Intro
A Complete Blood Count (CBC) is a fundamental medical test that provides a wealth of information about the body's overall health. It is a crucial diagnostic tool that helps doctors identify various health conditions, monitor treatment progress, and detect potential health risks. In this article, we will delve into the world of CBC blood counts, exploring their importance, components, and implications for our health.
A CBC test is a simple and non-invasive procedure that involves taking a blood sample from a vein, usually in the arm. The sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis, where it is examined for various parameters that provide insights into the body's blood cell production, immune function, and overall health. The results of a CBC test can help doctors diagnose a range of conditions, from anemia and infection to cancer and blood disorders.
The significance of CBC blood counts cannot be overstated. They are a vital component of routine medical check-ups, allowing doctors to monitor patients' health and detect potential problems early on. By analyzing the different components of a CBC test, doctors can identify patterns and abnormalities that may indicate underlying health issues. In this article, we will explore the various components of a CBC test, their significance, and what they can reveal about our health.
Introduction to CBC Components
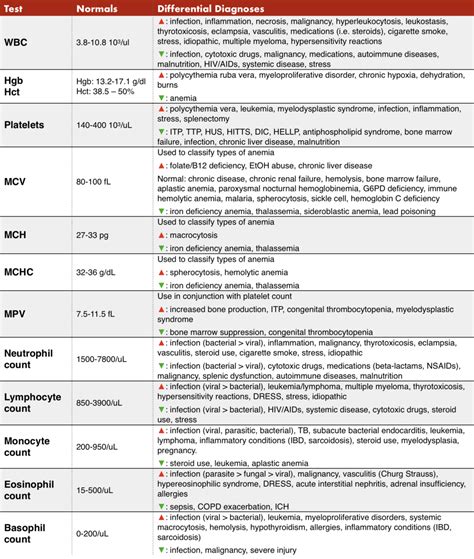
A CBC test typically includes several components, each measuring different aspects of the blood. These components include white blood cell count, red blood cell count, hemoglobin, hematocrit, and platelet count. Each of these parameters provides valuable information about the body's blood cell production, immune function, and overall health. By analyzing these components, doctors can identify potential health risks and develop targeted treatment plans.
White Blood Cell Count (WBC)
The white blood cell count (WBC) measures the number of white blood cells in the blood. White blood cells, also known as leukocytes, play a crucial role in the immune system, helping to fight off infections and diseases. A high WBC count may indicate the presence of an infection, inflammation, or immune disorder, while a low WBC count can increase the risk of infection.Red Blood Cell Count (RBC) and Hemoglobin
The red blood cell count (RBC) measures the number of red blood cells in the blood. Red blood cells, also known as erythrocytes, carry oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that helps to transport oxygen. A low RBC count or hemoglobin level can indicate anemia, which can cause fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
Hematocrit (HCT) and Platelet Count
The hematocrit (HCT) measures the proportion of red blood cells in the blood. A low HCT level can indicate anemia, while a high HCT level can indicate dehydration or polycythemia. The platelet count measures the number of platelets in the blood. Platelets, also known as thrombocytes, play a crucial role in blood clotting. A low platelet count can increase the risk of bleeding, while a high platelet count can increase the risk of blood clots.Interpreting CBC Results
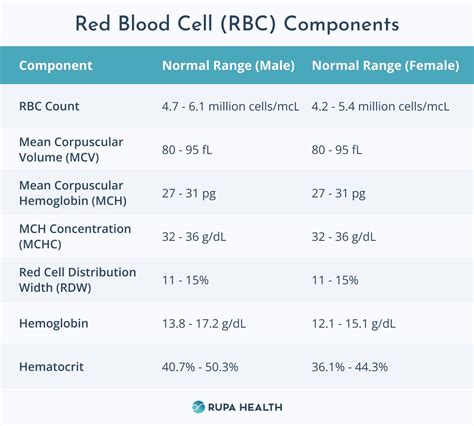
Interpreting CBC results requires a thorough understanding of the different components and their significance. Doctors will typically review the results in conjunction with other medical tests and the patient's medical history. Abnormal results may indicate the presence of an underlying health condition, and further testing or treatment may be necessary. It is essential to discuss the results with a doctor to understand their implications and develop a plan to address any potential health issues.
CBC and Disease Diagnosis
CBC tests are a crucial diagnostic tool for various diseases and conditions. For example, a high WBC count may indicate the presence of an infection, such as pneumonia or sepsis. A low RBC count or hemoglobin level may indicate anemia, which can be caused by iron deficiency, vitamin deficiency, or chronic disease. A low platelet count can increase the risk of bleeding, while a high platelet count can increase the risk of blood clots.CBC and Health Monitoring
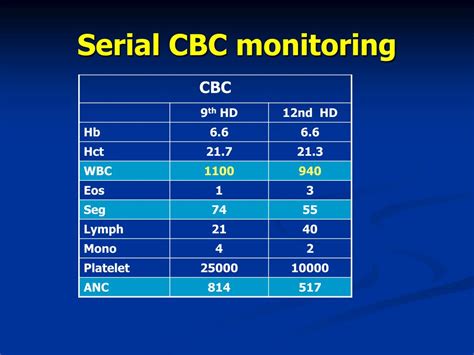
CBC tests are not only used for disease diagnosis but also for health monitoring. Regular CBC tests can help doctors monitor patients' health and detect potential problems early on. For example, patients with chronic diseases, such as diabetes or kidney disease, may require regular CBC tests to monitor their condition and adjust their treatment plan as needed.
CBC and Blood Disorders
CBC tests are also used to diagnose and monitor blood disorders, such as anemia, leukemia, and lymphoma. For example, a high WBC count may indicate the presence of leukemia, while a low RBC count or hemoglobin level may indicate anemia. Regular CBC tests can help doctors monitor patients with blood disorders and adjust their treatment plan as needed.CBC and Treatment Planning
CBC tests play a crucial role in treatment planning. By analyzing the different components of a CBC test, doctors can develop targeted treatment plans that address the underlying health condition. For example, patients with anemia may require iron supplements or blood transfusions, while patients with leukemia may require chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
CBC and Patient Education
Patient education is essential for effective CBC testing and treatment planning. Patients should understand the different components of a CBC test, their significance, and what they can reveal about their health. By educating patients about CBC tests, doctors can empower them to take an active role in their healthcare and make informed decisions about their treatment plan.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, CBC blood counts are a vital diagnostic tool that provides a wealth of information about our health. By understanding the different components of a CBC test, their significance, and what they can reveal about our health, we can take an active role in our healthcare and make informed decisions about our treatment plan. If you have any questions or concerns about CBC tests or your health, consult with your doctor or healthcare provider.
What is a CBC test, and why is it important?
+A CBC test is a medical test that measures the different components of the blood, including white blood cell count, red blood cell count, hemoglobin, hematocrit, and platelet count. It is essential for diagnosing and monitoring various health conditions, including anemia, infection, and blood disorders.
What are the different components of a CBC test, and what do they measure?
+The different components of a CBC test include white blood cell count, red blood cell count, hemoglobin, hematocrit, and platelet count. Each component measures different aspects of the blood, including immune function, oxygen transport, and blood clotting.
How often should I get a CBC test, and what are the risks and benefits?
+The frequency of CBC tests depends on individual health needs and medical conditions. Generally, healthy adults may require a CBC test every 1-2 years, while patients with chronic diseases or blood disorders may require more frequent testing. The risks and benefits of CBC tests should be discussed with a doctor or healthcare provider.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of CBC blood counts and their significance in maintaining our health. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others. Remember, taking an active role in your healthcare is essential for maintaining your overall well-being.
