Intro
Decoding Urine Test Results: Understand abnormal findings, kidney function, and diabetes indicators with our guide to interpreting urine analysis, including pH, protein, and blood levels.
Urine tests are a crucial diagnostic tool used by healthcare professionals to assess various aspects of a patient's health. These tests can help identify underlying medical conditions, monitor the progression of diseases, and even detect the presence of illicit substances. With the advancements in medical technology, urine tests have become more sophisticated, allowing for the detection of a wide range of substances and conditions. As a result, understanding urine test results has become increasingly important for both healthcare professionals and patients alike.
The importance of urine test results cannot be overstated, as they provide valuable insights into a patient's overall health. By analyzing the components of urine, healthcare professionals can identify potential health risks, diagnose medical conditions, and develop effective treatment plans. Moreover, urine tests are non-invasive, relatively inexpensive, and can be performed quickly, making them a popular diagnostic tool. However, interpreting urine test results can be complex, and it requires a thorough understanding of the various components and their corresponding reference ranges.
In recent years, there has been a significant increase in the use of urine tests for diagnostic purposes. This is largely due to the advancements in technology, which have enabled the development of more sophisticated testing methods. As a result, urine tests are now used to diagnose a wide range of medical conditions, including kidney disease, diabetes, and urinary tract infections. Furthermore, urine tests are also used to monitor the progression of diseases, making them an essential tool for healthcare professionals. With the increasing reliance on urine tests, it is essential to understand the various components of urine and how to interpret test results.
Introduction to Urine Test Results

Understanding Urine Test Components
Specific Gravity
Specific gravity measures the concentration of urine, which can indicate hydration levels and kidney function. A high specific gravity can indicate dehydration, while a low specific gravity can indicate overhydration. The reference range for specific gravity is typically between 1.002 and 1.035.pH
pH measures the acidity of urine, which can indicate various health conditions. A low pH can indicate kidney disease, while a high pH can indicate urinary tract infections. The reference range for pH is typically between 4.5 and 8.0.Interpreting Urine Test Results
Identifying Abnormal Results
Identifying abnormal results is crucial for accurate interpretation of urine test results. Abnormal results can indicate various health conditions, and understanding their significance is essential for developing effective treatment plans. For example, a high protein level can indicate kidney damage, while a high glucose level can indicate diabetes.Developing Treatment Plans
Developing treatment plans based on urine test results requires a thorough understanding of the various components and their corresponding reference ranges. Healthcare professionals use urine test results to identify potential health risks, diagnose medical conditions, and develop effective treatment plans. For example, a high protein level may require medication to reduce proteinuria, while a high glucose level may require lifestyle modifications to manage diabetes.Common Urine Test Results
Proteinuria
Proteinuria is a common urine test result that can indicate kidney damage. The presence of protein in urine can be caused by various factors, including diabetes, hypertension, and kidney disease.Hematuria
Hematuria is another common urine test result that can indicate urinary tract infections or kidney stones. The presence of blood in urine can be caused by various factors, including kidney disease, urinary tract infections, and trauma.Urine Test Results in Clinical Practice
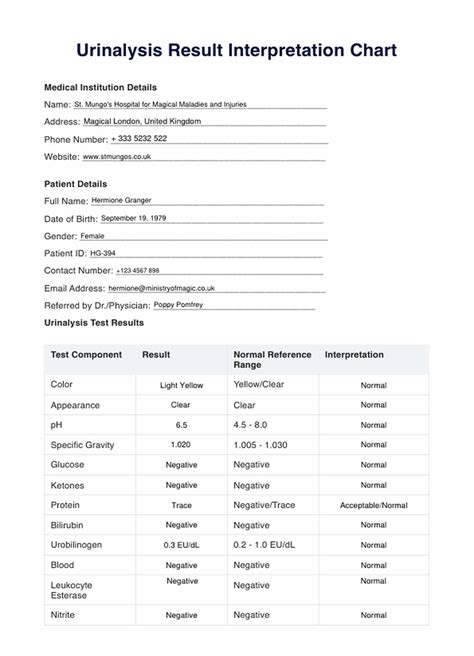
Diagnosing Medical Conditions
Urine test results can be used to diagnose various medical conditions, including kidney disease, diabetes, and urinary tract infections. The presence of protein, glucose, or blood in urine can indicate underlying health conditions.Monitoring Disease Progression
Urine test results can also be used to monitor the progression of diseases, such as kidney disease or diabetes. Regular urine tests can help healthcare professionals track changes in a patient's condition and adjust treatment plans accordingly.Limitations of Urine Test Results

False Negative Results
False negative results can occur when a urine test fails to detect an underlying health condition. This can be caused by various factors, including laboratory errors or the presence of substances that interfere with test results.False Positive Results
False positive results can occur when a urine test indicates an underlying health condition that is not present. This can be caused by various factors, including laboratory errors or the presence of substances that interfere with test results.What is the purpose of a urine test?
+A urine test is used to assess various aspects of a patient's health, including kidney function, diabetes, and urinary tract infections.
How are urine test results interpreted?
+Urine test results are interpreted by comparing the levels of various components, such as protein, glucose, and ketones, to established reference ranges.
What are the limitations of urine test results?
+Urine test results have limitations, including the possibility of false negative or false positive results, and may not detect all underlying health conditions.
We hope this comprehensive guide to understanding urine test results has been informative and helpful. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from this information. By working together, we can promote better health and wellness for all.
