Intro
The importance of understanding urine creatinine levels cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in assessing kidney function and overall health. Creatinine is a waste product that is generated by the body's metabolic processes and is filtered out by the kidneys. By analyzing urine creatinine levels, healthcare professionals can gain valuable insights into the efficiency of the kidneys and identify potential issues before they become severe. In this article, we will delve into the world of urine creatinine levels, exploring what they mean, how they are measured, and what the results can indicate about our health.
Urine creatinine levels are a vital component of a comprehensive health checkup, as they can reveal underlying kidney problems, such as kidney disease or kidney damage. The kidneys are responsible for filtering waste and excess fluids from the blood, and creatinine is one of the waste products that they remove. By measuring the amount of creatinine in the urine, healthcare professionals can assess how well the kidneys are functioning and identify any potential issues. Additionally, urine creatinine levels can also be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatments for kidney disease and other related conditions.
The significance of urine creatinine levels extends beyond kidney function, as they can also be used to diagnose and monitor other health conditions, such as muscle disorders and certain types of cancer. For instance, high levels of creatinine in the urine can indicate muscle damage or disease, while low levels can suggest kidney failure or other kidney-related issues. Furthermore, urine creatinine levels can also be used to monitor the progression of certain diseases, such as chronic kidney disease, and to adjust treatment plans accordingly.
What are Urine Creatinine Levels?
How are Urine Creatinine Levels Measured?
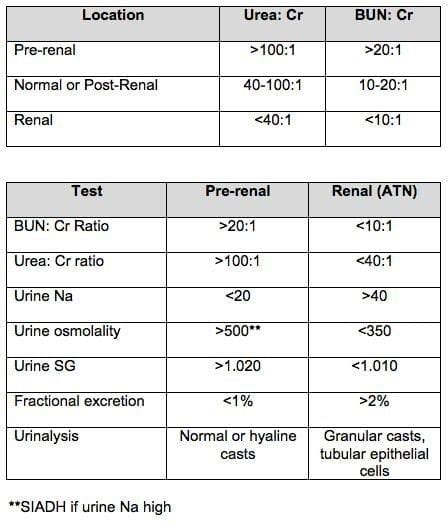
Urine creatinine levels are typically measured using a urine test, which involves collecting a sample of urine and analyzing it for creatinine content. The test is usually performed in a laboratory, and the results are typically available within a few hours. The measurement of urine creatinine levels can be done using various methods, including spectrophotometry, enzymatic assays, and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Each method has its own advantages and limitations, and the choice of method depends on the specific requirements of the test and the laboratory equipment available.Interpreting Urine Creatinine Levels

Factors that Influence Urine Creatinine Levels
Several factors can influence urine creatinine levels, including: * Age: Urine creatinine levels tend to decrease with age, especially in older adults. * Sex: Males tend to have higher urine creatinine levels than females. * Muscle mass: Individuals with more muscle mass tend to have higher urine creatinine levels. * Diet: A diet high in protein can increase urine creatinine levels, while a diet low in protein can decrease levels. * Hydration: Dehydration can increase urine creatinine levels, while overhydration can decrease levels. * Medications: Certain medications, such as diuretics and certain antibiotics, can affect urine creatinine levels.Urine Creatinine Levels and Kidney Function
Stages of Kidney Disease
Kidney disease is typically classified into five stages, based on the level of kidney function. The stages are: * Stage 1: Normal kidney function, with a glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of 90% or higher. * Stage 2: Mild kidney disease, with a GFR of 60-89%. * Stage 3: Moderate kidney disease, with a GFR of 30-59%. * Stage 4: Severe kidney disease, with a GFR of 15-29%. * Stage 5: End-stage kidney disease, with a GFR of less than 15%.Urine Creatinine Levels and Other Health Conditions

Common Health Conditions Associated with Urine Creatinine Levels
Some common health conditions associated with urine creatinine levels include: * Kidney disease: High levels of creatinine in the urine can indicate kidney disease or kidney damage. * Muscle disorders: High levels of creatinine in the urine can indicate muscle damage or disease. * Cancer: Certain types of cancer, such as kidney cancer, can cause high levels of creatinine in the urine. * Diabetes: High levels of creatinine in the urine can indicate kidney damage or disease in individuals with diabetes.Managing Urine Creatinine Levels
Tips for Maintaining Healthy Urine Creatinine Levels
Some tips for maintaining healthy urine creatinine levels include: * Drinking at least 8-10 glasses of water per day. * Eating a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. * Exercising regularly, such as walking or jogging for at least 30 minutes per day. * Managing underlying health conditions, such as diabetes and high blood pressure. * Getting regular health checkups to monitor kidney function and overall health.What is the normal range for urine creatinine levels?
+The normal range for urine creatinine levels varies depending on age, sex, and muscle mass, but in general, a level of 50-120 mg/dL (4.4-10.6 μmol/L) is considered normal.
What can cause high levels of creatinine in the urine?
+High levels of creatinine in the urine can be caused by kidney disease or kidney damage, muscle disorders, and certain types of cancer.
How can I manage my urine creatinine levels?
+Managing urine creatinine levels requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and medical treatment. Some ways to manage urine creatinine levels include staying hydrated, eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and managing underlying health conditions.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of urine creatinine levels and their importance in assessing kidney function and overall health. By understanding the factors that influence urine creatinine levels and taking steps to manage them, you can help to maintain healthy kidneys and reduce the risk of kidney disease and other health problems. If you have any questions or concerns about urine creatinine levels or kidney health, we encourage you to speak with a healthcare professional or share your thoughts in the comments below. Additionally, we invite you to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about urine creatinine levels and kidney health.
