Intro
Discover the devastating lead poisoning effects on human health, including neurological damage, cognitive impairment, and organ failure, caused by lead exposure and contamination, affecting children and adults alike.
Lead poisoning is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Despite its well-known dangers, lead poisoning remains a significant public health concern, particularly in developing countries and low-income communities. The effects of lead poisoning can be devastating, ranging from mild symptoms to severe and irreversible damage to the brain, kidneys, and other vital organs. In this article, we will delve into the world of lead poisoning, exploring its causes, symptoms, and effects, as well as the measures that can be taken to prevent and treat this condition.
Lead poisoning is a cumulative process, meaning that the effects of lead exposure can build up over time, even at low levels. The human body has no use for lead, and it does not break down or exit the body easily. As a result, lead can accumulate in the body, causing damage to the brain, nervous system, and other organs. The most vulnerable populations to lead poisoning are children under the age of six, pregnant women, and people with certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease or anemia. These individuals are more susceptible to the effects of lead poisoning due to their developing brains, compromised immune systems, or pre-existing health conditions.
The importance of understanding lead poisoning cannot be overstated. Lead poisoning is a preventable condition, and awareness is key to reducing the risk of exposure. By educating ourselves and others about the dangers of lead poisoning, we can take steps to minimize our exposure to lead and protect our health and the health of our loved ones. In the following sections, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and effects of lead poisoning in more detail, as well as the measures that can be taken to prevent and treat this condition.
What is Lead Poisoning?

Causes of Lead Poisoning
The causes of lead poisoning are varied and can be attributed to several factors. Some of the most common causes of lead poisoning include: * Lead-based paint: Lead-based paint is a significant source of lead exposure, particularly in older homes and buildings. * Contaminated soil: Soil can become contaminated with lead through the breakdown of lead-based paint, industrial activities, or the use of leaded gasoline. * Lead-tainted water: Water can become contaminated with lead through corroded pipes, fixtures, and soldering. * Occupational exposure: People who work with lead, such as construction workers, miners, and smelters, are at risk of lead poisoning. * Consumer products: Some consumer products, such as toys, jewelry, and cosmetics, may contain lead.Symptoms of Lead Poisoning

Effects of Lead Poisoning on the Body
The effects of lead poisoning on the body can be severe and long-lasting. Some of the most significant effects of lead poisoning include: * Brain damage: Lead poisoning can cause damage to the brain, leading to cognitive impairment, memory loss, and learning disabilities. * Kidney damage: Lead poisoning can cause damage to the kidneys, leading to kidney disease and failure. * Nervous system damage: Lead poisoning can cause damage to the nervous system, leading to numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hands and feet. * Reproductive problems: Lead poisoning can cause reproductive problems, including infertility, miscarriage, and birth defects.Prevention and Treatment of Lead Poisoning

Treatment for lead poisoning typically involves removing the source of lead exposure and providing supportive care to manage symptoms. In severe cases, chelation therapy may be necessary to remove lead from the body.
Chelation Therapy for Lead Poisoning
Chelation therapy is a medical treatment that involves using medications to remove heavy metals, including lead, from the body. Chelation therapy is typically used in severe cases of lead poisoning, where the lead levels are extremely high. The medications used in chelation therapy work by binding to the lead and removing it from the body through urine or stool.Real-Life Examples of Lead Poisoning

Statistical Data on Lead Poisoning
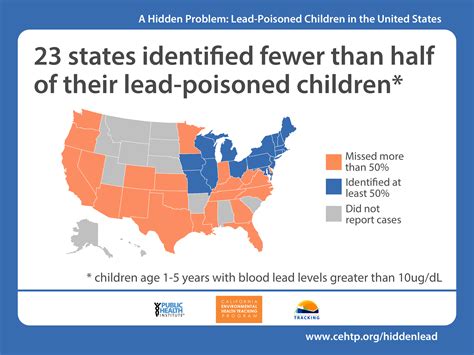
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), lead poisoning is a significant public health concern, affecting millions of people worldwide. Some statistical data on lead poisoning includes: * In 2019, the WHO estimated that lead poisoning was responsible for 540,000 deaths worldwide. * In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that over 400,000 children under the age of six have elevated blood lead levels. * According to the CDC, lead poisoning costs the US economy over $50 billion annually in medical costs and lost productivity.Conclusion and Call to Action
What are the most common sources of lead exposure?
+The most common sources of lead exposure are lead-based paint, contaminated soil, and lead-tainted water.
What are the symptoms of lead poisoning?
+The symptoms of lead poisoning can vary depending on the level and duration of exposure, but common symptoms include headaches, fatigue, irritability, and abdominal pain.
How can I prevent lead poisoning?
+Prevention is key to reducing the risk of lead poisoning. Measures that can be taken to prevent lead poisoning include removing lead-based paint from homes and buildings, using lead-free products, avoiding contaminated soil and water, and wearing protective gear when working with lead.
What is chelation therapy, and how does it work?
+Chelation therapy is a medical treatment that involves using medications to remove heavy metals, including lead, from the body. The medications used in chelation therapy work by binding to the lead and removing it from the body through urine or stool.
How many people are affected by lead poisoning worldwide?
+According to the World Health Organization (WHO), lead poisoning is a significant public health concern, affecting millions of people worldwide. In 2019, the WHO estimated that lead poisoning was responsible for 540,000 deaths worldwide.
