Intro
Amoxicillin is a type of antibiotic that belongs to the penicillin class of medications. It is widely used to treat various bacterial infections, including pneumonia, bronchitis, and infections of the skin, ear, and urinary tract. Amoxicillin works by stopping the growth of bacteria, which helps to alleviate symptoms and prevent the spread of infection. It is available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and liquid suspensions, making it a versatile treatment option for patients of all ages.
The importance of understanding amoxicillin and its uses cannot be overstated. With the rise of antibiotic resistance, it is crucial to use antibiotics responsibly and only when necessary. Amoxicillin is a commonly prescribed medication, and its effectiveness in treating bacterial infections has made it a staple in many healthcare settings. However, it is essential to use amoxicillin under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as misuse or overuse can lead to adverse effects and contribute to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Amoxicillin has been a cornerstone in the treatment of bacterial infections for decades. Its broad-spectrum activity and relatively low cost make it an attractive option for healthcare providers. Moreover, amoxicillin is generally well-tolerated, with mild side effects that are often temporary and manageable. As a result, amoxicillin has become a popular choice for treating a wide range of infections, from mild to severe. In this article, we will delve into the world of amoxicillin, exploring its mechanisms, benefits, and potential drawbacks, as well as providing practical guidance on its use and administration.
What is Amoxicillin Used For?
Amoxicillin is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, and urinary tract infections. It is also used to treat infections caused by specific bacteria, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Escherichia coli. Amoxicillin is often prescribed for patients with pneumonia, bronchitis, and sinusitis, as well as for those with ear infections, such as otitis media. Additionally, amoxicillin is used to treat infections of the skin and soft tissues, including cellulitis, abscesses, and wound infections.
Types of Infections Treated with Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin is effective against a range of bacterial infections, including: * Respiratory tract infections, such as pneumonia and bronchitis * Skin and soft tissue infections, such as cellulitis and abscesses * Urinary tract infections, such as cystitis and pyelonephritis * Ear infections, such as otitis media * Infections caused by specific bacteria, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzaeHow Does Amoxicillin Work?
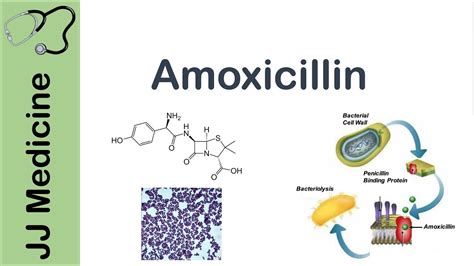
Amoxicillin works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria. It does this by interfering with the production of the bacterial cell wall, which is essential for the bacteria's survival. Amoxicillin binds to the bacterial cell wall, preventing the formation of a stable cell wall and ultimately leading to the death of the bacteria. This mechanism of action makes amoxicillin effective against a wide range of bacterial infections.
Benefits of Amoxicillin
The benefits of amoxicillin include: * Broad-spectrum activity against a range of bacterial infections * Relatively low cost compared to other antibiotics * Generally well-tolerated, with mild side effects * Available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and liquid suspensions * Effective against infections caused by specific bacteria, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzaeAdministration and Dosage

Amoxicillin is typically administered orally, either as a capsule, tablet, or liquid suspension. The dosage and duration of treatment will depend on the type and severity of the infection, as well as the patient's age and weight. It is essential to follow the prescribed dosage and administration instructions carefully, as misuse or overuse can lead to adverse effects and contribute to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Dosage Guidelines
The dosage guidelines for amoxicillin vary depending on the infection being treated and the patient's age and weight. Typical dosage ranges include: * Adults: 500-1000 mg every 8-12 hours * Children: 25-50 mg/kg/day, divided into 2-3 doses * Infants: 20-30 mg/kg/day, divided into 2-3 dosesSide Effects and Interactions

Like all medications, amoxicillin can cause side effects and interact with other medications. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. More severe side effects can include allergic reactions, such as anaphylaxis, and liver or kidney damage. Amoxicillin can also interact with other medications, including blood thinners, such as warfarin, and medications that reduce stomach acid, such as antacids.
Precautions and Contraindications
Precautions and contraindications for amoxicillin include: * Allergic reactions to penicillin or other antibiotics * Pregnancy and breastfeeding * Kidney or liver disease * Use of blood thinners or other medications that interact with amoxicillinResistance and Misuse
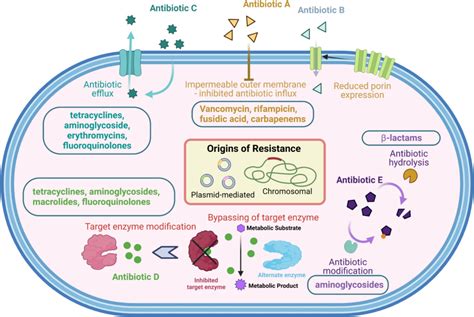
The misuse and overuse of amoxicillin have contributed to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. This has significant implications for public health, as antibiotic-resistant bacteria can spread rapidly and cause severe infections that are difficult to treat. It is essential to use amoxicillin responsibly and only when necessary, as prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Strategies to Prevent Resistance
Strategies to prevent antibiotic resistance include: * Using antibiotics only when necessary * Following prescribed dosage and administration instructions carefully * Completing the full course of treatment, even if symptoms improve * Avoiding the use of antibiotics for viral infections, such as the common cold or fluWhat is amoxicillin used for?
+Amoxicillin is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, and urinary tract infections.
How does amoxicillin work?
+Amoxicillin works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria, interfering with the production of the bacterial cell wall, and ultimately leading to the death of the bacteria.
What are the common side effects of amoxicillin?
+Common side effects of amoxicillin include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. More severe side effects can include allergic reactions, such as anaphylaxis, and liver or kidney damage.
In conclusion, amoxicillin is a widely used antibiotic that is effective against a range of bacterial infections. Its benefits include broad-spectrum activity, relatively low cost, and general tolerability. However, it is essential to use amoxicillin responsibly and only when necessary, as prescribed by a healthcare professional. By understanding the mechanisms, benefits, and potential drawbacks of amoxicillin, patients can make informed decisions about their treatment and contribute to the prevention of antibiotic resistance. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with amoxicillin, and to take an active role in promoting responsible antibiotic use.
