Intro
Discover 5 essential uses of Amoxicillin, a broad-spectrum antibiotic, for treating bacterial infections, pneumonia, skin infections, urinary tract infections, and more, with its mechanism, benefits, and side effects, for effective health management and disease prevention.
Amoxicillin is a widely prescribed antibiotic that belongs to the penicillin class of medications. It is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including those affecting the respiratory tract, skin, and urinary tract. The importance of amoxicillin lies in its effectiveness against a broad range of bacteria, making it a go-to treatment for many common infections. Understanding the uses of amoxicillin is crucial for patients to ensure they are taking the medication correctly and for healthcare providers to prescribe it appropriately. In this article, we will delve into the 5 primary uses of amoxicillin, its working mechanisms, benefits, and other key information related to this antibiotic.
The versatility of amoxicillin stems from its ability to combat various types of bacterial infections. From pneumonia to dental infections, amoxicillin has proven to be an invaluable treatment option. Its widespread use is also due to its relatively mild side effect profile compared to other antibiotics, making it suitable for a broad range of patients, including children and the elderly. However, like all antibiotics, amoxicillin should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional to ensure its effectiveness and to minimize the risk of antibiotic resistance.
Amoxicillin's effectiveness is attributed to its mechanism of action, which involves inhibiting the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall. This leads to the weakening and eventual lysis of the bacterial cells, thereby eliminating the infection. The drug is available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and oral suspensions, making it easy to administer to patients of all ages. Despite its many benefits, amoxicillin, like all medications, has potential side effects and interactions that patients should be aware of to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Respiratory Tract Infections
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
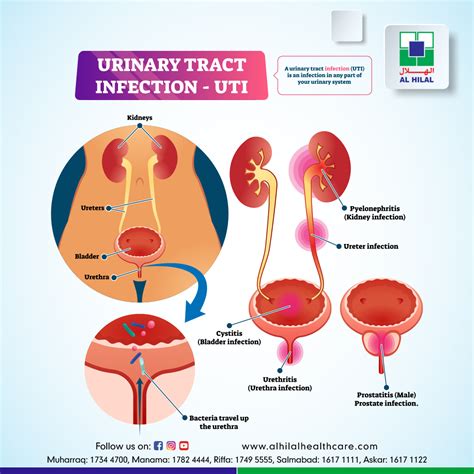
Urinary Tract Infections
Dental Infections
Helicobacter pylori Infections
In addition to these primary uses, amoxicillin may also be prescribed for other bacterial infections, including those affecting the gastrointestinal tract, bones, and joints. Its use in these cases depends on the susceptibility of the causative bacteria to amoxicillin and the severity of the infection.
When taking amoxicillin, it's crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and duration of treatment to ensure the infection is fully cleared and to minimize the risk of antibiotic resistance. Patients should also be aware of potential side effects, such as diarrhea, nausea, and allergic reactions, and report these to their healthcare provider promptly.
Benefits of Amoxicillin
The benefits of amoxicillin include: - Broad-spectrum activity against a wide range of bacteria - Availability in various formulations for ease of administration - Generally well-tolerated with a mild side effect profile - Cost-effective compared to some newer antibiotics - Can be used in pediatric and geriatric populations with appropriate dosingWorking Mechanism
Amoxicillin works by inhibiting the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall, leading to cell lysis and death. This mechanism is effective against bacteria that are susceptible to amoxicillin, making it a valuable treatment option for various infections.Steps for Effective Treatment
For effective treatment with amoxicillin: 1. **Complete the full course of treatment** as prescribed by your healthcare provider. 2. **Take the medication at the correct dosage and time** to maintain adequate drug levels in the body. 3. **Report any side effects** to your healthcare provider to manage them appropriately. 4. **Avoid sharing your medication** with others, as this can lead to inappropriate use and antibiotic resistance.In conclusion, amoxicillin is a versatile and effective antibiotic used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. Its broad-spectrum activity, ease of administration, and generally mild side effect profile make it a valuable treatment option for patients of all ages. By understanding the uses, benefits, and working mechanism of amoxicillin, patients and healthcare providers can ensure its safe and effective use, contributing to better health outcomes and the fight against antibiotic resistance.
To further engage with the topic, we invite readers to share their experiences with amoxicillin or ask questions about its use in the comments section below. Sharing this article with others who may benefit from the information can also help spread awareness about the importance of responsible antibiotic use.
What is amoxicillin used for?
+Amoxicillin is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, urinary tract infections, dental infections, and Helicobacter pylori infections.
How does amoxicillin work?
+Amoxicillin works by inhibiting the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall, leading to cell lysis and death. This mechanism is effective against bacteria that are susceptible to amoxicillin.
What are the benefits of taking amoxicillin?
+The benefits of amoxicillin include its broad-spectrum activity, availability in various formulations, generally mild side effect profile, cost-effectiveness, and suitability for use in pediatric and geriatric populations.
