Intro
Discover how CT scans work with 5 key methods, utilizing X-rays, detectors, and computer algorithms to produce detailed cross-sectional images, enhancing medical diagnosis and imaging techniques.
The importance of medical imaging in diagnosing and treating various health conditions cannot be overstated. Among the numerous imaging modalities available, CT scans have emerged as a crucial diagnostic tool, offering unparalleled insights into the human body. CT scans, or computed tomography scans, utilize X-rays and computer technology to produce detailed cross-sectional images of the body, allowing healthcare professionals to diagnose a wide range of medical conditions. The significance of CT scans lies in their ability to provide high-resolution images that can help identify internal injuries, cancers, vascular diseases, and other health issues. As technology continues to advance, the applications of CT scans are expanding, making them an indispensable part of modern healthcare.
The working mechanism of CT scans is rooted in the principles of X-ray technology and computer-aided imaging. When a patient undergoes a CT scan, they are positioned on a table that slides into a large, doughnut-shaped machine. The machine is equipped with X-ray detectors and emitters that rotate around the patient, capturing images from multiple angles. The X-rays pass through the patient's body, and the detectors measure the amount of radiation that is absorbed or deflected by different tissues. This information is then transmitted to a computer, which reconstructs the data into detailed images of the body's internal structures. The resulting images can be manipulated and enhanced using specialized software, allowing healthcare professionals to zoom in, rotate, and analyze specific areas of interest.
The versatility of CT scans has led to their widespread adoption in various medical specialties, including radiology, oncology, cardiology, and neurology. CT scans can be used to guide biopsies, detect tumors, and monitor the effectiveness of treatments. They are also essential in emergency medicine, where they can help diagnose life-threatening conditions such as internal bleeding, strokes, and spinal cord injuries. Furthermore, CT scans have become a vital tool in medical research, enabling scientists to study the human body in unprecedented detail and develop new treatments for various diseases. As the field of medical imaging continues to evolve, it is likely that CT scans will remain a cornerstone of diagnostic medicine, providing healthcare professionals with the insights they need to deliver high-quality patient care.
Introduction to Ct Scan Technology

How Ct Scans Work
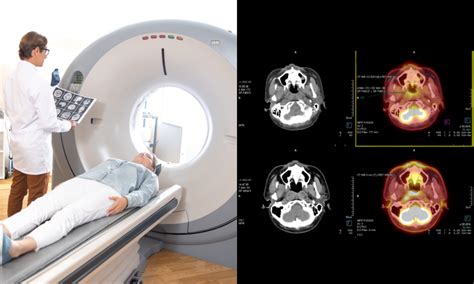
Benefits of Ct Scans
The benefits of CT scans are numerous and well-documented. They offer high-resolution images of the body's internal structures, allowing healthcare professionals to diagnose and treat a wide range of medical conditions with greater accuracy and precision. CT scans are also non-invasive and relatively quick, making them a convenient and comfortable option for patients. Additionally, CT scans can be used to guide biopsies, detect tumors, and monitor the effectiveness of treatments, making them an essential tool in modern healthcare.Types of Ct Scans

Ct Scan Procedure
Risks and Side Effects
While CT scans are generally safe, there are some risks and side effects associated with the procedure. These include: * Radiation exposure: CT scans use X-rays, which can increase the risk of cancer and other health problems. * Allergic reactions: some patients may be allergic to the contrast agents used in CT scans. * Kidney damage: the contrast agents used in CT scans can cause kidney damage in some patients. * Claustrophobia: some patients may experience claustrophobia or anxiety during the CT scan procedure.Ct Scan Applications
Future of Ct Scans

As we continue to explore the possibilities of CT scan technology, it is likely that these imaging modalities will remain a cornerstone of diagnostic medicine, providing healthcare professionals with the insights they need to deliver high-quality patient care. Whether you are a healthcare professional or a patient, understanding the basics of CT scans can help you appreciate the importance of these imaging modalities in modern healthcare.
The importance of CT scans in modern healthcare cannot be overstated. These imaging modalities have revolutionized the field of diagnostic medicine, enabling healthcare professionals to diagnose and treat a wide range of medical conditions with greater accuracy and precision. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that CT scans will remain a vital tool in healthcare, providing insights into the human body that were previously unimaginable.
In the coming years, we can expect to see significant advancements in CT scan technology, including the development of new applications, improved image resolution, and increased accessibility. As these advancements emerge, it is essential that healthcare professionals and patients stay informed about the benefits and limitations of CT scans, ensuring that these imaging modalities are used effectively and safely.
If you have any questions or concerns about CT scans, we encourage you to reach out to a healthcare professional or share your thoughts in the comments below. By working together, we can harness the power of CT scan technology to improve patient outcomes and advance the field of diagnostic medicine.
What is a CT scan?
+A CT scan, or computed tomography scan, is a medical imaging modality that uses X-rays and computer technology to produce detailed cross-sectional images of the body.
How do CT scans work?
+CT scans work by using X-rays to capture images of the body's internal structures. The X-rays pass through the patient's body, and the detectors measure the amount of radiation that is absorbed or deflected by different tissues.
What are the benefits of CT scans?
+The benefits of CT scans include high-resolution images of the body's internal structures, non-invasive and relatively quick procedure, and ability to guide biopsies and monitor treatments.
