Vyvanse is a prescription medication that has been widely used to treat Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in both children and adults. The importance of understanding Vyvanse and its effects cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts the daily lives of those who rely on this medication. With its increasing use, there's a growing need for accurate and comprehensive information about Vyvanse. This article aims to delve into the key aspects of Vyvanse, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, potential side effects, and other crucial information that individuals and their families should know.
The impact of ADHD on individuals and their families can be significant, affecting daily routines, academic performance, and professional productivity. Vyvanse, with its unique formulation, has emerged as a significant treatment option, offering hope for improved management of ADHD symptoms. However, like any medication, it comes with its set of benefits and risks, which need to be thoroughly understood. By exploring the facts surrounding Vyvanse, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment plans and better navigate the challenges associated with ADHD.
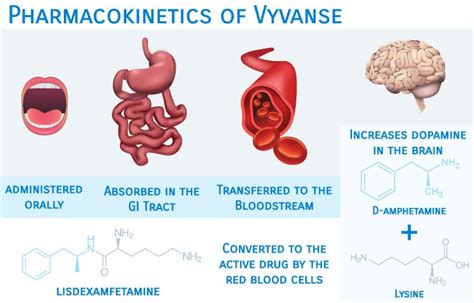
Understanding Vyvanse requires a look into its composition, how it works, and its effects on the body. Vyvanse, or lisdexamfetamine, is a central nervous system stimulant that affects chemicals in the brain and nerves that contribute to hyperactivity and impulse control. It's known for its efficacy in managing ADHD symptoms, such as inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. The medication has a unique mechanism of action, which sets it apart from other stimulants used in ADHD treatment. As the medical community and patients continue to learn more about Vyvanse, its role in ADHD management is becoming more defined, highlighting the need for ongoing education and discussion about its use.
Introduction to Vyvanse
Vyvanse is prescribed to patients with ADHD to help increase their attention, decrease impulsivity, and decrease hyperactivity. It's also approved for the treatment of moderate to severe binge eating disorder in adults. The medication comes in capsule form and is usually taken once a day in the morning. Vyvanse should be used as part of a total treatment program for ADHD that may include counseling or other therapies.
How Vyvanse Works
The mechanism of action of Vyvanse involves the inhibition of the reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine into the presynaptic neuron after they have been released into the synaptic cleft. This increase in the level of these neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft is thought to contribute to the therapeutic effects and side effects of Vyvanse. The unique aspect of Vyvanse is its prodrug formulation, which means it is inactive until it is metabolized by the body into its active form, d-amphetamine. This characteristic may contribute to a lower potential for abuse compared to other stimulant medications.
Benefits of Vyvanse
The benefits of Vyvanse include its efficacy in improving attention and reducing impulsivity and hyperactivity in individuals with ADHD. Clinical trials have demonstrated that Vyvanse can significantly improve ADHD symptoms in both children and adults. Additionally, its once-daily dosing can improve compliance, making it easier for patients to maintain their treatment regimen. The medication has also been approved for the treatment of binge eating disorder, providing an option for individuals struggling with this condition.
Potential Side Effects
Like any medication, Vyvanse can cause side effects, which may vary from person to person. Common side effects include decreased appetite, insomnia, irritability, and anxiety. Less common but more serious side effects can include increased heart rate and blood pressure, which may be a concern for individuals with pre-existing heart conditions. It's essential for patients to discuss their medical history and any concerns with their healthcare provider before starting Vyvanse.
Dosage and Administration
The dosage of Vyvanse should be individualized according to the therapeutic needs and response of the patient. The recommended starting dose for ADHD is 30 mg once daily in the morning. The dosage may be increased in increments of 10 mg to 20 mg at approximately weekly intervals. The maximum recommended dose is 70 mg per day. For binge eating disorder, the recommended dose is 50 mg to 70 mg once daily.
Interactions and Warnings
Vyvanse can interact with other medications, including certain antidepressants, and may not be suitable for everyone, especially those with certain medical conditions. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking and any medical conditions they have. Additionally, Vyvanse has a boxed warning regarding the risk of abuse and dependence. It's classified as a Schedule II controlled substance, indicating a high potential for abuse.
Long-Term Effects
The long-term effects of Vyvanse are a subject of ongoing research. While it has been shown to be effective in managing ADHD symptoms over time, the potential for long-term side effects, such as growth suppression in children, needs to be monitored. Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are essential to assess the effectiveness of the medication and manage any side effects.
Alternatives to Vyvanse
For individuals who may not respond well to Vyvanse or experience significant side effects, there are alternative treatments available. These include other stimulant medications, such as Ritalin or Adderall, and non-stimulant medications like Strattera. Behavioral therapy and lifestyle changes can also be effective in managing ADHD symptoms. The choice of treatment should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider, taking into account the individual's specific needs and medical history.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, Vyvanse is a valuable treatment option for ADHD and binge eating disorder, offering significant benefits for many individuals. However, like any medication, it must be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider, with careful monitoring of side effects and interactions. As research continues to uncover more about the mechanisms and effects of Vyvanse, it's essential for patients, families, and healthcare providers to stay informed and work together to optimize treatment outcomes.
To further enhance your understanding of Vyvanse and its implications, we invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, or questions in the comments below. Your engagement can help create a supportive community and facilitate the exchange of valuable information. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this comprehensive overview of Vyvanse.
What is Vyvanse used for?
+
Vyvanse is used to treat Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in children and adults, and it is also approved for the treatment of moderate to severe binge eating disorder in adults.
How does Vyvanse work?
+
Vyvanse works by increasing the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, such as dopamine and norepinephrine, which helps to improve attention and reduce impulsivity and hyperactivity.
What are the common side effects of Vyvanse?
+
Common side effects of Vyvanse include decreased appetite, insomnia, irritability, and anxiety. Less common but more serious side effects can include increased heart rate and blood pressure.
Can Vyvanse be used in conjunction with other medications?
+
Vyvanse can interact with other medications, so it's essential to inform your healthcare provider about all medications you are taking before starting Vyvanse.
Is Vyvanse addictive?
+
Vyvanse has a potential for abuse and dependence, and it is classified as a Schedule II controlled substance. However, when used as directed by a healthcare provider, the risk of addiction can be minimized.