Intro
Discover 5 uses of Acyclovir, an antiviral medication, for treating herpes, shingles, and cold sores, with applications in genital herpes, chickenpox, and viral infections management, offering relief and prevention.
The importance of antiviral medications cannot be overstated, especially in the context of managing and treating viral infections. Among these, Acyclovir stands out as a pivotal drug in the arsenal against viral diseases. Its versatility and efficacy in combating a range of viral infections have made it a cornerstone in modern medicine. Acyclovir's impact is felt across various medical specialties, from dermatology to neurology, underscoring its broad utility. As we delve into the 5 uses of Acyclovir, it becomes clear that this medication plays a critical role in improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
The development of Acyclovir marked a significant milestone in the fight against viral infections, particularly those caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV) and varicella-zoster virus (VZV). Its mechanism of action, which involves the selective inhibition of viral DNA synthesis, has been a subject of extensive study. By understanding how Acyclovir works, healthcare professionals can better appreciate its potential applications and limitations. Furthermore, the drug's safety profile and relatively low toxicity have contributed to its widespread adoption in clinical practice.
As research into viral diseases continues to evolve, the role of Acyclovir in treatment protocols remains a topic of interest. From its use in managing recurrent outbreaks of genital herpes to its application in preventing viral infections in immunocompromised patients, Acyclovir's benefits are multifaceted. The drug's ability to reduce the severity and duration of viral infections has a direct impact on patient morbidity and mortality, making it an essential component of modern healthcare.
Introduction to Acyclovir
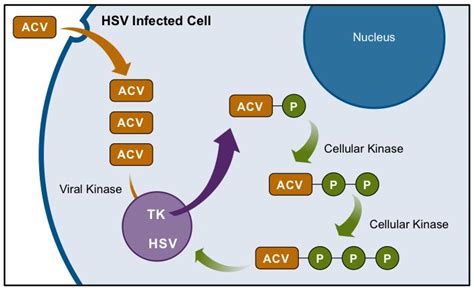
Acyclovir is an antiviral medication that belongs to the class of nucleoside analogs. It is primarily used to treat viral infections caused by the herpes viruses, including herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2), varicella-zoster virus (VZV), and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). The drug works by inhibiting the replication of viral DNA, thereby reducing the severity and duration of viral infections.
How Acyclovir Works
Acyclovir's mechanism of action involves the inhibition of viral DNA synthesis. The drug is converted into its active form, acyclovir triphosphate, which then competes with the natural nucleosides for incorporation into the viral DNA. This competition leads to the termination of viral DNA synthesis, effectively preventing the virus from replicating.Uses of Acyclovir
The uses of Acyclovir are diverse and can be categorized based on the type of viral infection being treated. Some of the primary uses of Acyclovir include:
- Treatment of genital herpes: Acyclovir is effective in reducing the severity and duration of genital herpes outbreaks.
- Treatment of cold sores: The drug can help alleviate the symptoms of cold sores, including pain and discomfort.
- Treatment of shingles: Acyclovir is used to manage the symptoms of shingles, including pain and rash.
- Prevention of viral infections in immunocompromised patients: Acyclovir can be used to prevent viral infections in patients with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy.
- Treatment of chickenpox: The drug is effective in managing the symptoms of chickenpox, including fever and rash.
Benefits of Acyclovir
The benefits of Acyclovir are numerous and can be summarized as follows:- Reduced severity and duration of viral infections
- Improved patient outcomes and quality of life
- Effective in preventing viral infections in immunocompromised patients
- Relatively low toxicity and safe to use
- Can be administered orally or intravenously, depending on the severity of the infection
Administration and Dosage

The administration and dosage of Acyclovir depend on the type and severity of the viral infection being treated. The drug can be administered orally or intravenously, and the dosage is typically adjusted based on the patient's age, weight, and renal function.
- Oral administration: The typical oral dosage of Acyclovir for adults is 200-400 mg every 4-6 hours, depending on the type and severity of the infection.
- Intravenous administration: The typical intravenous dosage of Acyclovir for adults is 5-10 mg/kg every 8 hours, depending on the type and severity of the infection.
Side Effects and Interactions
While Acyclovir is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects and interact with other medications. Some common side effects of Acyclovir include:- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Rash
Acyclovir can also interact with other medications, including:
- Probenecid: Can increase the levels of Acyclovir in the blood
- Cimetidine: Can decrease the absorption of Acyclovir
- Theophylline: Can increase the levels of theophylline in the blood
Precautions and Contraindications

While Acyclovir is generally safe to use, there are certain precautions and contraindications that need to be considered.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Acyclovir is classified as a category B drug, which means that it is safe to use during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Renal impairment: The dosage of Acyclovir needs to be adjusted in patients with renal impairment.
- Hypersensitivity: Patients who are hypersensitive to Acyclovir or any of its components should avoid using the drug.
Resistance and Future Directions
The development of resistance to Acyclovir is a concern, particularly in patients with recurrent viral infections. To address this issue, researchers are exploring new antiviral agents and combination therapies that can overcome resistance and improve patient outcomes.In conclusion, Acyclovir is a versatile antiviral medication that plays a critical role in managing and treating viral infections. Its efficacy, safety, and relatively low toxicity make it an essential component of modern healthcare. As research into viral diseases continues to evolve, the role of Acyclovir in treatment protocols is likely to remain a topic of interest.
Final Thoughts

The importance of Acyclovir in modern medicine cannot be overstated. Its ability to reduce the severity and duration of viral infections has a direct impact on patient morbidity and mortality. As healthcare professionals, it is essential to stay up-to-date with the latest research and guidelines on the use of Acyclovir and other antiviral medications.
We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with Acyclovir in the comments section below. Your feedback and insights can help others better understand the benefits and limitations of this medication. Additionally, we encourage readers to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about Acyclovir and its uses.
What is Acyclovir used for?
+Acyclovir is an antiviral medication used to treat viral infections caused by the herpes viruses, including genital herpes, cold sores, and shingles.
How does Acyclovir work?
+Acyclovir works by inhibiting the replication of viral DNA, thereby reducing the severity and duration of viral infections.
What are the side effects of Acyclovir?
+Common side effects of Acyclovir include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, and fatigue. Rare side effects can include rash, itching, and difficulty breathing.
Can Acyclovir be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding?
+Acyclovir is classified as a category B drug, which means that it is safe to use during pregnancy and breastfeeding. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before using any medication during these times.
How long does it take for Acyclovir to start working?
+The onset of action of Acyclovir can vary depending on the type and severity of the viral infection. In general, it can take several hours to several days for the medication to start working.
