Intro
Discover 5 uses of Metronidazole, an antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication, treating infections, bacterial vaginosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, giardiasis, and amoebiasis, with its antimicrobial properties.
Metronidazole is a versatile antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication that has been widely used for several decades. Its effectiveness against a range of infections has made it a staple in the treatment of various conditions. The importance of metronidazole lies in its ability to target and eliminate harmful microorganisms, thereby alleviating symptoms and promoting recovery. Understanding the uses of metronidazole is crucial for healthcare professionals and patients alike, as it can help in making informed decisions about treatment options. The versatility of metronidazole is evident in its application across different medical specialties, from gastroenterology to gynecology.
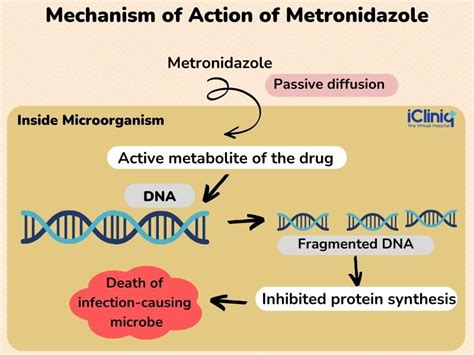
The mechanism of action of metronidazole involves interfering with the DNA of microorganisms, ultimately leading to their death. This process is crucial for treating infections caused by susceptible organisms. Metronidazole's spectrum of activity includes anaerobic bacteria, protozoa, and certain types of fungi, making it a valuable asset in the fight against a variety of infectious diseases. Its use has been documented in numerous clinical settings, highlighting its efficacy and safety profile when used appropriately. The application of metronidazole is not limited to human medicine; it is also used in veterinary practice to treat infections in animals.
Metronidazole's role in modern medicine is multifaceted, reflecting its broad-spectrum activity. It is used to treat infections of the abdomen, skin, tissue, and nervous system, among others. The drug is particularly useful in cases where the infection is caused by anaerobic bacteria, which are bacteria that thrive in environments lacking oxygen. Its antiprotozoal properties make it an essential component in the treatment of certain parasitic infections. Furthermore, metronidazole has been used in combination with other medications to enhance its effectiveness against complex infections. The combination therapies involving metronidazole have shown promising results in clinical trials, underscoring the drug's potential in addressing challenging infectious diseases.
Introduction to Metronidazole

Uses of Metronidazole

Benefits of Metronidazole
The benefits of metronidazole are numerous, reflecting its broad spectrum of activity and its efficacy in treating various infections. Some of the key benefits include: - **Effective Against Anaerobic Bacteria:** Metronidazole's ability to target and eliminate anaerobic bacteria makes it a valuable asset in the treatment of infections that are difficult to manage with other antibiotics. - **Antiprotozoal Activity:** Its effectiveness against certain protozoa, such as Trichomonas vaginalis and Giardia lamblia, underscores its utility in treating parasitic infections. - **Wide Range of Applications:** Metronidazole can be used to treat infections in different parts of the body, from the gastrointestinal tract to the genital area. - **Combination Therapies:** It can be used in combination with other medications to enhance its effectiveness against complex or resistant infections.Working Mechanism of Metronidazole
Steps for Taking Metronidazole
To ensure the effective use of metronidazole, patients should follow these steps: 1. **Take as Directed:** Metronidazole should be taken exactly as directed by the healthcare provider. The dosage and duration of treatment depend on the type and severity of the infection. 2. **Complete the Course:** It is essential to complete the full course of treatment, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication. Stopping the treatment early can lead to the development of resistance. 3. **Avoid Alcohol:** Patients should avoid consuming alcohol during and for a short period after treatment with metronidazole, as it can cause unpleasant reactions. 4. **Monitor for Side Effects:** Patients should be aware of potential side effects and report them to their healthcare provider if they occur.Practical Examples and Statistical Data
Common Side Effects of Metronidazole
While metronidazole is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects in some individuals. Common side effects include: - **Gastrointestinal Disturbances:** Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea are among the most common side effects. - **Metallic Taste:** Some patients may experience a metallic taste during treatment. - **Headache:** Headaches can occur in some individuals taking metronidazole. - **Allergic Reactions:** Rarely, metronidazole can cause allergic reactions, which can be severe.Conclusion and Future Directions

Final Thoughts
Metronidazole's impact on modern medicine is undeniable. Its ability to treat a wide range of infections has improved patient outcomes and saved countless lives. As we move forward, it is essential to continue monitoring the effectiveness of metronidazole and to explore new ways to enhance its efficacy while minimizing its potential for side effects. By doing so, we can ensure that metronidazole remains a valuable tool in the fight against infectious diseases.What is metronidazole used for?
+Metronidazole is used to treat various infections caused by anaerobic bacteria and protozoa, including bacterial vaginosis, trichomoniasis, and giardiasis.
How does metronidazole work?
+Metronidazole works by interfering with the DNA of microorganisms, ultimately leading to their death. It is particularly effective against anaerobic bacteria and certain protozoa.
What are the common side effects of metronidazole?
+Common side effects of metronidazole include gastrointestinal disturbances, metallic taste, headache, and allergic reactions. Rarely, it can cause severe side effects, and patients should report any unusual symptoms to their healthcare provider.
We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with metronidazole in the comments section below. Your input can help others understand the benefits and potential drawbacks of this medication. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from the information. Let's work together to promote awareness and understanding of metronidazole and its role in managing infectious diseases.
