Intro
Learn about bradycardia, a heart condition characterized by slow heart rate, its causes, symptoms, and treatments, including arrhythmia management and cardiac monitoring.
Bradycardia is a medical condition characterized by a slow heart rate, typically defined as a resting heart rate of less than 60 beats per minute in adults. This condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetic predisposition, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions. In some cases, bradycardia can be a normal variant, particularly in athletes or individuals who are physically fit. However, in other cases, it can be a sign of an underlying health issue that requires medical attention. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for bradycardia is essential for individuals who are affected by this condition.
The heart rate is controlled by the autonomic nervous system, which regulates the body's automatic functions, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing. In individuals with bradycardia, the autonomic nervous system may not be functioning properly, leading to a slow heart rate. This can cause a range of symptoms, including fatigue, dizziness, and shortness of breath. In severe cases, bradycardia can lead to more serious complications, such as fainting or even heart failure.
The importance of understanding bradycardia cannot be overstated. This condition can have a significant impact on an individual's quality of life, making it essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time. By understanding the causes and treatment options for bradycardia, individuals can take steps to manage their condition and reduce their risk of complications. Whether you are an individual who has been diagnosed with bradycardia or simply looking to learn more about this condition, this article will provide a comprehensive overview of the topic, including the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
What Causes Bradycardia
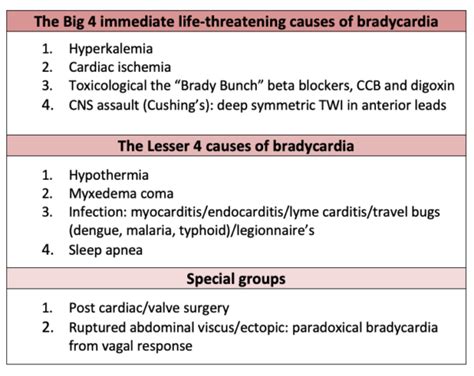
- Genetic predisposition: Some individuals may be born with a slow heart rate due to genetic factors.
- Certain medications: Certain medications, such as beta blockers and calcium channel blockers, can slow the heart rate and lead to bradycardia.
- Underlying medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as hypothyroidism, anemia, and sleep apnea, can cause bradycardia.
- Athletes: Athletes or individuals who are physically fit may have a slow heart rate due to their high level of physical conditioning.
- Age: Bradycardia can occur in individuals of any age, but it is more common in older adults.
Types of Bradycardia
There are several types of bradycardia, including: * Sinus bradycardia: This is the most common type of bradycardia, characterized by a slow heart rate that originates in the sinoatrial node. * Junctional bradycardia: This type of bradycardia occurs when the heart rate is controlled by the atrioventricular node, rather than the sinoatrial node. * Ventricular bradycardia: This type of bradycardia occurs when the heart rate is controlled by the ventricles, rather than the sinoatrial node.Symptoms of Bradycardia
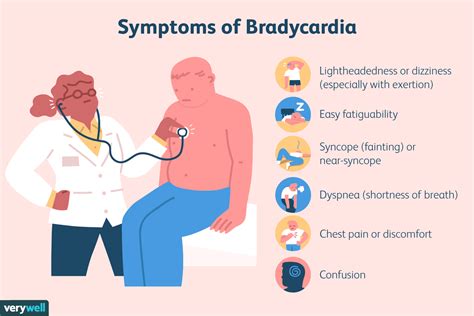
Diagnosing Bradycardia
Diagnosing bradycardia typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. Some common diagnostic tests used to diagnose bradycardia include: * Electrocardiogram (ECG): An ECG is a test that measures the electrical activity of the heart. * Holter monitor: A Holter monitor is a portable device that records the heart's electrical activity over a 24-hour period. * Echocardiogram: An echocardiogram is a test that uses sound waves to create images of the heart. * Blood tests: Blood tests may be ordered to rule out underlying medical conditions that can cause bradycardia.Treatment Options for Bradycardia
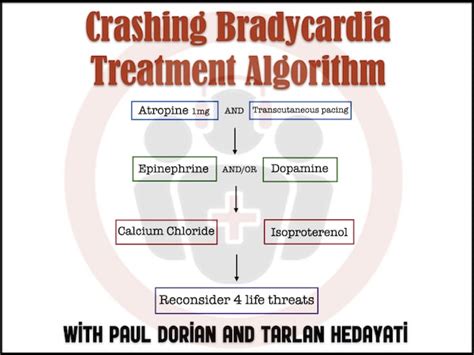
Living with Bradycardia
Living with bradycardia requires ongoing management and monitoring to prevent complications. Some tips for living with bradycardia include: * Monitoring heart rate: Individuals with bradycardia should monitor their heart rate regularly to ensure that it is within a normal range. * Avoiding certain activities: Individuals with bradycardia may need to avoid certain activities such as strenuous exercise or heavy lifting. * Managing stress: Stress can exacerbate symptoms of bradycardia, so it is essential to manage stress through techniques such as meditation or deep breathing. * Following a healthy diet: Eating a healthy diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help to manage symptoms of bradycardia.Complications of Bradycardia
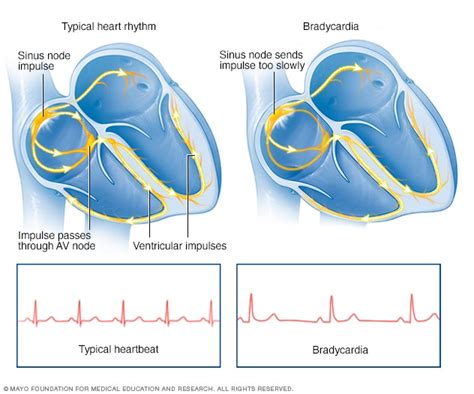
Preventing Bradycardia
Preventing bradycardia requires a combination of lifestyle changes and medical management. Some tips for preventing bradycardia include: * Maintaining a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of bradycardia, so it is essential to maintain a healthy weight through a combination of diet and exercise. * Engaging in regular physical activity: Regular physical activity can help to strengthen the heart and reduce the risk of bradycardia. * Quitting smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of bradycardia, so it is essential to quit smoking to reduce this risk. * Managing stress: Stress can exacerbate symptoms of bradycardia, so it is essential to manage stress through techniques such as meditation or deep breathing.What is the normal heart rate for an adult?
+A normal heart rate for an adult is between 60 and 100 beats per minute.
What are the symptoms of bradycardia?
+The symptoms of bradycardia include fatigue, dizziness, shortness of breath, chest pain, and fainting.
How is bradycardia diagnosed?
+Bradycardia is diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests such as electrocardiogram (ECG), Holter monitor, and echocardiogram.
In conclusion, bradycardia is a medical condition characterized by a slow heart rate that can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetic predisposition, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for bradycardia is essential for individuals who are affected by this condition. By taking steps to manage symptoms and prevent complications, individuals with bradycardia can reduce their risk of complications and improve their overall quality of life. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with bradycardia in the comments below, and to share this article with anyone who may be affected by this condition.
