Intro
Discover the 7 causes of goiter disease, including iodine deficiency, thyroid disorders, and autoimmune issues, to understand this thyroid enlargement condition and its related health implications.
The thyroid gland plays a vital role in regulating various bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, and development. However, when the thyroid gland becomes enlarged, it can lead to a condition known as goiter. Goiter is a common health issue that affects millions of people worldwide, and it is essential to understand the causes and risk factors associated with this condition. In this article, we will delve into the 7 causes of goiter disease and explore the importance of early diagnosis and treatment.
Goiter can be caused by a variety of factors, including iodine deficiency, thyroid nodules, and autoimmune disorders. It is crucial to recognize the signs and symptoms of goiter, such as a swollen neck, difficulty swallowing, and shortness of breath. If left untreated, goiter can lead to more severe health complications, including thyroid cancer and respiratory problems. Therefore, it is vital to seek medical attention if you are experiencing any symptoms of goiter.
The prevalence of goiter varies widely depending on geographical location, dietary habits, and socioeconomic factors. In areas where iodine deficiency is common, goiter is more prevalent, especially among women and children. Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, can increase the risk of developing goiter. By understanding the causes and risk factors associated with goiter, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent and manage this condition.
Introduction to Goiter Disease
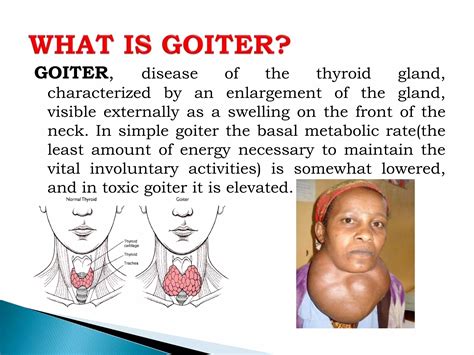
Cause 1: Iodine Deficiency

Risk Factors for Iodine Deficiency
The risk factors for iodine deficiency include: * Living in areas with low iodine levels in the soil and water * Consuming a diet that is low in iodine-rich foods, such as seafood and dairy products * Having a medical condition that affects iodine absorption, such as celiac disease or Crohn's disease * Taking certain medications that interfere with iodine absorption, such as lithium and sulfa drugsCause 2: Thyroid Nodules
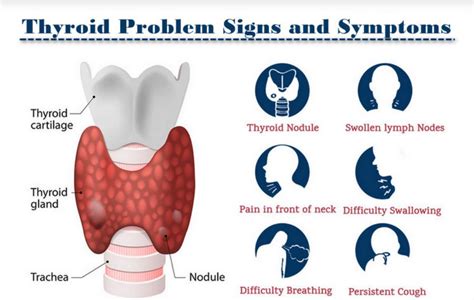
Types of Thyroid Nodules
There are several types of thyroid nodules, including: * Benign nodules: These are non-cancerous nodules that do not pose a significant health risk. * Malignant nodules: These are cancerous nodules that require prompt medical attention. * Cystic nodules: These are fluid-filled nodules that can be caused by a variety of factors, including iodine deficiency and radiation exposure.Cause 3: Autoimmune Disorders
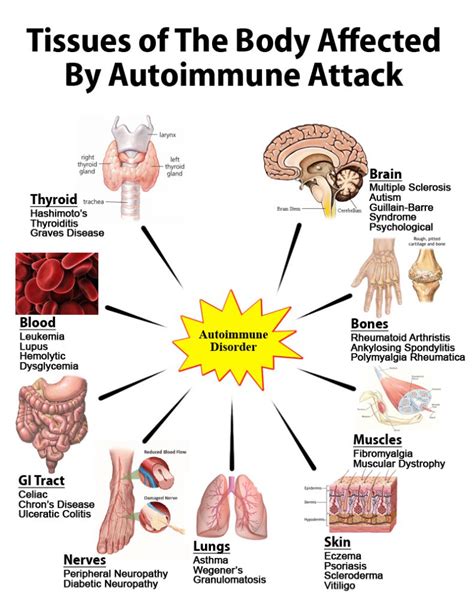
Types of Autoimmune Disorders
There are several types of autoimmune disorders that can cause goiter, including: * Hashimoto's thyroiditis: This is an autoimmune disorder that causes the immune system to attack the thyroid gland, leading to inflammation and damage. * Graves' disease: This is an autoimmune disorder that causes the immune system to produce antibodies that stimulate the thyroid gland, leading to hyperthyroidism and goiter.Cause 4: Radiation Exposure
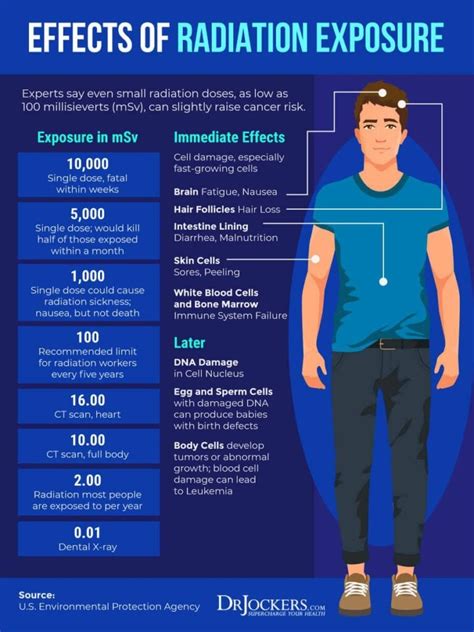
Risk Factors for Radiation Exposure
The risk factors for radiation exposure include: * Undergoing medical imaging procedures that use radiation, such as CT scans and PET scans * Living in areas with high levels of background radiation, such as areas with high levels of radon * Working with radioactive materials, such as nuclear power plant workersCause 5: Genetic Mutations
Types of Genetic Mutations
There are several types of genetic mutations that can cause goiter, including: * Mutations in the TSHR gene: This gene regulates the production of thyroid-stimulating hormone, which stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones. * Mutations in the TG gene: This gene regulates the production of thyroglobulin, which is a protein that is involved in the production of thyroid hormones.Cause 6: Certain Medications
Types of Medications that Can Cause Goiter
There are several types of medications that can cause goiter, including: * Lithium: This medication is used to treat bipolar disorder and can interfere with thyroid function, leading to goiter. * Sulfa drugs: These medications are used to treat bacterial infections and can interfere with thyroid function, leading to goiter.Cause 7: Pregnancy

Risk Factors for Goiter During Pregnancy
The risk factors for goiter during pregnancy include: * Having a history of thyroid problems, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism * Having a family history of thyroid problems * Being over the age of 35What are the symptoms of goiter disease?
+The symptoms of goiter disease include a swollen neck, difficulty swallowing, shortness of breath, and respiratory complications.
How is goiter disease diagnosed?
+Goiter disease is diagnosed using a physical exam, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as ultrasound and thyroid function tests.
How is goiter disease treated?
+Goiter disease is treated using a variety of methods, including medication, surgery, and radiation therapy. The treatment approach depends on the underlying cause of the goiter and the severity of the symptoms.
Can goiter disease be prevented?
+Yes, goiter disease can be prevented by maintaining a healthy diet that is rich in iodine, avoiding radiation exposure, and managing underlying medical conditions, such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism.
What are the complications of goiter disease?
+The complications of goiter disease include respiratory problems, difficulty swallowing, and thyroid cancer. If left untreated, goiter disease can lead to more severe health complications, including respiratory failure and cardiac problems.
In conclusion, goiter disease is a complex condition that can be caused by a variety of factors, including iodine deficiency, thyroid nodules, autoimmune disorders, radiation exposure, genetic mutations, certain medications, and pregnancy. By understanding the causes and risk factors associated with goiter disease, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent and manage this condition. If you are experiencing any symptoms of goiter disease, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly to prevent more severe health complications. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with goiter disease in the comments section below and to share this article with others who may be affected by this condition.
