Intro
Discover the meaning of a bun in blood test, understanding its significance in measuring urea levels, kidney function, and waste removal, with related terms like bun blood test, blood urea nitrogen, and kidney health.
The BUN, or Blood Urea Nitrogen, test is a crucial diagnostic tool used to assess kidney function and detect potential kidney problems. Urea is a waste product produced by the body's metabolic processes, and it is normally filtered out by the kidneys and excreted in the urine. When kidney function is impaired, urea can build up in the blood, leading to elevated BUN levels. In this article, we will delve into the meaning of BUN in blood tests, its significance, and what the results can indicate about a person's health.
Elevated BUN levels can be caused by a variety of factors, including dehydration, kidney disease, and certain medications. It is essential to understand the significance of BUN levels and how they relate to overall health. The BUN test is often used in conjunction with other tests, such as the creatinine test, to provide a comprehensive picture of kidney function. By analyzing BUN levels, healthcare professionals can diagnose and monitor kidney disease, as well as assess the effectiveness of treatment.
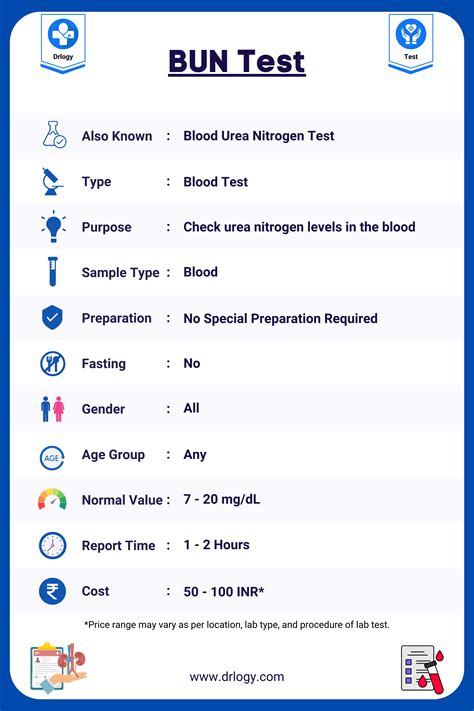
The BUN test is a simple and non-invasive procedure that requires a blood sample. The sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis, where the BUN level is measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). The normal range for BUN levels varies depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, but it is generally considered to be between 6 and 24 mg/dL. Levels above this range may indicate kidney problems or other health issues.
What is BUN in Blood Test

How is BUN Test Performed
The BUN test is a simple and non-invasive procedure that requires a blood sample. The sample is typically taken from a vein in the arm, and it is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The BUN level is measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), and the results are usually available within a few hours. The BUN test can be performed at any time, but it is often done in the morning, as BUN levels can fluctuate throughout the day.Normal BUN Levels
Elevated BUN Levels
Elevated BUN levels can be caused by a variety of factors, including: * Dehydration: Dehydration can cause a decrease in blood volume, which can lead to elevated BUN levels. * Kidney disease: Kidney disease can impair the kidneys' ability to filter waste products, leading to elevated BUN levels. * Certain medications: Certain medications, such as diuretics and antibiotics, can affect kidney function and lead to elevated BUN levels. * Dietary habits: A high-protein diet can increase urea production, leading to elevated BUN levels.Low BUN Levels

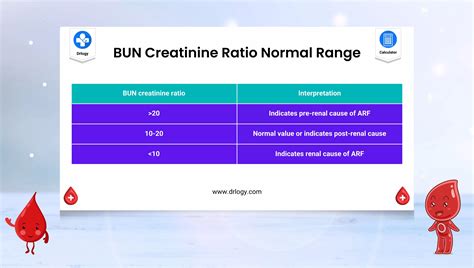
BUN-to-Creatinine Ratio
The BUN-to-creatinine ratio is a calculation that compares the BUN level to the creatinine level in the blood. This ratio can help healthcare professionals diagnose and monitor kidney disease. A high BUN-to-creatinine ratio may indicate dehydration or kidney disease, while a low ratio may indicate liver disease or malnutrition.BUN Test Results
What to Do If You Have Elevated BUN Levels
If you have elevated BUN levels, it is essential to consult with your healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause. Your healthcare professional may recommend additional tests, such as a creatinine test or a urine test, to diagnose and monitor kidney disease. Treatment may involve medication, dietary changes, or other interventions to manage kidney disease and prevent further complications.Prevention and Management

Kidney Disease Treatment
Treatment for kidney disease depends on the underlying cause and severity of the disease. Some common treatments for kidney disease include: * Medication: Medication can help manage symptoms and slow the progression of kidney disease. * Dialysis: Dialysis is a treatment that uses a machine to filter waste products from the blood when the kidneys are no longer able to do so. * Kidney transplant: A kidney transplant is a surgical procedure that involves replacing a diseased kidney with a healthy one.Conclusion and Next Steps

What is the normal range for BUN levels?
+The normal range for BUN levels varies depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, but it is generally considered to be between 6 and 24 mg/dL.
What can cause elevated BUN levels?
+Elevated BUN levels can be caused by dehydration, kidney disease, certain medications, and dietary habits.
How is the BUN test performed?
+The BUN test is a simple and non-invasive procedure that requires a blood sample, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the BUN test and its significance in assessing kidney function. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others who may benefit from this information. By working together, we can promote kidney health and reduce the risk of kidney disease.
