Intro
Discover what Amiodarone is, an antiarrhythmic medication, and its uses in treating irregular heartbeats, arrhythmias, and tachycardia, with insights into its side effects and interactions.
Amiodarone is a medication that has been widely used for decades to treat various heart rhythm disorders, including arrhythmias and tachycardia. It is a complex drug with a unique mechanism of action, and its use has been associated with both benefits and risks. In this article, we will delve into the world of amiodarone, exploring its history, pharmacology, indications, side effects, and controversies.
Amiodarone was first introduced in the 1960s as an anti-anginal medication, but its use was soon expanded to include the treatment of arrhythmias. The drug's popularity grew rapidly, and it became one of the most widely prescribed anti-arrhythmic medications in the world. Today, amiodarone is used to treat a range of heart rhythm disorders, including atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, and Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.
Pharmacology of Amiodarone
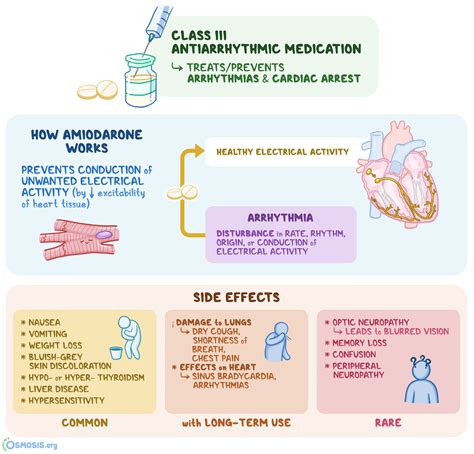
Mechanisms of Action
The mechanisms of action of amiodarone are not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of ion channel blockade, anti-adrenergic effects, and modulation of the heart's electrical activity. Amiodarone has a high iodine content, which can affect thyroid function and contribute to its anti-arrhythmic effects.Indications for Amiodarone
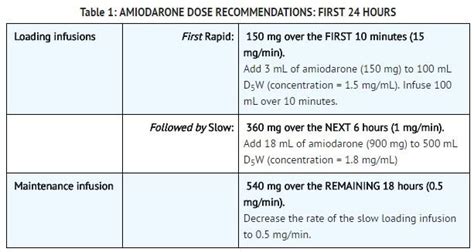
Amiodarone can be used to convert abnormal heart rhythms to a normal sinus rhythm, or to prevent the recurrence of arrhythmias. It can be used in both acute and chronic settings, and is often prescribed for long-term use.
Benefits of Amiodarone
The benefits of amiodarone include its effectiveness in controlling arrhythmias, its relatively long half-life, and its ability to be used in a variety of clinical settings. Amiodarone has been shown to reduce the risk of arrhythmic death and to improve symptoms in patients with heart failure.Side Effects of Amiodarone

More serious side effects of amiodarone can include:
- Thyroid dysfunction
- Pulmonary fibrosis
- Liver damage
- Cardiac effects, such as bradycardia and QT prolongation
Risks and Controversies
The use of amiodarone has been associated with several risks and controversies, including its potential to cause thyroid dysfunction, pulmonary fibrosis, and liver damage. The drug's high iodine content can affect thyroid function, and patients on long-term amiodarone therapy may require regular thyroid function tests.Monitoring and Follow-Up
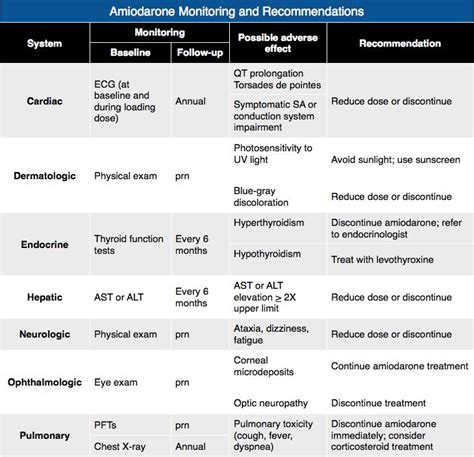
Alternative Treatments
For patients who are unable to tolerate amiodarone or who experience significant side effects, alternative treatments may be considered. These may include other anti-arrhythmic medications, such as beta blockers or calcium channel blockers, or non-pharmacological treatments, such as catheter ablation or pacemaker implantation.Conclusion and Future Directions

What is amiodarone used for?
+Amiodarone is used to treat various heart rhythm disorders, including atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, and Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.
What are the common side effects of amiodarone?
+Common side effects of amiodarone include nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue, dizziness, headache, and skin rash.
How is amiodarone monitored?
+Patients on amiodarone therapy require regular monitoring and follow-up to minimize the risk of side effects and to ensure the drug's effectiveness. This may include regular electrocardiograms (ECGs), thyroid function tests, liver function tests, pulmonary function tests, and regular check-ups with a healthcare provider.
We hope this article has provided a comprehensive overview of amiodarone, its uses, benefits, and risks. If you have any questions or comments, please don't hesitate to share them with us. We encourage you to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about amiodarone and its role in treating heart rhythm disorders.
