Intro
The world of medicine is vast and complex, with numerous treatments and medications available for various health conditions. One such medication that has been widely used for decades is beta blockers. These medications have been a cornerstone in the treatment of certain health conditions, particularly those related to the cardiovascular system. In this article, we will delve into the world of beta blockers, exploring their uses, benefits, and mechanisms of action.
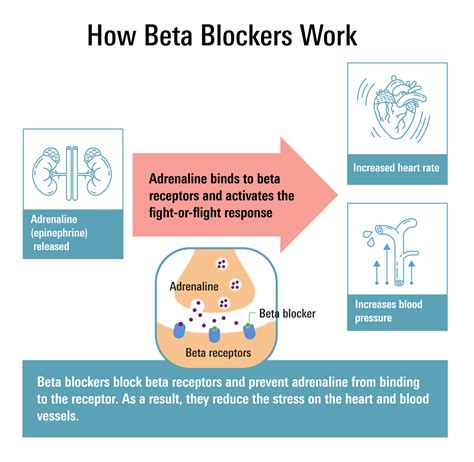
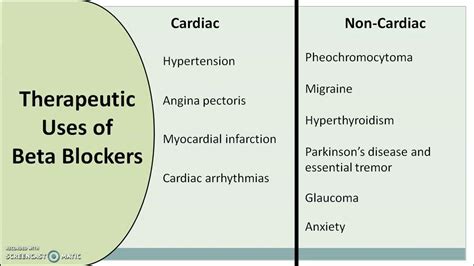
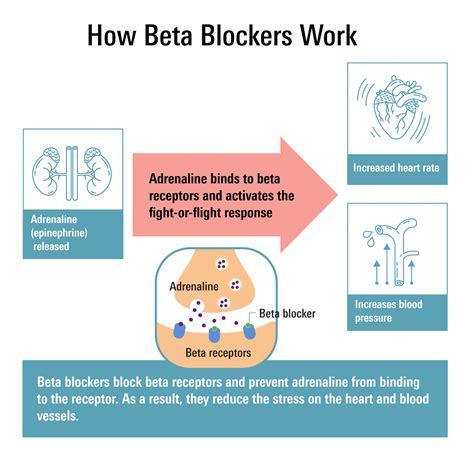
Beta blockers are a class of medications that work by blocking the effects of the hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline, and by slowing the heart rate and reducing its workload. This makes them an effective treatment for a range of health conditions, including high blood pressure, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias. The uses of beta blockers are diverse and have been extensively studied, making them a vital part of modern medicine.
The importance of beta blockers cannot be overstated, as they have been shown to reduce the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events. They have also been used to treat conditions such as glaucoma, migraines, and performance anxiety. With their wide range of applications, it is essential to understand how beta blockers work, their benefits, and their potential side effects. In the following sections, we will explore these topics in greater detail, providing a comprehensive overview of beta blockers and their uses.
What are Beta Blockers?
Types of Beta Blockers
There are several types of beta blockers, each with its own unique characteristics and uses. Some of the most common types of beta blockers include: * Non-selective beta blockers: These medications block both beta-1 and beta-2 receptors, which can cause a range of side effects, including bronchospasm and hypoglycemia. * Selective beta blockers: These medications block only beta-1 receptors, which reduces the risk of side effects such as bronchospasm. * Combined alpha and beta blockers: These medications block both alpha and beta receptors, which can be useful in treating conditions such as hypertension and heart failure.Uses of Beta Blockers
Benefits of Beta Blockers
The benefits of beta blockers are numerous and well-documented. Some of the most significant benefits include: * Reduced risk of heart attacks and strokes: Beta blockers have been shown to reduce the risk of heart attacks and strokes, particularly in people with a history of cardiovascular disease. * Improved survival rates: Beta blockers have been shown to improve survival rates in people with heart failure and other cardiovascular conditions. * Reduced symptoms: Beta blockers can reduce the symptoms of conditions such as angina, arrhythmias, and migraines, improving quality of life. * Low cost: Beta blockers are generally inexpensive, making them a cost-effective treatment option.How Beta Blockers Work
Side Effects of Beta Blockers
While beta blockers are generally well-tolerated, they can cause a range of side effects, including: * Fatigue: Beta blockers can cause fatigue, particularly when first starting treatment. * Dizziness: Beta blockers can cause dizziness, particularly when standing up quickly. * Shortness of breath: Beta blockers can cause shortness of breath, particularly in people with pre-existing respiratory conditions. * Cold hands and feet: Beta blockers can cause cold hands and feet, particularly in people with poor circulation. * Weight gain: Beta blockers can cause weight gain, particularly in people who are already overweight or obese.Precautions and Interactions

Contraindications
Beta blockers are contraindicated in certain situations, including: * Asthma: Beta blockers can worsen asthma symptoms, particularly in people with severe asthma. * COPD: Beta blockers can worsen COPD symptoms, particularly in people with severe COPD. * Heart block: Beta blockers can worsen heart block, particularly in people with severe heart block. * Bradycardia: Beta blockers can worsen bradycardia, particularly in people with severe bradycardia.Conclusion and Future Directions

Final Thoughts
Beta blockers are a powerful tool in the treatment of various health conditions, particularly those related to the cardiovascular system. By understanding how beta blockers work, their benefits, and their potential side effects, we can make informed decisions about their use. Whether you are a healthcare professional or a patient, it is essential to stay up-to-date with the latest research and developments in the field of beta blockers.What are the most common uses of beta blockers?
+Beta blockers are commonly used to treat high blood pressure, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias. They are also used to treat glaucoma, migraines, and performance anxiety.
How do beta blockers work?
+Beta blockers work by blocking the effects of the hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline. They do this by binding to beta receptors in the heart, blood vessels, and other tissues, which reduces the heart rate and the force of contraction.
What are the potential side effects of beta blockers?
+Beta blockers can cause a range of side effects, including fatigue, dizziness, shortness of breath, cold hands and feet, and weight gain. They can also interact with other medications, such as calcium channel blockers and anti-arrhythmic medications.
Can beta blockers be used in people with asthma or COPD?
+Beta blockers are contraindicated in people with asthma or COPD, as they can worsen symptoms. However, in some cases, beta blockers may be used under close medical supervision.
What is the future of beta blockers in the treatment of cardiovascular disease?
+The future of beta blockers in the treatment of cardiovascular disease is promising, with ongoing research exploring new and innovative uses for these medications. As our understanding of the mechanisms of action and benefits of beta blockers continues to evolve, we can expect to see new and exciting developments in the field.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of beta blockers, their uses, benefits, and potential side effects. If you have any questions or comments, please do not hesitate to reach out. Share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about beta blockers, and stay tuned for future updates and developments in the field of cardiovascular medicine.
