Intro
Discover 5 crucial facts about C. diff, a bacterial infection causing diarrhea, colitis, and life-threatening complications, with insights into prevention, symptoms, and treatment options for Clostridioides difficile.
The importance of understanding Clostridioides difficile, commonly referred to as C. diff, cannot be overstated. This bacterium is a leading cause of healthcare-associated infections, affecting millions of people worldwide each year. C. diff infections can range from mild diarrhea to life-threatening colitis, making it a critical concern for healthcare providers and the general public alike. As we delve into the world of C. diff, it becomes clear that there is more to this bacterium than meets the eye. From its unique characteristics to the latest advancements in treatment and prevention, there is a wealth of information to explore.
C. diff is a type of bacteria that can be found in the environment, in the human gut, and even on surfaces in healthcare facilities. While it is a normal inhabitant of the gut in small numbers, an overgrowth of C. diff can lead to infection. This overgrowth often occurs after the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics, which can disrupt the balance of the gut microbiome. As a result, C. diff infections are a significant concern in healthcare settings, where the use of antibiotics is common. However, it's not just healthcare-associated infections that are a concern; C. diff can also be spread through contaminated food, water, and surfaces.
The impact of C. diff infections cannot be overstated. Not only can they lead to severe and potentially life-threatening complications, but they also place a significant burden on the healthcare system. The economic costs of C. diff infections are substantial, with estimates suggesting that they add billions of dollars to healthcare expenditures each year. Furthermore, the emotional toll on patients and their families should not be overlooked. As we navigate the complexities of C. diff, it's essential to consider the human impact of these infections and the importance of developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Understanding C. diff Infections
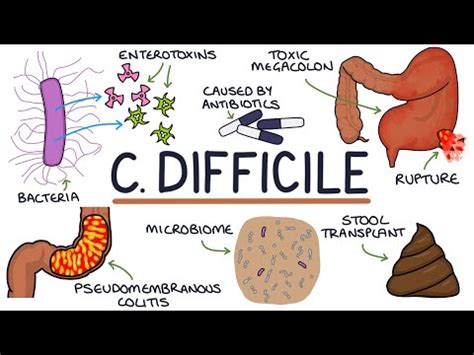
To grasp the significance of C. diff, it's crucial to understand how these infections occur. C. diff bacteria produce spores that can survive in harsh environments, including on surfaces and in soil. When these spores are ingested, they can germinate in the gut, leading to an overgrowth of C. diff. This overgrowth can produce toxins that cause diarrhea, colitis, and other complications. The primary risk factors for C. diff infections include the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics, advanced age, and underlying medical conditions. Healthcare workers, patients, and visitors can all play a role in the spread of C. diff, highlighting the need for rigorous infection control practices.
Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies
Some of the key risk factors for C. diff infections include: * The use of broad-spectrum antibiotics * Advanced age * Underlying medical conditions, such as inflammatory bowel disease * Weakened immune system * Exposure to contaminated surfaces or healthcare equipment To prevent C. diff infections, healthcare facilities and individuals can take several steps: * Practice good hand hygiene * Use personal protective equipment (PPE) when interacting with patients * Clean and disinfect surfaces and equipment regularly * Avoid unnecessary use of antibiotics * Implement antibiotic stewardship programsC. diff Treatment Options
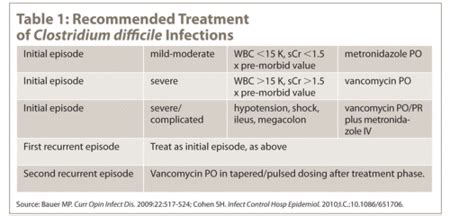
Treatment for C. diff infections typically involves stopping the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics and starting a course of antibiotics that target C. diff. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to manage complications. Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) has also emerged as a promising treatment option for recurrent C. diff infections. This procedure involves transferring fecal matter from a healthy donor into the gut of the patient to restore the balance of the gut microbiome. While FMT has shown significant promise, it is not without risks, and more research is needed to fully understand its potential.
Emerging Trends in C. diff Research
Researchers are continually exploring new ways to prevent and treat C. diff infections. Some of the emerging trends in C. diff research include: * The development of novel antibiotics that target C. diff * The use of probiotics and prebiotics to restore the balance of the gut microbiome * The application of FMT in clinical practice * The development of vaccines against C. diff These advancements hold significant promise for reducing the burden of C. diff infections and improving patient outcomes.C. diff Infection Control Measures

Infection control measures are critical in preventing the spread of C. diff. Healthcare facilities can implement several strategies to reduce the risk of transmission, including:
- Implementing contact precautions for patients with C. diff infections
- Using dedicated equipment and supplies for patients with C. diff
- Cleaning and disinfecting surfaces and equipment regularly
- Promoting good hand hygiene among healthcare workers
- Educating patients and visitors about the risks of C. diff and the importance of infection control practices
Challenges in C. diff Infection Control
Despite the importance of infection control measures, there are several challenges that healthcare facilities face in preventing the spread of C. diff. These challenges include: * Limited resources and funding for infection control programs * Difficulty in maintaining compliance with infection control practices among healthcare workers * The presence of C. diff spores in the environment, which can be difficult to eradicate * The risk of transmission through contaminated food, water, and surfacesC. diff and Antibiotic Stewardship

The overuse and misuse of antibiotics are significant contributors to the development of C. diff infections. Antibiotic stewardship programs aim to promote the responsible use of antibiotics and reduce the risk of antibiotic-resistant infections. These programs involve:
- Implementing guidelines for antibiotic use
- Monitoring antibiotic use and resistance patterns
- Educating healthcare workers about the importance of antibiotic stewardship
- Promoting the use of alternative treatments, such as probiotics and prebiotics
Benefits of Antibiotic Stewardship
The benefits of antibiotic stewardship programs are numerous and include: * Reduced risk of antibiotic-resistant infections * Improved patient outcomes * Decreased length of hospital stay * Reduced healthcare costs * Improved quality of careC. diff and the Gut Microbiome
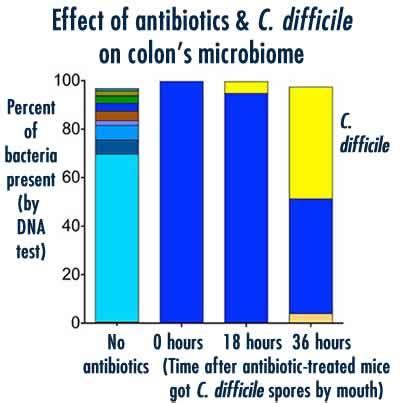
The gut microbiome plays a critical role in our overall health and well-being. An imbalance of the gut microbiome, also known as dysbiosis, can contribute to a range of diseases, including C. diff infections. Restoring the balance of the gut microbiome through the use of probiotics, prebiotics, and FMT has shown promise in preventing and treating C. diff infections.
Key Players in the Gut Microbiome
Some of the key players in the gut microbiome include: * Bifidobacterium * Lactobacillus * Clostridium * Bacteroides * Escherichia These microorganisms work together to maintain a healthy balance of the gut microbiome and prevent the overgrowth of pathogens like C. diff.C. diff and Public Health

C. diff infections are a significant public health concern, with thousands of cases reported each year. The economic burden of C. diff infections is substantial, with estimates suggesting that they add billions of dollars to healthcare expenditures annually. Public health initiatives, such as infection control programs and antibiotic stewardship, are critical in reducing the spread of C. diff and promoting healthy behaviors.
Public Health Strategies
Some of the key public health strategies for reducing the spread of C. diff include: * Implementing infection control programs in healthcare facilities * Promoting antibiotic stewardship * Educating the public about the risks of C. diff and the importance of infection control practices * Monitoring C. diff cases and outbreaks * Developing and implementing policies to reduce the spread of C. diffWhat is C. diff?
+C. diff, or Clostridioides difficile, is a type of bacteria that can cause diarrhea, colitis, and other complications.
How is C. diff spread?
+C. diff can be spread through contaminated surfaces, healthcare equipment, and the hands of healthcare workers.
What are the symptoms of C. diff?
+The symptoms of C. diff can range from mild diarrhea to life-threatening colitis and include abdominal pain, fever, and blood in the stool.
How is C. diff treated?
+C. diff is typically treated with antibiotics that target the bacteria, as well as measures to restore the balance of the gut microbiome.
Can C. diff be prevented?
+Yes, C. diff can be prevented through good hand hygiene, proper cleaning and disinfection of surfaces, and responsible use of antibiotics.
As we conclude our exploration of C. diff, it's essential to remember that this bacterium is a significant public health concern that requires a multifaceted approach to prevention and treatment. By understanding the risks, symptoms, and treatment options for C. diff, we can work together to reduce the spread of this infection and promote healthy behaviors. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with C. diff, and to join the conversation about this critical public health issue. Together, we can make a difference and create a healthier future for all.
