Intro
Discover the Furosemide Medication Guide, covering dosage, side effects, and interactions. Learn about diuretic therapy, edema treatment, and loop diuretics for hypertension and fluid retention management.
The importance of understanding medications cannot be overstated, especially when it comes to managing conditions that affect the heart, liver, or kidneys. One such medication that has been widely used for decades is furosemide, known by its brand name Lasix among others. Furosemide is a loop diuretic that helps the body get rid of excess water and salt by increasing urine production. It is commonly prescribed for patients with edema (swelling) associated with congestive heart failure, liver disease, or a kidney disorder such as nephrotic syndrome. Understanding how furosemide works, its benefits, potential side effects, and how to take it safely is crucial for patients to manage their condition effectively.
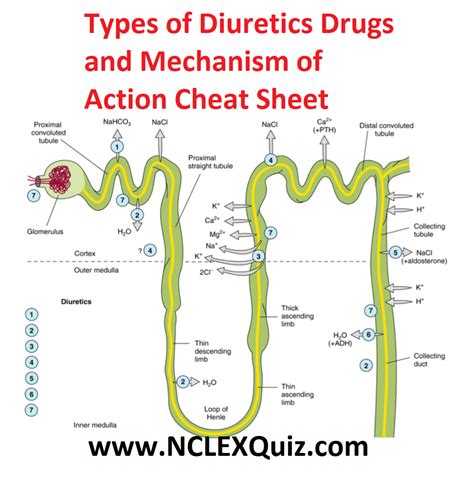
Furosemide has been a cornerstone in the treatment of fluid retention for many years due to its effectiveness in rapidly reducing swelling and improving symptoms such as shortness of breath. Its mechanism of action involves inhibiting the sodium-potassium-chloride cotransporter in the ascending limb of the loop of Henle, which leads to increased excretion of sodium, chloride, potassium, and water. This action helps in reducing the amount of fluid in the body and alleviating the strain on the heart and lungs. However, like all medications, furosemide must be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider, as improper use can lead to serious side effects, including dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
The management of conditions like heart failure, liver disease, and kidney disorders often requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and medication therapy. Furosemide plays a significant role in this management plan by helping to control fluid buildup, which can be life-threatening if left untreated. Patients taking furosemide need to be aware of the signs of dehydration, such as excessive thirst, dark urine, and dizziness, and should report these symptoms to their healthcare provider promptly. Additionally, regular monitoring of kidney function and electrolyte levels is essential to ensure the safe use of this medication.
How Furosemide Works
Benefits of Furosemide
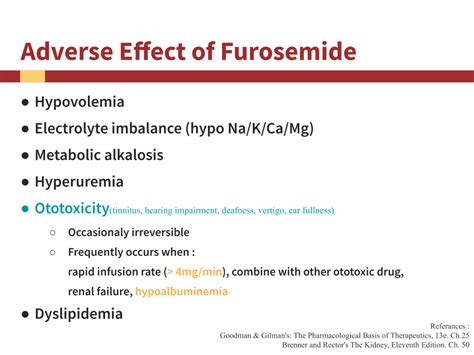
The benefits of furosemide are numerous and well-documented. It provides rapid relief from edema, improves respiratory symptoms in patients with heart failure, and helps manage ascites (fluid accumulation in the abdomen) associated with liver disease. Furosemide is also effective in treating nephrotic syndrome, a condition characterized by excessive loss of protein in the urine, leading to edema.Side Effects of Furosemide
Precautions and Warnings
Patients taking furosemide need to be cautious and aware of the potential for dehydration and electrolyte disturbances. It is essential to drink plenty of water to replace lost fluids and to monitor urine output. Furosemide should be used with caution in patients with certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease, gout, or diabetes, and in those taking other medications that may interact with furosemide.Dosage and Administration

Interactions with Other Medications
Furosemide can interact with several medications, including other diuretics, certain antibiotics, and medications used to treat high blood pressure or heart conditions. These interactions can increase the risk of side effects or reduce the effectiveness of furosemide. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.Patient Education and Support

Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to medication, lifestyle modifications can help manage conditions for which furosemide is prescribed. These modifications include reducing salt intake, limiting fluid consumption, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding alcohol and tobacco. Patients should work closely with their healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan that includes these lifestyle changes and medication therapy.Monitoring and Follow-Up
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, furosemide is a valuable medication in the management of fluid retention associated with various medical conditions. Its effectiveness in reducing swelling and alleviating symptoms makes it a crucial component of treatment plans for many patients. However, it is essential to use furosemide under the guidance of a healthcare provider, with careful monitoring for side effects and adherence to the prescribed dosage regimen. As medical research continues to advance, there may be future developments in the treatment of edema and related conditions, potentially leading to new medications or therapies that can offer even more effective management options.What is the primary use of furosemide?
+Furosemide is primarily used to treat fluid retention (edema) associated with congestive heart failure, liver disease, or a kidney disorder such as nephrotic syndrome.
How does furosemide work?
+Furosemide works by inhibiting the reabsorption of sodium and chloride in the kidneys, leading to increased urine production and reduction in fluid volume.
What are the common side effects of furosemide?
+Common side effects include increased urination, thirst, dizziness, and lightheadedness. More severe side effects can include dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
Can furosemide be used in patients with kidney disease?
+Furosemide should be used with caution in patients with kidney disease. The dose may need to be adjusted, and patients should be closely monitored for signs of decreased kidney function.
How can patients minimize the risk of side effects while taking furosemide?
+Patients can minimize the risk of side effects by drinking plenty of water, monitoring urine output, and reporting any signs of dehydration or electrolyte imbalances to their healthcare provider promptly.
We hope this comprehensive guide to furosemide has provided valuable information for patients and caregivers. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with furosemide, please don't hesitate to comment below. Sharing this article with others who might benefit from this information is also appreciated. Remember, it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment plans.
