Intro
Boost vitamin B12 levels naturally with 5 proven methods, addressing deficiency symptoms, energy enhancement, and nutritional benefits, using supplements, diet, and lifestyle changes to optimize overall health and wellbeing.
Vitamin B12 is a crucial nutrient that plays a significant role in the production of red blood cells, nerve function, and DNA synthesis. A deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to various health issues, including fatigue, weakness, and neurological problems. With the increasing awareness of the importance of vitamin B12, many people are looking for ways to boost their levels of this essential vitamin. In this article, we will explore the importance of vitamin B12, its benefits, and provide tips on how to increase its levels in the body.
Vitamin B12 is found primarily in animal products, such as meat, fish, and dairy products. However, with the rising trend of plant-based diets, many people are at risk of vitamin B12 deficiency. Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as celiac disease and Crohn's disease, can also lead to a deficiency in vitamin B12. It is essential to be aware of the risks and take proactive steps to maintain adequate levels of vitamin B12.
The benefits of vitamin B12 are numerous, and it is essential to ensure that we are getting enough of this vitamin in our diet. Vitamin B12 helps to regulate the nervous system, and a deficiency can lead to neurological problems, such as numbness, tingling, and weakness in the limbs. It also plays a crucial role in the production of red blood cells, and a deficiency can lead to anemia. Furthermore, vitamin B12 is essential for the health of the cardiovascular system, and a deficiency can increase the risk of heart disease.
Understanding Vitamin B12

Benefits of Vitamin B12
The benefits of vitamin B12 are numerous, and it is essential to ensure that we are getting enough of this vitamin in our diet. Some of the benefits of vitamin B12 include: * Regulating the nervous system * Producing red blood cells * Maintaining the health of the cardiovascular system * Supporting bone health * Regulating the immune systemBoosting Vitamin B12 Levels

Dietary Sources of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is found primarily in animal products, including: * Meat: Beef, pork, lamb, and venison are all good sources of vitamin B12. * Fish: Fatty fish, such as salmon and tuna, are good sources of vitamin B12. * Dairy products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt are all good sources of vitamin B12. * Eggs: Eggs are a good source of vitamin B12. * Fortified foods: Some plant-based milk and cereals are fortified with vitamin B12.Vitamin B12 Deficiency
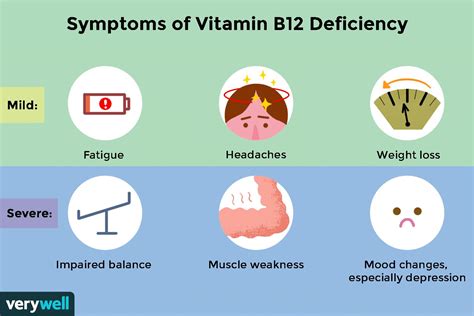
Symptoms of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
The symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency can vary depending on the severity of the deficiency. Some common symptoms include: * Fatigue and weakness * Shortness of breath * Dizziness and lightheadedness * Pale skin * Diarrhea or constipation * Loss of appetiteDiagnosing Vitamin B12 Deficiency

Treatment of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
The treatment of vitamin B12 deficiency depends on the severity of the deficiency and the underlying cause. Treatment options include: * Dietary changes: Increasing the intake of animal products and fortified foods can help to increase vitamin B12 levels. * Supplements: Vitamin B12 supplements can help to increase vitamin B12 levels. * Injections: Vitamin B12 injections can help to increase vitamin B12 levels quickly. * Nasal sprays: Vitamin B12 nasal sprays can help to increase vitamin B12 levels.Preventing Vitamin B12 Deficiency

Importance of Vitamin B12 for Athletes
Vitamin B12 is essential for athletes, as it helps to regulate the nervous system and produce red blood cells. A deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to fatigue, weakness, and poor performance. Athletes can increase their vitamin B12 levels by eating a balanced diet, taking supplements, and managing medical conditions.Vitamin B12 and Mental Health

Vitamin B12 and Cardiovascular Health
Vitamin B12 is essential for cardiovascular health, as it helps to regulate the production of homocysteine, an amino acid that can increase the risk of heart disease. A deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to an increase in homocysteine levels, which can increase the risk of heart disease. Increasing vitamin B12 levels can help to reduce the risk of heart disease and improve cardiovascular health.What are the symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency?
+The symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency can vary depending on the severity of the deficiency, but common symptoms include fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, dizziness, and pale skin.
How can I increase my vitamin B12 levels?
+You can increase your vitamin B12 levels by eating a balanced diet that includes animal products and fortified foods, taking supplements, and managing medical conditions.
What are the benefits of vitamin B12?
+The benefits of vitamin B12 include regulating the nervous system, producing red blood cells, maintaining the health of the cardiovascular system, supporting bone health, and regulating the immune system.
Can vitamin B12 deficiency be prevented?
+Yes, vitamin B12 deficiency can be prevented by eating a balanced diet, taking supplements, managing medical conditions, and getting regular check-ups with a healthcare provider.
What is the recommended daily intake of vitamin B12?
+The recommended daily intake of vitamin B12 varies depending on age, sex, and other factors, but the general recommended daily intake is 2.4-2.6 micrograms per day.
In conclusion, vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions. A deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to various health issues, including fatigue, weakness, and neurological problems. Increasing vitamin B12 levels can be achieved through dietary changes, supplements, and lifestyle modifications. It is essential to be aware of the risks and take proactive steps to maintain adequate levels of vitamin B12. We encourage you to share this article with others and to comment below with any questions or concerns you may have. Additionally, if you found this article helpful, please consider sharing it on social media to help spread awareness about the importance of vitamin B12.
