Intro
Discover the causes of blood clots, including deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and stroke, and learn about risk factors like genetics, injury, and blood disorders that increase clot formation and cardiovascular disease.
Blood clots are a serious medical condition that can have severe consequences if left untreated. They are formed when blood cells, platelets, and other substances in the blood come together to create a gel-like mass. This can happen for a variety of reasons, including injury, genetics, and certain medical conditions. Understanding the causes of blood clots is crucial in preventing and treating them effectively. In this article, we will delve into the world of blood clots, exploring their causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
The formation of blood clots is a complex process that involves multiple factors. When a blood vessel is injured, the body's natural response is to send platelets to the affected area to stop the bleeding. However, in some cases, this process can go awry, leading to the formation of a blood clot. This can happen due to a variety of reasons, including genetics, age, and certain medical conditions. For instance, people with a family history of blood clots are more likely to develop them. Additionally, age is also a significant factor, as the risk of developing blood clots increases with age.
The risk of developing blood clots is also increased by certain medical conditions, such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism (PE), and atrial fibrillation. DVT occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, typically in the legs. PE, on the other hand, occurs when a blood clot breaks loose and travels to the lungs, blocking blood flow. Atrial fibrillation, a type of irregular heartbeat, can also increase the risk of blood clots. Other medical conditions, such as cancer, diabetes, and high blood pressure, can also contribute to the formation of blood clots.
What are the Risk Factors for Blood Clots?
Some of the common risk factors for blood clots include:
- Age: The risk of developing blood clots increases with age
- Genetics: A family history of blood clots can increase the risk
- Medical conditions: DVT, PE, atrial fibrillation, cancer, diabetes, and high blood pressure can all increase the risk of blood clots
- Environmental factors: Smoking, obesity, lack of exercise, and long periods of immobility can all contribute to the formation of blood clots
- Surgery: Certain surgeries, such as hip or knee replacement, can increase the risk of blood clots
- Trauma: Severe trauma, such as a car accident, can increase the risk of blood clots
How are Blood Clots Diagnosed?
Some of the common diagnostic tests used to diagnose blood clots include:
- Ultrasound: This non-invasive test uses sound waves to create images of the blood vessels and detect any blockages
- CT scan: This test uses X-rays and a computer to create detailed images of the blood vessels and detect any blockages
- MRI: This test uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images of the blood vessels and detect any blockages
- Blood tests: These tests can detect any abnormalities in the blood that may indicate the presence of a blood clot
How are Blood Clots Treated?
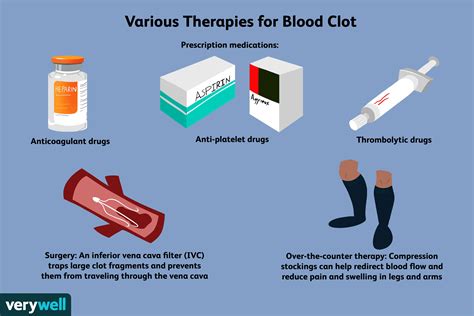
Some of the common treatment options for blood clots include:
- Anticoagulants: These medications can help prevent the clot from growing and causing further damage
- Thrombolytics: These medications can help dissolve the clot
- Compression stockings: These can help improve blood flow and reduce swelling
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the clot or repair any damage to the blood vessels
Preventing Blood Clots
Preventing blood clots is crucial in reducing the risk of developing them. This can be achieved through a combination of lifestyle changes and medical interventions. Some of the common ways to prevent blood clots include: * Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help keep the blood thin and reduce the risk of clots * Exercising regularly: Regular exercise can help improve blood flow and reduce the risk of clots * Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess weight can increase the risk of blood clots * Avoiding smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of blood clots * Managing medical conditions: Managing conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and cancer can help reduce the risk of blood clotsComplications of Blood Clots

Living with Blood Clots

Current Research on Blood Clots
Research on blood clots is ongoing, with scientists exploring new ways to prevent, diagnose, and treat the condition. Some of the current areas of research include: * Developing new medications: Researchers are working on developing new medications that can help prevent and treat blood clots * Improving diagnostic tests: Researchers are working on improving diagnostic tests to make them more accurate and effective * Understanding the causes of blood clots: Researchers are working on understanding the causes of blood clots, including the role of genetics and environmental factorsWhat are the symptoms of blood clots?
+The symptoms of blood clots can vary depending on the location and severity of the clot. Common symptoms include pain, swelling, and redness in the affected area.
How can I prevent blood clots?
+Preventing blood clots can be achieved through a combination of lifestyle changes and medical interventions. This includes staying hydrated, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding smoking, and managing medical conditions.
What are the complications of blood clots?
+Blood clots can have severe complications if left untreated. Some of the common complications include pulmonary embolism, stroke, heart attack, and organ damage.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of blood clots, including their causes, symptoms, and treatment options. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional. Remember, preventing blood clots is crucial in reducing the risk of developing them. By making lifestyle changes and seeking medical attention if symptoms occur, you can reduce the risk of blood clots and live a healthy and fulfilling life. Share this article with your friends and family to help spread awareness about blood clots and their importance in maintaining overall health.
