Intro
Vaginal bleeding not menstrual can be caused by various factors, including hormonal changes, infections, and reproductive issues, requiring medical attention to diagnose and treat underlying conditions like endometrial hyperplasia or cervical polyps.
Vaginal bleeding that is not associated with menstruation can be a cause for concern for many women. It is essential to understand that vaginal bleeding can occur at any time and may be caused by a variety of factors. In some cases, it may be a sign of an underlying medical condition that requires attention. Women who experience vaginal bleeding that is not related to their menstrual cycle should seek medical attention to determine the cause and receive proper treatment.
Vaginal bleeding can be classified into different types, including spotting, light bleeding, and heavy bleeding. Spotting refers to a small amount of bleeding that may appear as a light stain on underwear or toilet paper. Light bleeding is a heavier flow than spotting but is still relatively light. Heavy bleeding, on the other hand, is a more significant flow that may require the use of pads or tampons to manage. The type and severity of vaginal bleeding can help healthcare providers determine the underlying cause.
Understanding the causes of vaginal bleeding is crucial for women to take control of their reproductive health. Vaginal bleeding can be caused by hormonal changes, infections, or physical trauma. Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menopause, or puberty can lead to vaginal bleeding. Infections such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) or sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can also cause bleeding. Physical trauma, such as a blow to the abdomen or vaginal area, can cause bleeding as well.
Vaginal Bleeding Causes
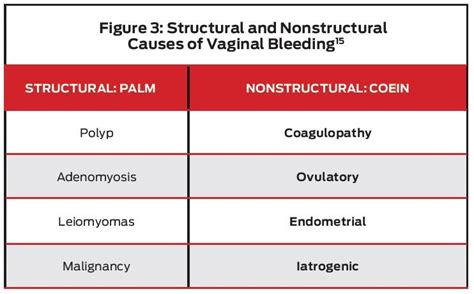
Hormonal Causes
Hormonal fluctuations can cause vaginal bleeding in women of all ages. During pregnancy, hormonal changes can lead to vaginal bleeding, especially during the first trimester. Menstrual irregularities, such as amenorrhea (absence of menstruation) or oligomenorrhea (infrequent menstruation), can also cause vaginal bleeding. Puberty is another time when hormonal fluctuations can lead to vaginal bleeding. The onset of menstruation can be irregular, and girls may experience vaginal bleeding as their bodies adjust to the new hormonal changes.Vaginal Bleeding Symptoms

Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing the cause of vaginal bleeding requires a thorough medical evaluation. Healthcare providers will typically perform a physical examination, take a medical history, and order diagnostic tests, such as a pregnancy test, ultrasound, or endometrial biopsy. The treatment for vaginal bleeding depends on the underlying cause. In some cases, treatment may involve medication, such as hormones or antibiotics, to manage symptoms and address the underlying condition. In other cases, treatment may involve surgical procedures, such as a dilation and curettage (D&C) or hysterectomy, to remove abnormal tissue or the uterus.Vaginal Bleeding Prevention

Risk Factors
Certain risk factors can increase a woman's likelihood of experiencing vaginal bleeding. Women who are pregnant, have a history of pelvic surgery, or have a family history of bleeding disorders are at higher risk of experiencing vaginal bleeding. Women who are taking certain medications, such as anticoagulants or hormone replacement therapy, are also at higher risk. Additionally, women who have certain medical conditions, such as PCOS or endometriosis, are at higher risk of experiencing vaginal bleeding.Vaginal Bleeding Complications

Emotional and Psychological Impact
Vaginal bleeding can have a significant emotional and psychological impact on women. Women who experience vaginal bleeding may feel anxious, scared, or embarrassed, especially if they are unsure of the cause. The uncertainty and unpredictability of vaginal bleeding can lead to feelings of frustration and helplessness. Women who experience vaginal bleeding should seek support from healthcare providers, family, and friends to manage their emotional and psychological well-being.Vaginal Bleeding Management

Future Directions
Future research should focus on developing more effective treatments for vaginal bleeding and improving our understanding of the underlying causes. Additionally, healthcare providers should prioritize patient education and awareness, ensuring that women have access to accurate and reliable information about vaginal bleeding. By working together, we can reduce the incidence and impact of vaginal bleeding, improving the health and well-being of women worldwide.Vaginal Bleeding Resources
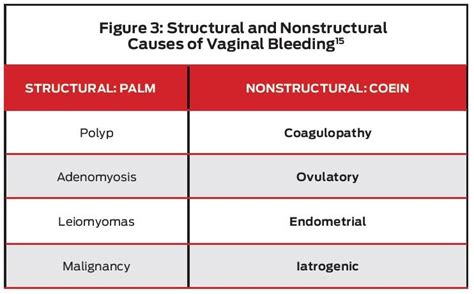
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, vaginal bleeding is a common condition that can have a significant impact on a woman's physical and emotional well-being. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, women can take control of their reproductive health. It is essential to seek medical attention if women experience any unusual vaginal bleeding, as prompt treatment can reduce the risk of complications and improve outcomes. Women who experience vaginal bleeding should prioritize their health and well-being, seeking support from healthcare providers, family, and friends.What are the common causes of vaginal bleeding?
+Vaginal bleeding can be caused by hormonal changes, infections, or physical trauma. Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menopause, or puberty can lead to vaginal bleeding. Infections such as PID or STIs can also cause bleeding. Physical trauma, such as a blow to the abdomen or vaginal area, can cause bleeding as well.
How is vaginal bleeding diagnosed?
+Diagnosing the cause of vaginal bleeding requires a thorough medical evaluation. Healthcare providers will typically perform a physical examination, take a medical history, and order diagnostic tests, such as a pregnancy test, ultrasound, or endometrial biopsy.
What are the treatment options for vaginal bleeding?
+The treatment for vaginal bleeding depends on the underlying cause. In some cases, treatment may involve medication, such as hormones or antibiotics, to manage symptoms and address the underlying condition. In other cases, treatment may involve surgical procedures, such as a D&C or hysterectomy, to remove abnormal tissue or the uterus.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of vaginal bleeding. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider. Remember to prioritize your health and well-being, and seek medical attention if you experience any unusual vaginal bleeding. Share this article with your friends and family to help raise awareness about vaginal bleeding and promote reproductive health.
