Intro
Discover the causes, symptoms, and treatments of viral infections, including contagious diseases, common colds, and flu, to understand how viruses spread and affect the body, and learn prevention methods to stay healthy.
The world of viral infections is complex and fascinating, with new discoveries being made regularly. Viral infections have been a part of human history, causing widespread illnesses and affecting millions of people worldwide. From the common cold to deadly diseases like Ebola and HIV, viral infections can have a significant impact on our daily lives. Understanding viral infections is crucial for developing effective treatments and prevention strategies. In this article, we will delve into the world of viral infections, exploring their causes, symptoms, and consequences.
Viral infections occur when a virus enters the body and begins to replicate, causing harm to the host. Viruses are tiny, infectious agents that can only reproduce inside the cells of an organism. They consist of genetic material, either DNA or RNA, surrounded by a protein coat. Viruses can infect all types of living organisms, from animals to plants, and even bacteria. The human body is constantly exposed to viruses, but not all of them cause infections. Some viruses can be harmless, while others can lead to severe illnesses.
The study of viral infections is a rapidly evolving field, with new technologies and discoveries being made regularly. Advances in genomics, proteomics, and immunology have greatly improved our understanding of viral infections and the development of effective treatments. However, viral infections continue to pose a significant threat to global health, with new outbreaks and epidemics occurring regularly. The COVID-19 pandemic, for example, has highlighted the importance of understanding viral infections and developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
What are Viral Infections?
Types of Viral Infections
There are several types of viral infections, including respiratory, gastrointestinal, and neurological infections. Respiratory infections, such as the common cold and influenza, affect the lungs and airways. Gastrointestinal infections, such as norovirus and rotavirus, affect the digestive system. Neurological infections, such as meningitis and encephalitis, affect the brain and nervous system. Each type of viral infection has distinct symptoms and consequences, and understanding these differences is crucial for developing effective treatments.Causes of Viral Infections

Risk Factors for Viral Infections
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of viral infection, including: * Weakened immune system * Age (older adults and young children are more susceptible) * Underlying health conditions (such as diabetes, heart disease, and lung disease) * Poor hygiene * Contaminated food and water * Close contact with an infected person * Travel to areas with high rates of viral infection Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take steps to reduce their risk of viral infection.Symptoms of Viral Infections

Diagnosis of Viral Infections
Diagnosing viral infections can be challenging, as the symptoms can be similar to those of other illnesses. A range of diagnostic tests can be used to confirm the presence of a viral infection, including: * Physical examination * Medical history * Laboratory tests (such as blood tests and stool tests) * Imaging tests (such as X-rays and CT scans) * Molecular tests (such as PCR and serology) Accurate diagnosis is crucial for developing effective treatment plans and preventing the spread of viral infections.Treatments for Viral Infections
Prevention of Viral Infections
Preventing viral infections is crucial for reducing the risk of illness and transmission. Several strategies can be used to prevent viral infections, including: * Practicing good hygiene (such as washing hands regularly) * Avoiding close contact with infected individuals * Staying up to date on recommended vaccinations * Avoiding contaminated food and water * Using protective equipment (such as masks and gloves) * Avoiding touching eyes, nose, and mouth Understanding the importance of prevention can help individuals take steps to reduce their risk of viral infection.Complications of Viral Infections
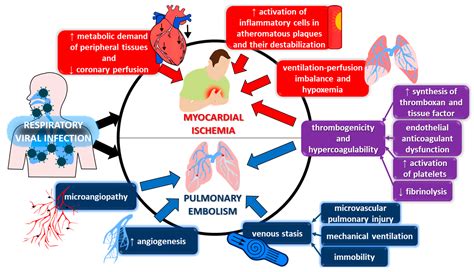
Long-term Consequences of Viral Infections
Viral infections can have long-term consequences, including chronic illness, disability, and increased risk of future infections. Some viral infections, such as HIV and hepatitis, can lead to chronic illness and require ongoing treatment. Others, such as polio and measles, can lead to disability and long-term health consequences. Understanding the potential long-term consequences of viral infections can help individuals take steps to reduce their risk and seek medical attention promptly if they experience symptoms.Current Research on Viral Infections
Future Directions for Viral Infection Research
Future research on viral infections will focus on several key areas, including: * Developing new treatments and vaccines * Improving diagnostic tests and surveillance * Understanding the mechanisms of viral replication and transmission * Exploring new approaches to prevention and treatment * Developing personalized medicine approaches to viral infections Understanding the future directions of viral infection research can help individuals stay informed about the latest developments and advancements in the field.What is the most common type of viral infection?
+The most common type of viral infection is the common cold, which is caused by a range of viruses, including rhinoviruses, coronaviruses, and adenoviruses.
How can I reduce my risk of viral infection?
+You can reduce your risk of viral infection by practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, staying up to date on recommended vaccinations, and avoiding contaminated food and water.
What are the symptoms of a viral infection?
+The symptoms of a viral infection can vary widely, depending on the type of virus and the host's immune response. Common symptoms include fever, headache, fatigue, muscle and joint pain, sore throat, cough, diarrhea, vomiting, rash, and confusion and disorientation.
As we conclude our exploration of viral infections, we hope that you have gained a deeper understanding of the complex and fascinating world of viral infections. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and consequences of viral infections, individuals can take steps to reduce their risk and seek medical attention promptly if they experience symptoms. We encourage you to share this article with others, and to stay informed about the latest developments and advancements in the field of viral infections. Together, we can work towards reducing the impact of viral infections and improving global health.
