Intro
Cipro antibiotic uses treat bacterial infections, including UTIs, pneumonia, and sinusitis, with broad-spectrum efficacy against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, providing effective infection control and prevention.
Ciprofloxacin, commonly known by its brand name Cipro, is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic that has been widely used to treat various bacterial infections. The importance of understanding the uses, benefits, and potential risks of Cipro cannot be overstated, as it is a powerful medication that should be used judiciously. In this article, we will delve into the world of Cipro, exploring its mechanisms, applications, and implications for healthcare.
The discovery of antibiotics revolutionized the field of medicine, enabling doctors to effectively combat bacterial infections that were once often fatal. Cipro, with its broad-spectrum activity, has become a staple in many medical practices, used to treat a range of infections from urinary tract infections to respiratory infections. Its efficacy and relatively fast action have made it a preferred choice for many physicians and patients alike. However, like all medications, Cipro must be used responsibly, with a full understanding of its potential side effects and interactions.
The mechanism of action of Cipro involves inhibiting bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, enzymes critical for DNA replication and repair. By blocking these enzymes, Cipro effectively prevents bacteria from reproducing, leading to their death. This mechanism is effective against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, making Cipro a versatile antibiotic. Its pharmacokinetics allow for oral and intravenous administration, with high bioavailability that ensures the drug reaches therapeutic levels quickly.
Cipro Antibiotic Uses and Applications
Cipro's broad-spectrum activity makes it suitable for treating a variety of bacterial infections. Some of the most common uses of Cipro include:
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Cipro is often prescribed for UTIs, including acute uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis.
- Respiratory Tract Infections: It is used to treat bacterial exacerbations of chronic bronchitis, community-acquired pneumonia, and acute sinusitis.
- Skin and Soft Tissue Infections: Cipro can be effective against infections such as cellulitis, abscesses, and infected wounds.
- Bone and Joint Infections: Osteomyelitis and septic arthritis are among the conditions treated with Cipro.
- Intra-abdominal Infections: It is used in the treatment of infections such as peritonitis and abscesses within the abdominal cavity.
- Typhoid Fever: Cipro is effective against Salmonella Typhi, the causative agent of typhoid fever.
- Prostatitis: Chronic bacterial prostatitis is another condition for which Cipro may be prescribed.
Benefits of Cipro
The benefits of using Cipro are numerous, including its broad-spectrum activity, oral and IV formulations, and generally good tolerance. Cipro's ability to penetrate into various body tissues and fluids ensures that the antibiotic reaches the site of infection effectively. Its pharmacokinetic properties allow for once or twice daily dosing, which enhances patient compliance. Furthermore, Cipro has been shown to be effective against bacteria that have developed resistance to other antibiotics, making it a valuable option in the treatment of resistant infections.Cipro Mechanism of Action
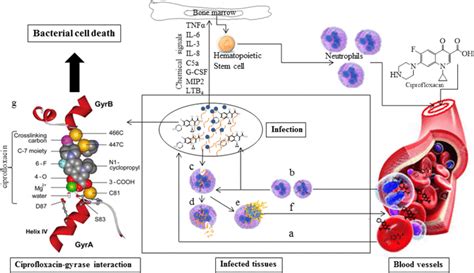
Understanding the mechanism of action of Cipro is crucial for appreciating its efficacy and potential limitations. By inhibiting DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, Cipro disrupts the bacterial DNA replication process. This action is bactericidal, meaning it kills the bacteria rather than just inhibiting their growth. The specificity of Cipro for bacterial enzymes over human enzymes reduces the risk of harmful effects on the host's cells, although side effects can still occur.
Potential Side Effects and Interactions
While Cipro is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects and interact with other medications. Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, dizziness, and headache. More serious but less common side effects can include tendonitis and tendon rupture, peripheral neuropathy, and central nervous system effects such as seizures. Cipro can also interact with a variety of medications, including antacids, warfarin, and certain anti-seizure drugs, either by enhancing their effects or reducing Cipro's efficacy.Cipro Dosage and Administration
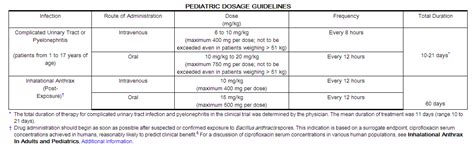
The dosage and administration of Cipro depend on the type and severity of the infection being treated. For most infections, the recommended dose for adults is 250-500 mg every 12 hours for 7-14 days. However, the dose can be adjusted based on the renal function of the patient, as Cipro is primarily excreted through the kidneys. It is essential to complete the full course of treatment as prescribed by the healthcare provider to ensure the infection is fully cleared and to reduce the risk of resistance development.
Resistance and Stewardship
The emergence of antibiotic resistance is a global health concern, and the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics like Cipro contributes to this issue. Therefore, it is crucial to practice antibiotic stewardship, ensuring that Cipro and other antibiotics are used judiciously and only when necessary. This includes prescribing antibiotics based on culture and sensitivity results whenever possible, using the narrowest spectrum of activity necessary, and promoting patient education on the proper use of antibiotics.Cipro in Pediatric and Geriatric Populations
The use of Cipro in pediatric and geriatric populations requires special consideration. In children, Cipro is generally not recommended due to the potential risk of cartilage damage. However, in certain cases, such as complicated urinary tract infections or pyelonephritis, the benefits may outweigh the risks, and Cipro may be prescribed under close supervision. In geriatric patients, dose adjustments may be necessary due to decreased renal function, and close monitoring for potential side effects is recommended.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, Cipro is a powerful antibiotic with a wide range of applications. Its effectiveness against various bacterial infections makes it a valuable tool in the fight against infectious diseases. However, its use must be balanced with the need to prevent antibiotic resistance and minimize side effects. As the medical community continues to navigate the challenges of antibiotic resistance, the development of new antibiotics and the responsible use of existing ones like Cipro will be crucial. By understanding the uses, mechanisms, and implications of Cipro, healthcare providers can make informed decisions that benefit their patients and contribute to the broader goal of preserving the efficacy of antibiotics for future generations.What is Cipro used for?
+Cipro is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including urinary tract infections, respiratory tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, and more.
How does Cipro work?
+Cipro works by inhibiting bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, enzymes critical for DNA replication and repair, thereby preventing bacterial growth and causing their death.
What are the common side effects of Cipro?
+Common side effects of Cipro include nausea, diarrhea, dizziness, and headache. More serious side effects can include tendonitis and tendon rupture, peripheral neuropathy, and central nervous system effects.
We hope this comprehensive overview of Cipro has provided valuable insights into its uses, benefits, and considerations. Whether you are a healthcare professional seeking detailed information or a patient looking to understand your treatment, it is essential to approach the use of antibiotics like Cipro with knowledge and caution. We invite you to share your thoughts, ask questions, or explore further resources on this critical topic in the comments below.
