Intro
Discover how Augmentin treats bacterial infections, including pneumonia and skin infections, with its antibiotic properties, fighting infection causes and promoting recovery with amoxicillin and clavulanate.
The rise of bacterial infections has become a significant concern in the medical field, with many individuals seeking effective treatment options. One of the most commonly prescribed antibiotics for bacterial infections is Augmentin. As a combination of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid, Augmentin has proven to be a potent and reliable treatment for various bacterial infections. In this article, we will delve into the world of Augmentin, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, and key information related to its use.
Bacterial infections can be debilitating and, if left untreated, can lead to severe complications. The importance of effective treatment cannot be overstated, as it can significantly improve patient outcomes and reduce the risk of long-term damage. With the increasing prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, it is crucial to understand the role of Augmentin in treating bacterial infections. By examining the benefits and mechanisms of Augmentin, we can better appreciate its value in the medical field and make informed decisions about its use.
The discovery of antibiotics has revolutionized the treatment of bacterial infections, saving countless lives and improving patient outcomes. Augmentin, in particular, has become a staple in the medical field, with its unique combination of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid providing a broad spectrum of activity against various bacterial pathogens. As we explore the world of Augmentin, we will examine its benefits, working mechanisms, and key information related to its use, providing readers with a comprehensive understanding of this essential antibiotic.
What is Augmentin?

How Does Augmentin Work?
Augmentin works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria, ultimately leading to their death. The amoxicillin component of Augmentin binds to the bacterial cell wall, preventing the formation of a stable cell wall and causing the bacteria to die. The clavulanic acid component, on the other hand, inhibits the production of beta-lactamase, an enzyme that can break down amoxicillin and render it ineffective. By overcoming this resistance mechanism, clavulanic acid helps to ensure that amoxicillin can effectively target and eliminate the bacteria.Benefits of Augmentin

Common Uses of Augmentin
Augmentin is commonly used to treat a range of bacterial infections, including: * Respiratory tract infections: Augmentin is effective against bacterial infections of the respiratory tract, such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and sinusitis. * Urinary tract infections: Augmentin is used to treat bacterial infections of the urinary tract, including cystitis and pyelonephritis. * Skin and soft tissue infections: Augmentin is effective against bacterial infections of the skin and soft tissues, such as cellulitis and abscesses. * Gastrointestinal infections: Augmentin is used to treat bacterial infections of the gastrointestinal tract, such as gastroenteritis and diverticulitis.Side Effects of Augmentin

Precautions and Contraindications
While Augmentin is a safe and effective treatment option for bacterial infections, there are some precautions and contraindications to be aware of. These include: * Allergy to penicillin: Individuals who are allergic to penicillin should not take Augmentin. * Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Augmentin should be used with caution in pregnant and breastfeeding women, as it can pass into breast milk and potentially harm the baby. * Kidney disease: Individuals with kidney disease should use Augmentin with caution, as it can increase the risk of kidney damage. * Liver disease: Individuals with liver disease should use Augmentin with caution, as it can increase the risk of liver damage.Augmentin Dosage and Administration
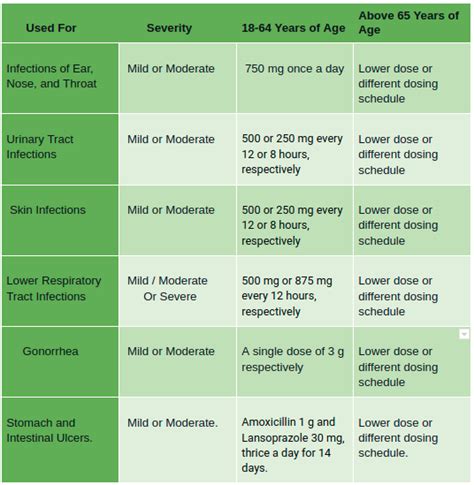
Interactions with Other Medications
Augmentin can interact with other medications, including: * Blood thinners: Augmentin can increase the risk of bleeding when taken with blood thinners. * Probenecid: Augmentin can decrease the effectiveness of probenecid, a medication used to treat gout. * Allopurinol: Augmentin can increase the risk of allergic reactions when taken with allopurinol, a medication used to treat gout. * Methotrexate: Augmentin can increase the risk of liver damage when taken with methotrexate, a medication used to treat cancer and autoimmune diseases.Resistance to Augmentin
Future Directions
The development of new antibiotics and antibiotic combinations is crucial to addressing the growing problem of antibiotic resistance. Researchers are exploring new targets and mechanisms of action, including the use of bacteriophage therapy and antimicrobial peptides. Additionally, the development of rapid diagnostic tests can help to identify bacterial infections and guide treatment decisions, reducing the risk of antibiotic resistance and improving patient outcomes.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with Augmentin in the comments below. Have you or a loved one used Augmentin to treat a bacterial infection? What were your experiences with the medication? Do you have any questions or concerns about Augmentin or antibiotic resistance? Join the conversation and let's work together to promote responsible use and stewardship of antibiotics.
What is Augmentin used to treat?
+Augmentin is used to treat a range of bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, and gastrointestinal infections.
How does Augmentin work?
+Augmentin works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria, ultimately leading to their death. The amoxicillin component of Augmentin binds to the bacterial cell wall, preventing the formation of a stable cell wall, while the clavulanic acid component inhibits the production of beta-lactamase, an enzyme that can break down amoxicillin.
What are the common side effects of Augmentin?
+Common side effects of Augmentin include gastrointestinal upset, allergic reactions, liver damage, and interactions with other medications.
Can I take Augmentin if I am allergic to penicillin?
+No, if you are allergic to penicillin, you should not take Augmentin. Augmentin is a combination of amoxicillin, a penicillin-type antibiotic, and clavulanic acid, and can cause a severe allergic reaction in individuals who are allergic to penicillin.
How can I minimize the risk of antibiotic resistance when taking Augmentin?
+To minimize the risk of antibiotic resistance when taking Augmentin, it is essential to use the medication judiciously and only when necessary. Additionally, individuals can take steps to prevent the spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, such as practicing good hygiene, getting vaccinated, and using antibiotics responsibly.
