Intro
Discover how dilation works through 5 key methods, leveraging pupil dilation, corneal dilation, and radial dilation for enhanced vision and medical procedures, utilizing dilating eye drops and surgical techniques.
Dilation is a fundamental concept in various fields, including mathematics, physics, and medicine. It refers to the process of expanding or enlarging an object, image, or opening. Understanding how dilation works is essential to grasp its applications and benefits. In this article, we will delve into the world of dilation, exploring its mechanisms, advantages, and uses.
The concept of dilation has been around for centuries, with ancient civilizations using it to create optical instruments, such as telescopes and microscopes. Today, dilation plays a crucial role in medical procedures, like eye exams and surgeries. Moreover, dilation is used in digital imaging, computer graphics, and even in the manufacturing of optical fibers. The versatility of dilation makes it a vital technique in numerous industries.
Dilation can be applied in various contexts, from the human body to digital images. In medicine, dilation is used to enlarge openings or passages, allowing for easier access or examination. For instance, during an eye exam, the pupil is dilated to enable the doctor to inspect the retina and optic nerve. Similarly, in digital imaging, dilation is used to enlarge or reduce images, making it a crucial technique in photo editing and computer graphics. The widespread use of dilation highlights its significance and importance in modern technology.
What is Dilation?

Types of Dilation
There are several types of dilation, each with its unique characteristics and applications. The most common types of dilation include: * Uniform dilation: This type of dilation enlarges or reduces an object by the same scale factor in all directions. * Non-uniform dilation: This type of dilation enlarges or reduces an object by different scale factors in different directions. * Isotropic dilation: This type of dilation enlarges or reduces an object by the same scale factor in all directions, resulting in a proportional change in size.How Dilation Works
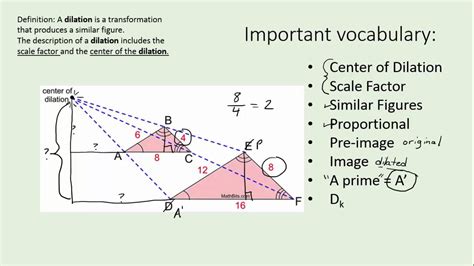
Benefits of Dilation
The benefits of dilation are numerous and varied. Some of the most significant advantages of dilation include: * Improved visibility: Dilation can enlarge openings or passages, allowing for easier access or examination. * Enhanced image quality: Dilation can improve the resolution and clarity of digital images. * Increased precision: Dilation can enable more precise measurements and calculations in various fields, such as engineering and architecture.Applications of Dilation
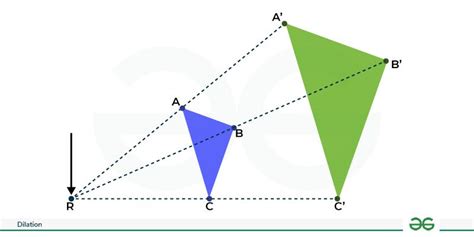
Real-World Examples of Dilation
Dilation is used in various real-world contexts, including: * Eye exams: Dilation is used to enlarge the pupil, allowing the doctor to inspect the retina and optic nerve. * Photo editing: Dilation is used to enlarge or reduce images, making it a crucial technique in photo editing software. * Optical fibers: Dilation is used in the manufacturing of optical fibers, which are used in telecommunications and other industries.Challenges and Limitations of Dilation

Future Developments in Dilation
The future of dilation is exciting and promising. Some of the most significant developments in dilation include: * Advances in digital imaging: Improvements in digital imaging technology are expected to enhance the quality and precision of dilation. * New applications in medicine: Dilation is expected to have new applications in medicine, particularly in the fields of ophthalmology and cardiology. * Increased use in manufacturing: Dilation is expected to play a more significant role in manufacturing, particularly in the production of optical fibers and other materials.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

What is dilation in mathematics?
+Dilation in mathematics is a transformation that changes the size of an object or figure by a certain scale factor.
What are the benefits of dilation in medicine?
+The benefits of dilation in medicine include improved visibility, enhanced image quality, and increased precision.
What are the challenges and limitations of dilation?
+The challenges and limitations of dilation include distortion, loss of detail, and complexity.
What are the future developments in dilation?
+The future developments in dilation include advances in digital imaging, new applications in medicine, and increased use in manufacturing.
How is dilation used in digital imaging?
+Dilation is used in digital imaging to enlarge or reduce images, making it a crucial technique in photo editing and computer graphics.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about dilation in the comments section below. If you found this article informative and helpful, please share it with your friends and colleagues. Additionally, if you have any specific topics or questions related to dilation, feel free to ask, and we will do our best to provide you with a comprehensive answer.
