Intro
Learn about high blood pressure, its symptoms, and causes. Understand hypertension, blood pressure readings, and cardiovascular risks to manage your health effectively.
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a common medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a condition where the blood pressure in the arteries is consistently too high, which can lead to serious health problems if left untreated. High blood pressure is often referred to as the "silent killer" because it can cause damage to the body without any noticeable symptoms. In this article, we will delve into the world of high blood pressure, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and management strategies.
The importance of understanding high blood pressure cannot be overstated. It is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, which is the leading cause of death worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), high blood pressure is responsible for approximately 12.8% of all deaths globally. Furthermore, high blood pressure can also lead to other serious health problems, such as kidney disease, stroke, and heart failure. Therefore, it is essential to understand the causes of high blood pressure, how it is diagnosed, and the various treatment options available.
High blood pressure is a complex condition that can be caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Some of the common causes of high blood pressure include a family history of hypertension, obesity, physical inactivity, smoking, and a diet high in salt and saturated fats. Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease, sleep apnea, and adrenal gland tumors, can also contribute to high blood pressure. Understanding the causes of high blood pressure is crucial in developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Understanding Blood Pressure
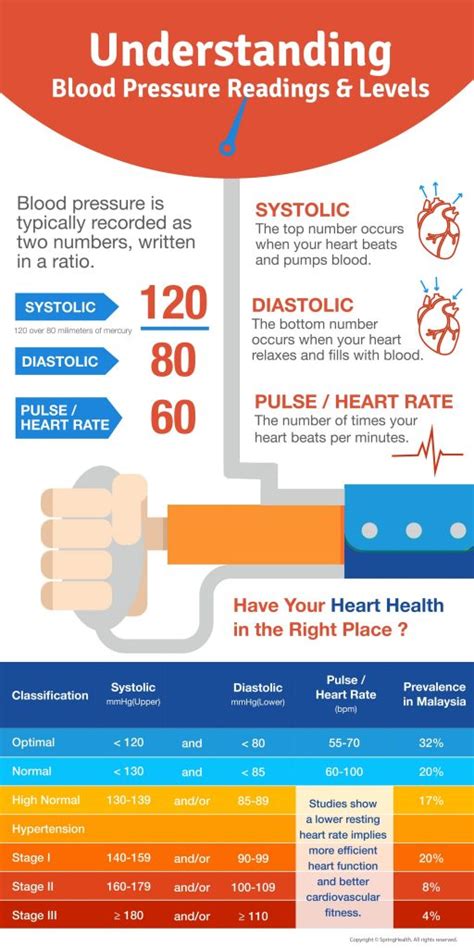
Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and is expressed as two numbers: systolic and diastolic. The systolic pressure is the top number, which represents the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats, while the diastolic pressure is the bottom number, which represents the pressure in the arteries between beats. A normal blood pressure reading is typically around 120/80 mmHg. However, blood pressure can fluctuate throughout the day, and it is not uncommon for blood pressure to be higher in the morning and lower at night.
Causes of High Blood Pressure
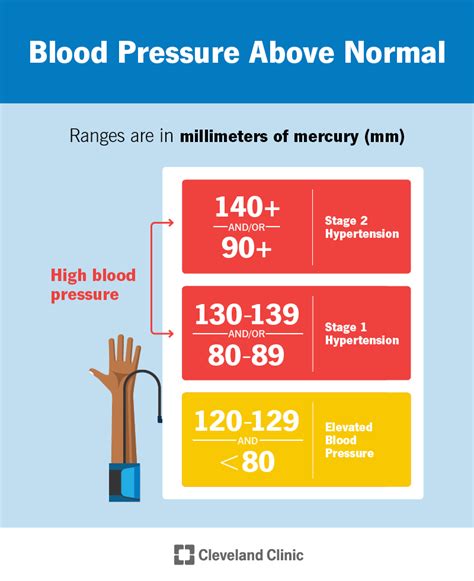
The causes of high blood pressure can be broadly categorized into primary and secondary hypertension. Primary hypertension is the most common type of high blood pressure and is often caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Secondary hypertension, on the other hand, is caused by an underlying medical condition, such as kidney disease or sleep apnea. Some of the common causes of high blood pressure include:
- Family history of hypertension
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Smoking
- High salt intake
- Saturated fat intake
- Stress
- Certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease, sleep apnea, and adrenal gland tumors
Symptoms of High Blood Pressure
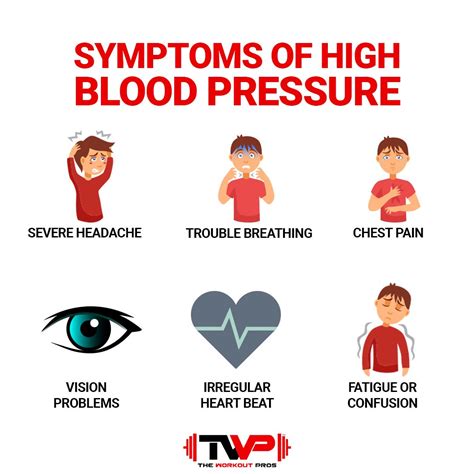
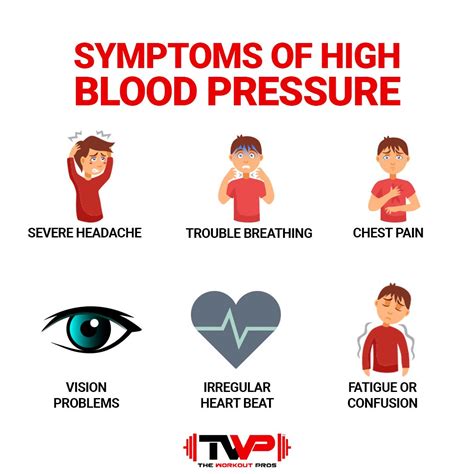
High blood pressure often does not have any noticeable symptoms, which is why it is often referred to as the "silent killer." However, some people may experience symptoms such as:
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Nosebleeds
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
It is essential to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other medical conditions, and the only way to confirm high blood pressure is through a blood pressure test.
Diagnosis of High Blood Pressure
Diagnosing high blood pressure typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and a blood pressure test. The blood pressure test is usually performed using a sphygmomanometer, which consists of a cuff that is wrapped around the upper arm and a gauge that measures the pressure. The American Heart Association recommends that adults have their blood pressure checked at least once every two years, or more often if they have a family history of hypertension or other risk factors.
Treatment Options for High Blood Pressure
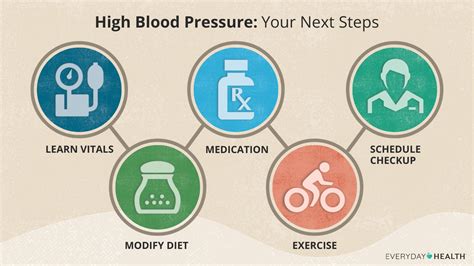
Treatment options for high blood pressure typically involve a combination of lifestyle changes and medication. Some of the lifestyle changes that can help lower blood pressure include:
- Losing weight
- Increasing physical activity
- Reducing salt intake
- Increasing potassium intake
- Quitting smoking
- Reducing stress
Medications that are commonly used to treat high blood pressure include:
- Diuretics
- Beta blockers
- ACE inhibitors
- Calcium channel blockers
- Alpha blockers
It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan that is tailored to individual needs and health status.
Managing High Blood Pressure

Managing high blood pressure requires a long-term commitment to lifestyle changes and medication adherence. Some of the strategies that can help manage high blood pressure include:
- Monitoring blood pressure regularly
- Taking medication as prescribed
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Eating a healthy diet
- Reducing stress
It is also essential to work with a healthcare provider to monitor blood pressure and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
Complications of High Blood Pressure
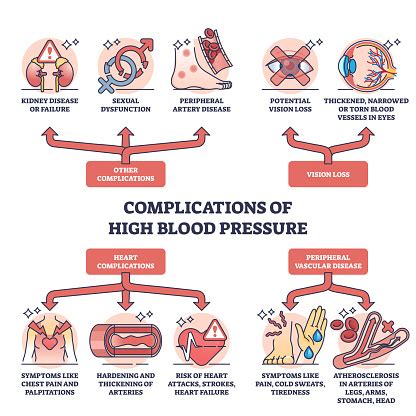
If left untreated, high blood pressure can lead to serious health complications, including:
- Heart disease
- Kidney disease
- Stroke
- Heart failure
- Vision loss
It is essential to take high blood pressure seriously and work with a healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan that can help prevent these complications.
Preventing High Blood Pressure
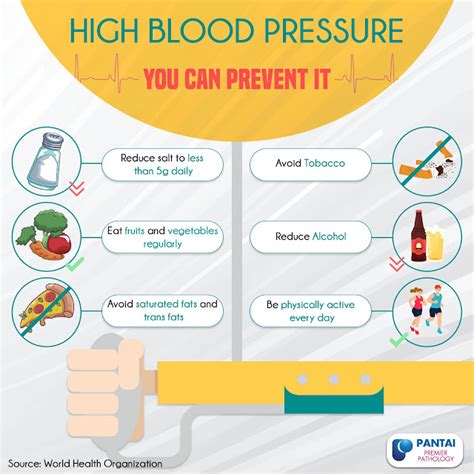
Preventing high blood pressure requires a long-term commitment to lifestyle changes, including:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Eating a healthy diet
- Reducing salt intake
- Increasing potassium intake
- Quitting smoking
- Reducing stress
It is also essential to work with a healthcare provider to monitor blood pressure and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
What is the normal blood pressure range?
+A normal blood pressure reading is typically around 120/80 mmHg.
What are the symptoms of high blood pressure?
+High blood pressure often does not have any noticeable symptoms, but some people may experience headaches, dizziness, nosebleeds, fatigue, shortness of breath, and chest pain.
How is high blood pressure diagnosed?
+Diagnosing high blood pressure typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and a blood pressure test.
What are the treatment options for high blood pressure?
+Treatment options for high blood pressure typically involve a combination of lifestyle changes and medication.
How can high blood pressure be prevented?
+Preventing high blood pressure requires a long-term commitment to lifestyle changes, including maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, eating a healthy diet, reducing salt intake, increasing potassium intake, quitting smoking, and reducing stress.
In conclusion, high blood pressure is a serious medical condition that requires prompt attention and treatment. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and management strategies, individuals can take control of their blood pressure and reduce their risk of developing serious health complications. We encourage readers to share their experiences and tips for managing high blood pressure in the comments section below. Additionally, we invite readers to share this article with friends and family members who may be affected by high blood pressure. Together, we can work towards creating a healthier and more informed community.
