Intro
Discover the signs and symptoms of dehydration, including fatigue, headaches, and dry mouth. Learn how dehydration can make you feel weak, dizzy, and thirsty, and find out how to prevent and treat it with proper hydration techniques and water intake management.
Dehydration is a common condition that occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in, causing an imbalance in the body's water and electrolyte levels. This can happen for a variety of reasons, such as not drinking enough water, excessive sweating, vomiting, or having a fever. When dehydration sets in, it can cause a range of symptoms that can make a person feel unwell.
Dehydration can affect anyone, regardless of age or health status. It's especially common in older adults, young children, and people with certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or kidney disease. In addition to the physical symptoms, dehydration can also affect a person's mood and cognitive function, making it harder to concentrate and think clearly.
The symptoms of dehydration can vary from mild to severe, depending on the level of dehydration. Mild dehydration might cause symptoms such as dry mouth, fatigue, and headaches, while severe dehydration can lead to more serious complications, such as organ failure and even death. It's essential to recognize the signs of dehydration and take steps to prevent it, especially in vulnerable populations.
What are the Symptoms of Dehydration?
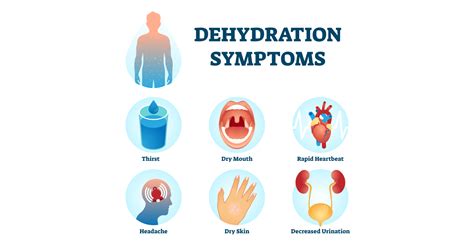
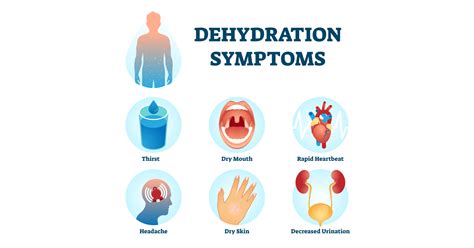
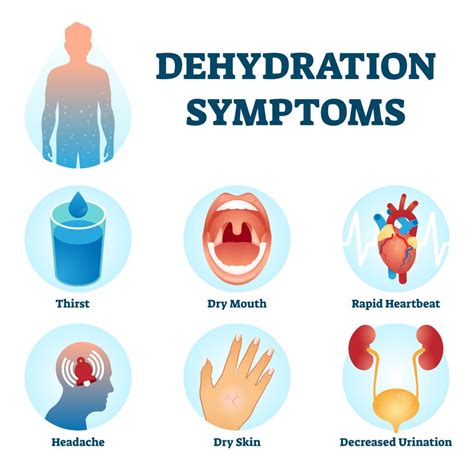
Physical Symptoms of Dehydration
The physical symptoms of dehydration are often the first signs that something is wrong. These can include: * Dry mouth and throat * Fatigue and weakness * Headaches and lightheadedness * Dark urine and decreased urine output * Dizziness and fainting * Rapid heartbeat and low blood pressure * Sunken eyes and decreased tear productionWhat Causes Dehydration?
Prevention and Treatment of Dehydration
Preventing dehydration is often a matter of making sure to drink enough water and electrolyte-rich fluids. The amount of water a person needs can vary depending on age, sex, weight, and activity level, but a general rule of thumb is to drink at least eight glasses of water per day. In addition to drinking enough water, it's also essential to eat foods that are rich in electrolytes, such as bananas, avocados, and nuts.Treating Dehydration

Complications of Dehydration
If left untreated, dehydration can lead to a range of complications, including: * Heat stroke and heat exhaustion * Kidney damage and failure * Shock and organ failure * Coma and death * Urinary tract infections and kidney stones * Electrolyte imbalances and seizuresWho is at Risk for Dehydration?
How to Recognize Dehydration in Others
Recognizing dehydration in others can be challenging, especially in older adults and young children. Some signs to look for include: * Dry mouth and throat * Fatigue and weakness * Headaches and lightheadedness * Dark urine and decreased urine output * Dizziness and fainting * Rapid heartbeat and low blood pressure * Sunken eyes and decreased tear productionPreventing Dehydration in Vulnerable Populations

Conclusion and Next Steps
Dehydration is a common condition that can affect anyone, regardless of age or health status. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of dehydration and taking steps to prevent it can help to reduce the risk of complications and improve overall health and well-being. By staying hydrated and being aware of the risks of dehydration, individuals can take control of their health and reduce their risk of dehydration-related complications.What are the symptoms of dehydration?
+The symptoms of dehydration include dry mouth, fatigue, headaches, dark urine, and dizziness. In severe cases, dehydration can cause seizures, coma, and even death.
How can I prevent dehydration?
+Preventing dehydration requires drinking enough water and electrolyte-rich fluids, eating foods that are rich in electrolytes, and monitoring urine output and color to detect dehydration early.
Who is at risk for dehydration?
+Certain groups of people are at a higher risk for dehydration, including older adults, young children, people with certain medical conditions, and people who are physically active or work outdoors.
How can I recognize dehydration in others?
+Recognizing dehydration in others can be challenging, but some signs to look for include dry mouth and throat, fatigue and weakness, headaches and lightheadedness, and dark urine and decreased urine output.
What are the complications of dehydration?
+If left untreated, dehydration can lead to a range of complications, including heat stroke and heat exhaustion, kidney damage and failure, shock and organ failure, coma, and death.
