Intro
Discover what Clonidine is, its uses, and side effects. Learn about this medication, a centrally acting alpha-2 adrenergic agonist, used to treat hypertension, ADHD, and anxiety disorders, with information on dosage, interactions, and warnings.
Clonidine is a medication that has been widely used for several decades to treat various medical conditions. It is an alpha-2 adrenergic agonist, which means it works by stimulating certain receptors in the brain to produce a therapeutic effect. Clonidine is primarily used to treat high blood pressure, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and certain pain conditions. In recent years, it has also been used off-label to treat anxiety disorders, insomnia, and withdrawal symptoms from substances like opioids.
The importance of clonidine lies in its ability to provide relief from symptoms that significantly impact an individual's quality of life. For instance, high blood pressure can lead to serious complications such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease if left uncontrolled. Similarly, ADHD can affect not only academic and professional performance but also social relationships and overall well-being. By effectively managing these conditions, clonidine plays a crucial role in improving the health and well-being of individuals.
Moreover, the versatility of clonidine in treating a range of conditions makes it a valuable medication in the pharmaceutical arsenal. Its mechanism of action, which involves the stimulation of alpha-2 adrenergic receptors, leads to decreased sympathetic outflow from the central nervous system, resulting in lowered blood pressure, heart rate, and symptoms of ADHD and anxiety. This unique mechanism of action distinguishes clonidine from other medications used to treat similar conditions, offering an alternative for patients who may not respond well to other treatments.
How Clonidine Works
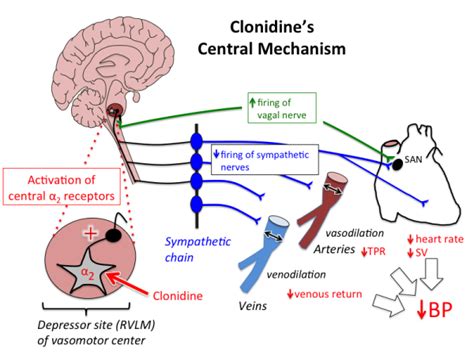
Clonidine works by binding to alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the brain, which are involved in regulating sympathetic nervous system activity. The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for the body's "fight or flight" response, which includes increased heart rate, blood pressure, and energy mobilization. By stimulating these receptors, clonidine decreases the release of norepinephrine, a neurotransmitter that stimulates the sympathetic nervous system, thereby reducing blood pressure, heart rate, and other symptoms associated with increased sympathetic activity.
In the context of ADHD, clonidine's ability to decrease impulsivity and hyperactivity is thought to be related to its effects on the prefrontal cortex, an area of the brain involved in attention and impulse control. For pain management, clonidine is believed to work by decreasing the transmission of pain signals in the spinal cord. Its use in anxiety disorders and insomnia is attributed to its sedative effects, which help in reducing anxiety and promoting sleep.
Benefits of Clonidine
The benefits of clonidine are multifaceted, reflecting its broad therapeutic applications. For patients with high blood pressure, clonidine offers an effective means of controlling blood pressure, thereby reducing the risk of cardiovascular complications. In ADHD, it provides an alternative or adjunct treatment option, especially for patients who may not respond adequately to or tolerate traditional stimulant medications. Clonidine's role in pain management, particularly for neuropathic pain and certain types of cancer pain, offers relief to patients who may have limited treatment options.Moreover, clonidine's off-label uses, including the treatment of anxiety disorders and insomnia, highlight its potential in addressing mental health issues. Its ability to induce sedation without the risk of dependence, as seen with benzodiazepines, makes it a valuable option for patients struggling with sleep disturbances or anxiety. However, it is crucial to use clonidine under the guidance of a healthcare provider, as its benefits must be weighed against potential side effects and interactions with other medications.
Side Effects and Precautions
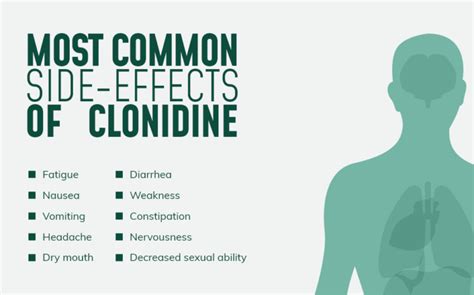
Like all medications, clonidine can cause side effects, some of which are dose-dependent. Common side effects include dry mouth, drowsiness, dizziness, and constipation. More serious side effects, although less common, can include orthostatic hypotension (a sudden drop in blood pressure upon standing), which can lead to fainting. Additionally, clonidine can cause rebound hypertension if it is suddenly stopped after prolonged use, emphasizing the importance of gradual tapering under medical supervision.
It is also important to consider potential interactions with other medications. For example, clonidine can enhance the effects of other blood pressure medications, potentially leading to hypotension. Its use with other sedatives can increase the risk of excessive sedation. Therefore, patients should inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking before starting clonidine.
Using Clonidine Safely
To use clonidine safely and effectively, patients should follow their healthcare provider's instructions carefully. This includes taking the medication exactly as prescribed, not stopping or changing the dose without consulting a doctor, and attending follow-up appointments to monitor blood pressure and adjust the dose as necessary. Patients should also be aware of the signs of side effects and report them to their healthcare provider promptly.Furthermore, lifestyle modifications can complement the effects of clonidine. For patients with high blood pressure, adopting a healthy diet, reducing sodium intake, exercising regularly, and managing stress can help control blood pressure. For those with ADHD, maintaining a structured daily routine, avoiding distractions, and engaging in physical activity can enhance the medication's effectiveness.
Clonidine in Special Populations

The use of clonidine in special populations, such as children, pregnant women, and the elderly, requires careful consideration. In children, clonidine is sometimes used to treat ADHD and certain sleep disorders, but its use must be closely monitored due to the potential for side effects. In pregnant women, clonidine should be used only when the benefits outweigh the risks, as there is limited data on its safety during pregnancy. In the elderly, clonidine can be effective for managing hypertension and certain symptoms of dementia, but its sedative effects must be carefully managed to avoid falls and other accidents.
Future Perspectives
Research into clonidine and its analogs continues, with a focus on developing new therapeutic applications and improving its safety profile. The exploration of clonidine's potential in treating substance use disorders, particularly opioid withdrawal, represents a promising area of investigation. Additionally, studies examining the genetic factors that influence an individual's response to clonidine may lead to more personalized treatment approaches in the future.As healthcare continues to evolve, the role of clonidine in managing chronic conditions and improving patient outcomes is likely to remain significant. Its versatility, combined with ongoing research into its mechanisms and applications, positions clonidine as a valuable medication in the treatment of a range of medical conditions.
Conclusion and Recommendations

In conclusion, clonidine is a medication with a broad spectrum of therapeutic applications, including the treatment of hypertension, ADHD, pain, and certain mental health conditions. Its unique mechanism of action and potential benefits make it a valuable option for patients who may not respond to or tolerate other treatments. However, its use must be carefully managed to minimize side effects and interactions with other medications.
For individuals considering clonidine or currently taking it, it is essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to ensure safe and effective use. This includes regular monitoring of blood pressure, reporting any side effects promptly, and making lifestyle adjustments to complement the medication's effects.
What is clonidine used for?
+Clonidine is used to treat high blood pressure, ADHD, certain pain conditions, and off-label for anxiety disorders and insomnia.
How does clonidine work?
+Clonidine works by stimulating alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the brain, leading to decreased sympathetic nervous system activity and lowering blood pressure, heart rate, and symptoms of ADHD and anxiety.
What are the common side effects of clonidine?
+Common side effects include dry mouth, drowsiness, dizziness, and constipation. More serious side effects can include orthostatic hypotension and rebound hypertension if suddenly stopped.
Can clonidine be used in special populations like children and pregnant women?
+Clonidine can be used in children for ADHD and certain sleep disorders, but its use must be closely monitored. In pregnant women, it should be used only when the benefits outweigh the risks. Its use in these populations requires careful consideration and medical supervision.
What are the future perspectives for clonidine?
+Research into clonidine continues, focusing on new therapeutic applications, improving its safety profile, and exploring its potential in treating substance use disorders and personalized medicine approaches.
We invite readers to share their experiences or ask questions about clonidine in the comments below. Your input can help others understand the benefits and challenges of using clonidine and contribute to a more informed discussion about its applications and management. Additionally, sharing this article with others who may benefit from the information can help spread awareness about the potential of clonidine in improving health outcomes.
