Intro
Discover Vitamin B6 benefits, including brain function, heart health, and immune system support, with uses in energy metabolism, nerve function, and mood regulation.
Vitamin B6 is one of the most versatile and essential nutrients in the human body. It plays a critical role in various bodily functions, including energy metabolism, nerve function, and immune system function. Vitamin B6, also known as pyridoxine, is a water-soluble vitamin that is found in a wide range of food sources, including meat, fish, poultry, whole grains, and legumes. With its numerous health benefits and uses, it's no wonder that vitamin B6 has become a popular topic of discussion in the health and wellness community.
The importance of vitamin B6 cannot be overstated. It is involved in over 100 biochemical reactions in the body, making it a vital nutrient for maintaining optimal health. Vitamin B6 is necessary for the production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body. It also helps to regulate homocysteine levels in the blood, which is associated with a reduced risk of heart disease. Additionally, vitamin B6 is involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, which play a crucial role in mood regulation and cognitive function.
As research continues to uncover the numerous benefits of vitamin B6, it's becoming increasingly clear that this nutrient is essential for maintaining optimal health. From reducing the risk of chronic diseases to improving cognitive function and mood, the benefits of vitamin B6 are vast and varied. Whether you're looking to improve your overall health or address a specific health concern, understanding the benefits and uses of vitamin B6 is essential.
Vitamin B6 Benefits

Vitamin B6 offers a wide range of health benefits, including reducing the risk of heart disease, improving cognitive function, and regulating mood. Some of the key benefits of vitamin B6 include:
- Reducing the risk of heart disease by regulating homocysteine levels in the blood
- Improving cognitive function and reducing the risk of age-related cognitive decline
- Regulating mood and reducing the risk of depression and anxiety
- Supporting immune system function and reducing the risk of illness and infection
- Aiding in the production of red blood cells and preventing anemia
Vitamin B6 and Heart Health
Vitamin B6 plays a critical role in maintaining heart health by regulating homocysteine levels in the blood. Elevated homocysteine levels have been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, including heart attacks, strokes, and high blood pressure. Vitamin B6 helps to convert homocysteine into other amino acids, reducing its levels in the blood and minimizing the risk of heart disease.Vitamin B6 Uses

Vitamin B6 has a wide range of uses, from reducing the risk of chronic diseases to improving cognitive function and mood. Some of the key uses of vitamin B6 include:
- Reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke
- Improving cognitive function and reducing the risk of age-related cognitive decline
- Regulating mood and reducing the risk of depression and anxiety
- Supporting immune system function and reducing the risk of illness and infection
- Aiding in the production of red blood cells and preventing anemia
Vitamin B6 and Cognitive Function
Vitamin B6 plays a critical role in maintaining cognitive function and reducing the risk of age-related cognitive decline. It is involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, which play a crucial role in mood regulation and cognitive function. Vitamin B6 has also been shown to improve memory and concentration, making it an essential nutrient for individuals looking to improve their cognitive function.Vitamin B6 Deficiency
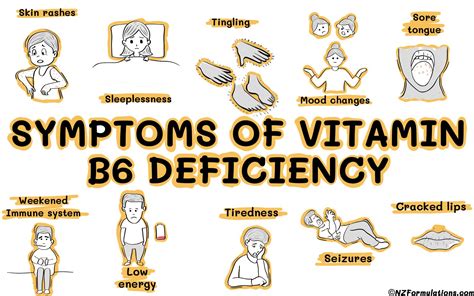
Vitamin B6 deficiency can occur due to a variety of factors, including a poor diet, certain medical conditions, and the use of certain medications. Some of the key causes of vitamin B6 deficiency include:
- A poor diet that is lacking in vitamin B6-rich foods
- Certain medical conditions, such as celiac disease and Crohn's disease
- The use of certain medications, such as anticonvulsants and immunosuppressants
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding, which can increase the body's demand for vitamin B6
Vitamin B6 Deficiency Symptoms
The symptoms of vitamin B6 deficiency can vary depending on the severity of the deficiency. Some common symptoms of vitamin B6 deficiency include: * Fatigue and weakness * Depression and anxiety * Cognitive impairment and memory loss * Numbness and tingling in the hands and feet * Seizures and convulsionsVitamin B6 Food Sources

Vitamin B6 is found in a wide range of food sources, including:
- Meat, fish, and poultry
- Whole grains, such as brown rice and quinoa
- Legumes, such as beans and lentils
- Nuts and seeds, such as sunflower seeds and pumpkin seeds
- Soy products, such as tofu and tempeh
Vitamin B6 Rich Foods
Some of the richest sources of vitamin B6 include: * Chicken and turkey * Fish, such as salmon and tuna * Beef and pork * Lamb and venison * Whole grains, such as brown rice and quinoaVitamin B6 Supplements

Vitamin B6 supplements are available in a variety of forms, including capsules, tablets, and injections. Vitamin B6 supplements can be beneficial for individuals who are at risk of deficiency or who have a confirmed deficiency. However, it's essential to talk to a healthcare professional before taking any supplements, as they can interact with certain medications and have adverse effects in high doses.
Vitamin B6 Dosage
The recommended daily intake of vitamin B6 varies depending on age, sex, and other factors. The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for vitamin B6 is: * 1.3 milligrams per day for adults * 1.5 milligrams per day for pregnant women * 1.6 milligrams per day for breastfeeding womenVitamin B6 Interactions
Vitamin B6 can interact with certain medications and have adverse effects in high doses. Some of the potential interactions and side effects of vitamin B6 include:
- Interactions with anticonvulsants, such as phenytoin and carbamazepine
- Interactions with immunosuppressants, such as cyclosporine and tacrolimus
- Numbness and tingling in the hands and feet
- Seizures and convulsions
Vitamin B6 Side Effects
The side effects of vitamin B6 can vary depending on the dose and individual factors. Some common side effects of vitamin B6 include: * Nausea and vomiting * Diarrhea and abdominal cramps * Headache and fatigue * Allergic reactions, such as hives and itchingWhat is vitamin B6 and what are its benefits?
+Vitamin B6, also known as pyridoxine, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a critical role in various bodily functions, including energy metabolism, nerve function, and immune system function. Its benefits include reducing the risk of heart disease, improving cognitive function, and regulating mood.
What are the symptoms of vitamin B6 deficiency?
+The symptoms of vitamin B6 deficiency can vary depending on the severity of the deficiency, but common symptoms include fatigue and weakness, depression and anxiety, cognitive impairment and memory loss, numbness and tingling in the hands and feet, and seizures and convulsions.
What are the best food sources of vitamin B6?
+Vitamin B6 is found in a wide range of food sources, including meat, fish, and poultry, whole grains, legumes, nuts and seeds, and soy products. Some of the richest sources of vitamin B6 include chicken and turkey, fish, beef and pork, lamb and venison, and whole grains.
In conclusion, vitamin B6 is an essential nutrient that plays a critical role in various bodily functions. Its benefits and uses are vast and varied, ranging from reducing the risk of heart disease and improving cognitive function to regulating mood and supporting immune system function. By understanding the importance of vitamin B6 and incorporating vitamin B6-rich foods into your diet, you can take a proactive approach to maintaining optimal health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with vitamin B6 in the comments below and to explore other articles on our website for more information on nutrition and health.
