Intro
Discover Ampicillin side effects, including allergic reactions, diarrhea, and rash. Learn about dosage, interactions, and warnings to minimize antibiotic resistance and ensure safe treatment.
Ampicillin is a type of antibiotic known as a penicillin antibiotic, which is used to treat various bacterial infections. It works by stopping the growth of bacteria and is commonly prescribed for infections such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and urinary tract infections. While ampicillin can be an effective treatment for bacterial infections, it can also cause side effects. Understanding the potential side effects of ampicillin is crucial for patients to ensure they are aware of what to expect when taking this medication.
Ampicillin is generally considered safe and effective when used as directed. However, like all medications, it can cause side effects in some individuals. Common side effects of ampicillin include diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. These side effects are usually mild and temporary, but in some cases, they can be severe and require medical attention. It is essential for patients to follow the dosage instructions carefully and complete the full course of treatment to minimize the risk of side effects and ensure the infection is fully cleared.
The importance of understanding ampicillin side effects cannot be overstated. Patients who are aware of the potential side effects can take steps to minimize their risk and seek medical attention if necessary. Additionally, understanding the side effects of ampicillin can help patients make informed decisions about their treatment. For example, patients who experience severe side effects may need to consider alternative treatments or adjust their dosage. By being aware of the potential side effects, patients can work closely with their healthcare provider to find the best treatment option for their individual needs.
Ampicillin Overview
How Ampicillin Works
Ampicillin works by binding to the bacterial cell wall and inhibiting the synthesis of the cell wall. This ultimately leads to the death of the bacterial cell. Ampicillin is effective against a wide range of bacterial infections, including those caused by Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, and Escherichia coli. The medication is usually taken orally, and the dosage and duration of treatment will depend on the type and severity of the infection.Ampicillin Side Effects
Severe Side Effects
Severe side effects of ampicillin can include: * Allergic reactions, such as anaphylaxis * Stevens-Johnson syndrome * Toxic epidermal necrolysis * Blood disorders, such as anemia or thrombocytopenia * Liver or kidney damage These side effects are rare but can be life-threatening. Patients who experience any of these symptoms should seek medical attention immediately.Ampicillin Interactions

Precautions
Patients who are taking ampicillin should be aware of the following precautions: * Allergic reactions: Patients who are allergic to penicillin or other antibiotics may be at risk of an allergic reaction to ampicillin. * Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Ampicillin is generally considered safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but patients should inform their healthcare provider of their pregnancy or breastfeeding status. * Kidney or liver disease: Patients with kidney or liver disease may need to adjust their dosage or monitoring.Ampicillin Dosage

Administration
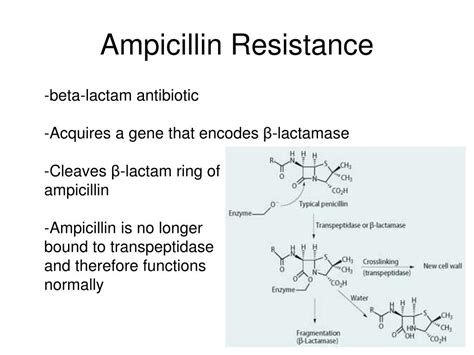
Ampicillin can be administered orally or intravenously. Oral ampicillin is usually taken with food to minimize gastrointestinal side effects. Intravenous ampicillin is usually administered in a hospital setting.Ampicillin Resistance
Prevention
Patients can take steps to prevent the development of ampicillin resistance, including: * Only using antibiotics when prescribed by a healthcare provider * Completing the full course of treatment * Not sharing antibiotics with others * Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularlyAmpicillin Alternatives

Comparison
A comparison of ampicillin and its alternatives can help patients make informed decisions about their treatment. Patients should discuss their options with their healthcare provider and consider factors such as: * Efficacy * Safety * Cost * ConvenienceWhat is ampicillin used for?
+Ampicillin is used to treat various bacterial infections, including pneumonia, bronchitis, and urinary tract infections.
What are the common side effects of ampicillin?
+Common side effects of ampicillin include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, rash, itching, and hives.
Can ampicillin be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding?
+Ampicillin is generally considered safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but patients should inform their healthcare provider of their pregnancy or breastfeeding status.
How long does it take for ampicillin to work?
+The length of time it takes for ampicillin to work will depend on the type and severity of the infection. Patients should follow the dosage instructions carefully and complete the full course of treatment.
Can ampicillin be used to treat viral infections?
+No, ampicillin is only effective against bacterial infections and should not be used to treat viral infections.
In conclusion, ampicillin is a commonly prescribed antibiotic that can be effective in treating various bacterial infections. However, it can also cause side effects, and patients should be aware of the potential risks and benefits. By understanding the side effects, interactions, and precautions associated with ampicillin, patients can make informed decisions about their treatment and work closely with their healthcare provider to find the best treatment option for their individual needs. We encourage readers to share their experiences with ampicillin and ask any questions they may have in the comments below. Additionally, we invite readers to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about ampicillin and its uses.
