Intro
Understand low glucose meaning, symptoms, and effects. Learn about hypoglycemia, blood sugar levels, and glucose monitoring to manage health and prevent complications.
Low glucose, also known as hypoglycemia, is a condition where the blood sugar levels in the body drop below the normal range. This can be a serious health issue if not addressed promptly, as it can lead to confusion, loss of consciousness, and even death in extreme cases. The importance of understanding low glucose levels cannot be overstated, as it affects not only individuals with diabetes but also those without the condition. In this article, we will delve into the world of low glucose, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and management.
The human body relies heavily on glucose as its primary source of energy. Glucose is a type of sugar that is obtained from the food we eat, and it is transported to the cells via the bloodstream. The pancreas plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels by producing insulin, a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose. When the glucose levels in the blood drop, the pancreas releases glucagon, a hormone that stimulates the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream. This delicate balance is essential for maintaining normal blood sugar levels.
However, when this balance is disrupted, low glucose levels can occur. This can happen for various reasons, including skipping meals, taking too much diabetes medication, or engaging in strenuous physical activity without adequate food intake. Individuals with diabetes are more prone to hypoglycemia due to their impaired ability to regulate blood sugar levels. Nevertheless, anyone can experience low glucose levels, regardless of their diabetes status. It is essential to recognize the symptoms of hypoglycemia, which can include shakiness, dizziness, sweating, hunger, irritability, confusion, and even loss of consciousness.
Understanding Low Glucose Levels

Low glucose levels can be categorized into different stages, ranging from mild to severe. Mild hypoglycemia can be treated with a quick-acting source of glucose, such as glucose tablets or fruit juice. However, severe hypoglycemia requires immediate medical attention, as it can lead to serious complications, including brain damage and death. It is crucial to understand the causes of low glucose levels, as this knowledge can help prevent hypoglycemic episodes. Some common causes of hypoglycemia include certain medications, such as beta-blockers and salicylates, which can interfere with glucose production or increase insulin sensitivity.
Causes of Low Glucose Levels
Other causes of hypoglycemia include underlying medical conditions, such as liver disease, kidney disease, and hypothyroidism. Additionally, certain lifestyle factors, such as excessive alcohol consumption, strenuous exercise, and skipping meals, can contribute to low glucose levels. It is essential to identify the underlying cause of hypoglycemia to develop an effective treatment plan. This may involve adjusting medication, changing dietary habits, or managing underlying medical conditions.Symptoms of Low Glucose Levels

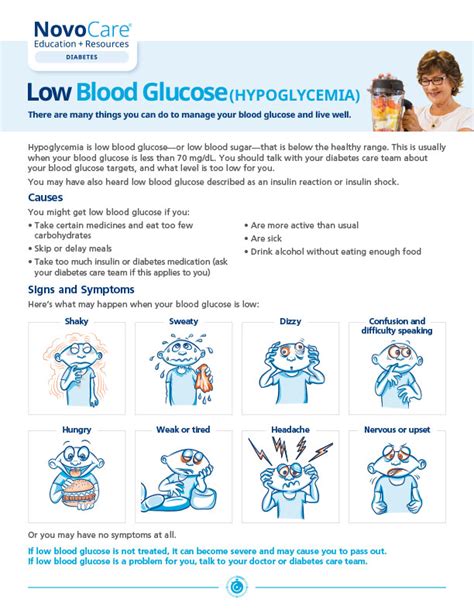
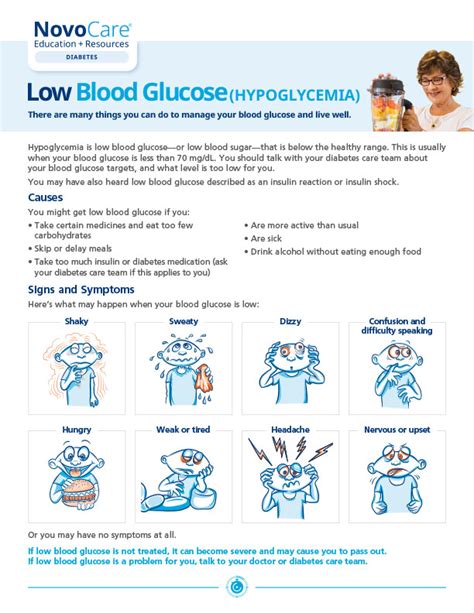
The symptoms of low glucose levels can vary from person to person, but they often include physical and emotional manifestations. Physical symptoms can include shakiness, dizziness, sweating, hunger, and pale skin. Emotional symptoms can include irritability, anxiety, and confusion. In severe cases, hypoglycemia can cause loss of consciousness, seizures, and even death. It is crucial to recognize these symptoms and take prompt action to prevent serious complications.
Treatment of Low Glucose Levels
The treatment of low glucose levels depends on the severity of the condition. Mild hypoglycemia can be treated with a quick-acting source of glucose, such as glucose tablets or fruit juice. However, severe hypoglycemia requires immediate medical attention, as it can lead to serious complications. In some cases, hospitalization may be necessary to monitor blood sugar levels and provide supportive care. It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan, as this can help prevent hypoglycemic episodes and manage underlying medical conditions.Diagnosis of Low Glucose Levels
The diagnosis of low glucose levels typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. A healthcare provider may perform a physical examination to look for signs of hypoglycemia, such as shakiness, sweating, and pale skin. A medical history can help identify underlying causes of hypoglycemia, such as certain medications or medical conditions. Laboratory tests, such as blood glucose tests, can help confirm the diagnosis and monitor blood sugar levels.
Prevention of Low Glucose Levels
Preventing low glucose levels is crucial, as it can help avoid serious complications and improve overall health. This can be achieved by eating regular meals, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, and engaging in regular physical activity. Additionally, individuals with diabetes should work with their healthcare provider to develop a personalized meal plan and medication regimen. This can help regulate blood sugar levels and prevent hypoglycemic episodes.Management of Low Glucose Levels

Managing low glucose levels requires a comprehensive approach that involves lifestyle changes, medication, and regular monitoring. This can include eating regular meals, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, and engaging in regular physical activity. Additionally, individuals with diabetes should work with their healthcare provider to develop a personalized meal plan and medication regimen. This can help regulate blood sugar levels and prevent hypoglycemic episodes.
Complications of Low Glucose Levels
The complications of low glucose levels can be serious and even life-threatening. Severe hypoglycemia can cause loss of consciousness, seizures, and even death. Additionally, repeated episodes of hypoglycemia can damage the brain and other organs, leading to long-term health problems. It is essential to recognize the symptoms of hypoglycemia and take prompt action to prevent serious complications.Living with Low Glucose Levels

Living with low glucose levels requires a comprehensive approach that involves lifestyle changes, medication, and regular monitoring. This can include eating regular meals, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, and engaging in regular physical activity. Additionally, individuals with diabetes should work with their healthcare provider to develop a personalized meal plan and medication regimen. This can help regulate blood sugar levels and prevent hypoglycemic episodes.
Coping with Low Glucose Levels
Coping with low glucose levels can be challenging, but there are several strategies that can help. This can include keeping a food diary to track glucose levels, carrying a quick-acting source of glucose, and wearing a medical alert bracelet. Additionally, individuals with diabetes should work with their healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan for managing hypoglycemic episodes. This can help reduce stress and anxiety and improve overall health.Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, low glucose levels are a serious health issue that requires prompt attention. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and management of hypoglycemia, individuals can take steps to prevent hypoglycemic episodes and improve their overall health. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of low glucose levels, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately. By working together, we can reduce the risk of hypoglycemia and improve the lives of individuals with diabetes.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with low glucose levels in the comments below. Your input can help others understand the importance of managing hypoglycemia and provide valuable insights into the challenges and successes of living with diabetes.
What are the symptoms of low glucose levels?
+The symptoms of low glucose levels can include shakiness, dizziness, sweating, hunger, irritability, confusion, and even loss of consciousness.
How can I prevent low glucose levels?
+Preventing low glucose levels can be achieved by eating regular meals, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, and engaging in regular physical activity. Additionally, individuals with diabetes should work with their healthcare provider to develop a personalized meal plan and medication regimen.
What should I do if I experience symptoms of low glucose levels?
+If you experience symptoms of low glucose levels, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately. You can also try to raise your blood sugar levels by consuming a quick-acting source of glucose, such as glucose tablets or fruit juice.
