy include:
- Genetics
- Amyloidosis
- Sarcoidosis
- Hemochromatosis
Treatment options for restrictive cardiomyopathy include:
- Medications to improve heart function and reduce symptoms
- Implantable devices such as pacemakers and defibrillators
- Heart transplantation in severe cases
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy

Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy is characterized by a replacement of the heart muscle with fatty tissue, leading to abnormal heart rhythms and increased risk of sudden cardiac death. The symptoms of arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy include:
- Palpitations
- Dizziness
- Fainting
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
The causes of arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy include:
- Genetics
- Viral infections
- Toxic substances
Treatment options for arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy include:
- Medications to reduce symptoms and improve heart function
- Implantable devices such as pacemakers and defibrillators
- Surgical procedures to remove excess fatty tissue
Left Ventricular Non-Compaction Cardiomyopathy

Left ventricular non-compaction cardiomyopathy is characterized by a thickening of the heart muscle, which leads to a reduction in the heart's ability to pump blood effectively. The symptoms of left ventricular non-compaction cardiomyopathy include:
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Swelling in the legs and feet
- Palpitations
- Chest pain
The causes of left ventricular non-compaction cardiomyopathy include:
- Genetics
- Viral infections
- Toxic substances
Treatment options for left ventricular non-compaction cardiomyopathy include:
- Medications to improve heart function and reduce symptoms
- Implantable devices such as pacemakers and defibrillators
- Heart transplantation in severe cases
Diagnosis Of Cardiomyopathy
The diagnosis of cardiomyopathy typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. The diagnostic tests used to diagnose cardiomyopathy include: * Electrocardiogram (ECG) * Echocardiogram * Cardiac catheterization * Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) * Computed tomography (CT) scanTreatment Options For Cardiomyopathy
The treatment options for cardiomyopathy depend on the type and severity of the disease. The treatment options include: * Medications to improve heart function and reduce symptoms * Implantable devices such as pacemakers and defibrillators * Surgical procedures to remove excess heart muscle tissue or repair damaged heart valves * Heart transplantation in severe casesWhat are the symptoms of cardiomyopathy?
+The symptoms of cardiomyopathy include shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling in the legs and feet, palpitations, and chest pain.
What are the causes of cardiomyopathy?
+The causes of cardiomyopathy include genetics, viral infections, toxic substances, nutritional deficiencies, and coronary artery disease.
How is cardiomyopathy diagnosed?
+The diagnosis of cardiomyopathy typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests such as electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiogram, cardiac catheterization, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and computed tomography (CT) scan.
What are the treatment options for cardiomyopathy?
+The treatment options for cardiomyopathy depend on the type and severity of the disease, and may include medications, implantable devices, surgical procedures, and heart transplantation.
Can cardiomyopathy be prevented?
+While cardiomyopathy cannot be completely prevented, certain risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and smoking can be managed to reduce the risk of developing the disease.
In conclusion, cardiomyopathy is a complex and multifaceted disease that requires a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment. By understanding the different types of cardiomyopathy, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition and improve their quality of life. If you or someone you know is affected by cardiomyopathy, we encourage you to share your experiences and ask questions in the comments section below. Additionally, please consider sharing this article with others who may benefit from this information, and take a moment to explore our other resources on heart health and wellness.
