Intro
Discover what Fluconazole is, a potent antifungal medication treating fungal infections, including candidiasis, thrush, and cryptococcosis, with its uses, dosage, and side effects.
Fluconazole is a type of antifungal medication that is widely used to treat various fungal infections. It belongs to a class of medications known as triazoles, which work by inhibiting the growth of fungi. Fluconazole is available in various forms, including tablets, capsules, and suspensions, and is commonly prescribed to treat infections such as vaginal yeast infections, thrush, and ringworm.
The importance of fluconazole lies in its ability to effectively treat fungal infections that can be debilitating and even life-threatening if left untreated. Fungal infections can affect anyone, but they are more common in people with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, cancer, or taking immunosuppressive medications. Fluconazole has been shown to be effective in treating a wide range of fungal infections, including those caused by Candida, Aspergillus, and Cryptococcus species.
In addition to its efficacy, fluconazole is also relatively safe and well-tolerated, making it a popular choice for treating fungal infections. However, like all medications, fluconazole can cause side effects, and it is essential to use it under the guidance of a healthcare professional. The benefits of fluconazole are numerous, and it has revolutionized the treatment of fungal infections, making it possible for people to recover quickly and effectively from these types of infections.
How Fluconazole Works
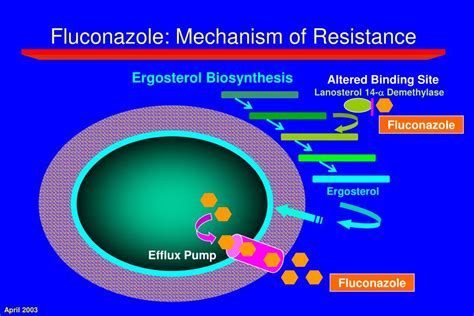
The mechanism of action of fluconazole involves the inhibition of the enzyme lanosterol 14-alpha-demethylase, which is responsible for converting lanosterol to ergosterol. This enzyme is essential for the production of ergosterol, and by inhibiting it, fluconazole prevents the production of ergosterol, ultimately leading to the death of the fungal cells. The effectiveness of fluconazole in treating fungal infections is due to its ability to selectively target the fungal cells, while leaving human cells unaffected.
Types of Fungal Infections Treated with Fluconazole
Fluconazole is used to treat a wide range of fungal infections, including: * Vaginal yeast infections * Thrush * Ringworm * Athlete's foot * Jock itch * Fungal meningitis * Cryptococcal meningitis * Coccidioidomycosis * HistoplasmosisThese infections can be caused by various types of fungi, including Candida, Aspergillus, and Cryptococcus species. Fluconazole is effective in treating these infections due to its ability to inhibit the growth of fungi and prevent the production of ergosterol.
Benefits of Fluconazole

In addition to its efficacy and safety, fluconazole is also relatively inexpensive compared to other antifungal medications, making it a cost-effective option for treating fungal infections. The benefits of fluconazole have made it a popular choice for treating fungal infections, and it has improved the quality of life for many people suffering from these types of infections.
Side Effects of Fluconazole
Like all medications, fluconazole can cause side effects, although they are relatively rare and usually mild. Some of the common side effects of fluconazole include: * Nausea and vomiting * Diarrhea * Abdominal pain * Headache * Dizziness * RashThese side effects are usually temporary and resolve on their own once the medication is stopped. However, in rare cases, fluconazole can cause more serious side effects, such as liver damage, allergic reactions, and interactions with other medications. It is essential to use fluconazole under the guidance of a healthcare professional to minimize the risk of side effects.
Precautions and Interactions

Fluconazole can also cause allergic reactions, and it is essential to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as hives, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing. Additionally, fluconazole can cause liver damage, and it is essential to monitor your liver function while taking this medication.
Contraindications
Fluconazole is contraindicated in people with certain medical conditions, including: * Liver disease * Kidney disease * Allergic reactions to fluconazole or other triazoles * Pregnancy and breastfeedingIt is essential to inform your healthcare professional about any medical conditions you have before starting fluconazole. Additionally, fluconazole should not be used in people with a history of allergic reactions to this medication or other triazoles.
Dosage and Administration
It is essential to take fluconazole exactly as prescribed by your healthcare professional, and not to stop taking it without consulting your doctor. Stopping the medication too soon can cause the infection to return, and it is essential to complete the full course of treatment to ensure that the infection is fully cleared.
Overdose and Toxicity
Fluconazole can cause overdose and toxicity if taken in excessive amounts. Symptoms of overdose and toxicity include: * Nausea and vomiting * Diarrhea * Abdominal pain * Headache * Dizziness * Confusion * SeizuresIf you suspect that you or someone else has taken an overdose of fluconazole, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately. Treatment of overdose and toxicity involves supportive care, such as hydration and monitoring of vital signs, and may require hospitalization in severe cases.
Conclusion and Future Perspectives
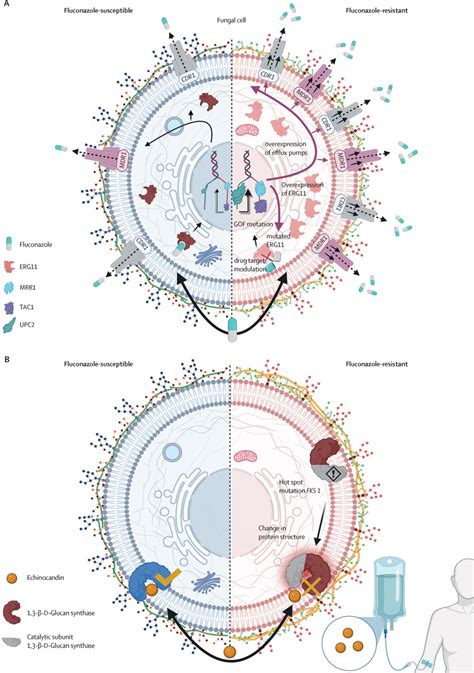
Future perspectives on fluconazole include the development of new formulations and delivery systems, such as topical creams and ointments, and the investigation of its potential use in treating other types of infections, such as bacterial and viral infections. Additionally, research is ongoing to develop new antifungal medications that can overcome the limitations of fluconazole, such as resistance and toxicity.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with fluconazole in the comments section below. Have you or someone you know used fluconazole to treat a fungal infection? What were your experiences with the medication? Share your story and help others understand the benefits and limitations of fluconazole.
What is fluconazole used for?
+Fluconazole is used to treat various fungal infections, including vaginal yeast infections, thrush, ringworm, and fungal meningitis.
How does fluconazole work?
+Fluconazole works by inhibiting the growth of fungi by interfering with the production of ergosterol, an essential component of fungal cell membranes.
What are the common side effects of fluconazole?
+The common side effects of fluconazole include nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, headache, and dizziness.
