Intro
Discover how Sed Rate works with 5 key methods, including inflammation detection, blood testing, and medical diagnosis, to measure erythrocyte sedimentation rate and diagnose conditions like arthritis and autoimmune diseases.
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate, commonly referred to as the sed rate, is a blood test that measures how quickly erythrocytes (red blood cells) settle in a test tube containing a blood sample. It indirectly measures how much inflammation is in the body. The sed rate is a simple yet effective tool used to diagnose and monitor various conditions, including inflammatory and autoimmune disorders. Understanding how the sed rate works is crucial for both healthcare professionals and patients alike, as it can provide valuable insights into the body's inflammatory response.
The process of sedimentation is influenced by several factors, including the presence of inflammatory proteins, the size and shape of red blood cells, and the concentration of fibrinogen in the blood. When inflammation is present, the liver produces more acute-phase proteins, such as fibrinogen and immunoglobulins, which cause red blood cells to clump together, forming stacks called rouleaux. This clumping increases the density of the red blood cells, allowing them to settle more quickly to the bottom of the test tube. The sed rate is typically measured in millimeters per hour (mm/hr) and can be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and track changes in inflammation over time.
The sed rate has been a cornerstone of diagnostic testing for many years, providing a non-specific yet sensitive indicator of inflammation. By understanding the mechanisms behind the sed rate, healthcare professionals can better interpret test results and make more informed decisions about patient care. The sed rate is often used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests, such as the C-reactive protein (CRP) test, to provide a more comprehensive picture of the body's inflammatory response. In this article, we will delve deeper into the world of sed rates, exploring the different ways they work and their significance in various medical contexts.
Introduction to Sed Rate
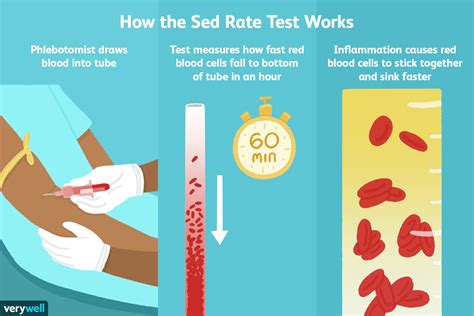
How Sed Rate Works
The sed rate works by measuring the rate at which red blood cells settle in a test tube. This process is influenced by several factors, including the presence of inflammatory proteins, the size and shape of red blood cells, and the concentration of fibrinogen in the blood. When inflammation is present, the liver produces more acute-phase proteins, such as fibrinogen and immunoglobulins, which cause red blood cells to clump together, forming stacks called rouleaux. This clumping increases the density of the red blood cells, allowing them to settle more quickly to the bottom of the test tube.Benefits of Sed Rate Testing
Common Uses of Sed Rate
The sed rate test is commonly used to diagnose and monitor a variety of inflammatory conditions, including: * Rheumatoid arthritis * Lupus * Inflammatory bowel disease * Cancer * Infections The sed rate test can also be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and track changes in inflammation over time. It is often used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests, such as the CRP test, to provide a more comprehensive picture of the body's inflammatory response.Interpreting Sed Rate Results
Factors that Affect Sed Rate Results
Several factors can affect sed rate results, including: * Age: Sed rates tend to increase with age * Sex: Sed rates tend to be higher in women than in men * Pregnancy: Sed rates can increase during pregnancy * Medications: Certain medications, such as corticosteroids, can affect sed rate results * Infections: Sed rates can increase in response to infections * Inflammatory conditions: Sed rates can increase in response to inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritisLimitations of Sed Rate Testing

Alternatives to Sed Rate Testing
Several alternatives to sed rate testing exist, including: * C-reactive protein (CRP) test: This test measures the level of CRP in the blood, which can indicate the presence of inflammation. * Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test: This test measures the rate at which red blood cells settle in a test tube, similar to the sed rate test. * White blood cell count: This test measures the number of white blood cells in the blood, which can indicate the presence of infection or inflammation.Conclusion and Future Directions

What is the normal range for sed rate?
+A normal sed rate is usually considered to be between 0 and 20 mm/hr, although this can vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's age and sex.
What can cause an elevated sed rate?
+An elevated sed rate can be caused by a variety of conditions, including inflammatory disorders, infections, and cancer. It can also be influenced by several factors, including age, sex, and medications.
How is sed rate testing used in clinical practice?
+Sed rate testing is commonly used to diagnose and monitor inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. It is also used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and track changes in inflammation over time.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the sed rate test and its uses in clinical practice. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more about sed rate testing, please don't hesitate to comment below. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please share it with others who may benefit from this knowledge.
