Intro
Discover foods high in phosphorus, including meat, fish, and dairy, which support bone health, energy production, and nerve function, with related nutrients like protein, calcium, and vitamin D.
Phosphorus is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in many bodily functions, including the formation of bones and teeth, the production of energy, and the maintenance of various metabolic processes. It is the second most abundant mineral in the body, after calcium, and is necessary for the proper functioning of cells, tissues, and organs. A diet that is rich in phosphorus can help to support overall health and well-being, and can also help to prevent a range of health problems, including osteoporosis, anemia, and fatigue.
Phosphorus is found in a wide variety of foods, including meat, fish, poultry, eggs, dairy products, and legumes. It is also found in many processed and packaged foods, such as cereals, bread, and snacks. However, it is generally recommended to get phosphorus from whole, unprocessed foods, as these tend to be lower in added sugars, salt, and unhealthy fats. Some of the richest sources of phosphorus include organ meats, such as liver and kidney, as well as fish and seafood, such as salmon and shrimp.
In addition to its role in maintaining overall health, phosphorus is also important for maintaining healthy bones and teeth. It works together with calcium to form hydroxyapatite, a hard, calcified tissue that gives bones and teeth their strength and rigidity. A diet that is deficient in phosphorus can lead to a range of health problems, including osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weak and brittle bones. Osteoporosis can increase the risk of fractures and other injuries, and can also lead to a range of other health problems, including back pain, loss of height, and disability.
Introduction to Phosphorus-Rich Foods

Phosphorus-rich foods can be incorporated into a healthy diet in a variety of ways. For example, organ meats, such as liver and kidney, can be grilled or sautéed and served as a main dish or added to soups and stews. Fish and seafood, such as salmon and shrimp, can be baked or broiled and served with a range of vegetables and whole grains. Legumes, such as beans and lentils, can be added to soups, stews, and salads, or used to make a range of dishes, including chili, curry, and hummus.
Benefits of Phosphorus-Rich Foods
The benefits of phosphorus-rich foods are numerous and well-documented. Some of the key benefits include: * Supporting bone health: Phosphorus works together with calcium to form hydroxyapatite, a hard, calcified tissue that gives bones and teeth their strength and rigidity. * Maintaining energy production: Phosphorus is necessary for the production of ATP, a molecule that provides energy for the body's cells and tissues. * Supporting metabolic function: Phosphorus is involved in many metabolic processes, including the breakdown of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. * Maintaining healthy teeth and gums: Phosphorus is necessary for the formation of healthy teeth and gums, and can help to prevent a range of oral health problems, including tooth decay and gum disease.Top Phosphorus-Rich Foods

Some of the top phosphorus-rich foods include:
- Organ meats, such as liver and kidney
- Fish and seafood, such as salmon and shrimp
- Legumes, such as beans and lentils
- Nuts and seeds, such as almonds and pumpkin seeds
- Whole grains, such as brown rice and quinoa
- Dairy products, such as milk and cheese
- Eggs
- Meat, such as beef and chicken
- Poultry, such as turkey and duck
- Soy products, such as tofu and tempeh
Phosphorus Content in Foods
The phosphorus content of foods can vary widely, depending on the type of food, the method of preparation, and the level of processing. Here are some examples of the phosphorus content of different foods: * Organ meats: 300-400 mg per 3 oz serving * Fish and seafood: 200-300 mg per 3 oz serving * Legumes: 150-250 mg per 1 cup cooked * Nuts and seeds: 100-200 mg per 1 oz serving * Whole grains: 100-150 mg per 1 cup cooked * Dairy products: 100-150 mg per 1 cup * Eggs: 90-100 mg per large egg * Meat: 70-90 mg per 3 oz serving * Poultry: 60-80 mg per 3 oz serving * Soy products: 50-70 mg per 3 oz servingHealth Benefits of Phosphorus

The health benefits of phosphorus are numerous and well-documented. Some of the key benefits include:
- Supporting bone health: Phosphorus works together with calcium to form hydroxyapatite, a hard, calcified tissue that gives bones and teeth their strength and rigidity.
- Maintaining energy production: Phosphorus is necessary for the production of ATP, a molecule that provides energy for the body's cells and tissues.
- Supporting metabolic function: Phosphorus is involved in many metabolic processes, including the breakdown of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
- Maintaining healthy teeth and gums: Phosphorus is necessary for the formation of healthy teeth and gums, and can help to prevent a range of oral health problems, including tooth decay and gum disease.
- Supporting kidney function: Phosphorus is necessary for the proper functioning of the kidneys, and can help to prevent a range of kidney problems, including kidney stones and kidney disease.
Phosphorus Deficiency
A phosphorus deficiency can occur when the body does not get enough phosphorus from the diet. This can be due to a range of factors, including a poor diet, certain medical conditions, and the use of certain medications. Symptoms of a phosphorus deficiency can include: * Weakness and fatigue * Bone pain and fragility * Tooth decay and gum disease * Kidney problems, including kidney stones and kidney disease * Numbness and tingling in the hands and feetFood Sources of Phosphorus

Phosphorus can be found in a wide variety of foods, including:
- Organ meats, such as liver and kidney
- Fish and seafood, such as salmon and shrimp
- Legumes, such as beans and lentils
- Nuts and seeds, such as almonds and pumpkin seeds
- Whole grains, such as brown rice and quinoa
- Dairy products, such as milk and cheese
- Eggs
- Meat, such as beef and chicken
- Poultry, such as turkey and duck
- Soy products, such as tofu and tempeh
Phosphorus Supplements
Phosphorus supplements are available in a range of forms, including tablets, capsules, and powders. These supplements can be used to help support overall health and well-being, and can also be used to treat a range of health problems, including osteoporosis and kidney disease. However, it is generally recommended to get phosphorus from whole, unprocessed foods, as these tend to be lower in added sugars, salt, and unhealthy fats.Phosphorus and Bone Health
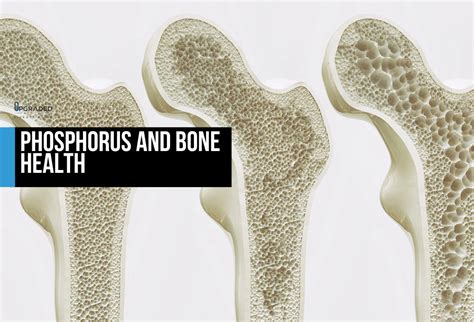
Phosphorus plays a crucial role in maintaining bone health, and is necessary for the formation of hydroxyapatite, a hard, calcified tissue that gives bones and teeth their strength and rigidity. A diet that is deficient in phosphorus can lead to a range of bone health problems, including osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weak and brittle bones. Osteoporosis can increase the risk of fractures and other injuries, and can also lead to a range of other health problems, including back pain, loss of height, and disability.
Phosphorus and Energy Production
Phosphorus is also necessary for the production of ATP, a molecule that provides energy for the body's cells and tissues. A diet that is deficient in phosphorus can lead to fatigue, weakness, and a range of other health problems, including anemia and impaired cognitive function.Phosphorus and Kidney Function
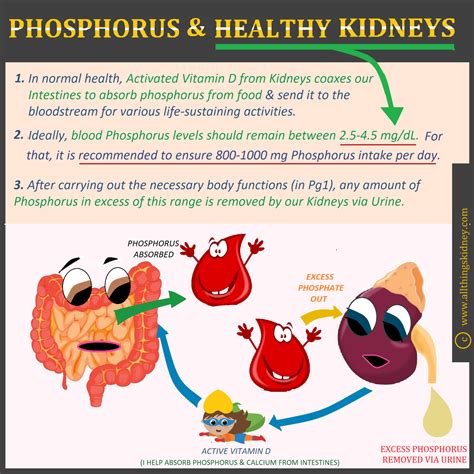
Phosphorus is also necessary for the proper functioning of the kidneys, and can help to prevent a range of kidney problems, including kidney stones and kidney disease. A diet that is deficient in phosphorus can lead to a range of kidney health problems, including impaired kidney function, kidney failure, and end-stage renal disease.
Phosphorus and Oral Health
Phosphorus is also necessary for the formation of healthy teeth and gums, and can help to prevent a range of oral health problems, including tooth decay and gum disease. A diet that is deficient in phosphorus can lead to a range of oral health problems, including tooth loss, gum recession, and impaired dental health.What are the benefits of phosphorus-rich foods?
+Phosphorus-rich foods can help to support overall health and well-being, and can also help to prevent a range of health problems, including osteoporosis, anemia, and fatigue.
What are some examples of phosphorus-rich foods?
+Some examples of phosphorus-rich foods include organ meats, such as liver and kidney, fish and seafood, such as salmon and shrimp, legumes, such as beans and lentils, and nuts and seeds, such as almonds and pumpkin seeds.
Can phosphorus supplements be used to treat health problems?
+Yes, phosphorus supplements can be used to treat a range of health problems, including osteoporosis and kidney disease. However, it is generally recommended to get phosphorus from whole, unprocessed foods, as these tend to be lower in added sugars, salt, and unhealthy fats.
In conclusion, phosphorus is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in many bodily functions, including the formation of bones and teeth, the production of energy, and the maintenance of various metabolic processes. A diet that is rich in phosphorus can help to support overall health and well-being, and can also help to prevent a range of health problems, including osteoporosis, anemia, and fatigue. By incorporating phosphorus-rich foods into your diet, you can help to support your overall health and well-being, and can also help to prevent a range of health problems. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with phosphorus-rich foods, and to ask any questions you may have about this important mineral.
