Intro
Discover what HIV is, its symptoms, transmission, and treatment options, understanding the virus and its impact on the immune system, AIDS, and prevention methods.
The Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a complex and multifaceted topic that has garnered significant attention and concern worldwide. As a global health issue, HIV affects millions of people, causing widespread suffering, death, and economic burden. Understanding the intricacies of HIV is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies, as well as promoting awareness and education. In this article, we will delve into the world of HIV, exploring its definition, transmission, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention methods.
HIV is a type of retrovirus that attacks the body's immune system, specifically targeting CD4 cells (T cells), which play a vital role in fighting off infections. When HIV infects a person, it gradually destroys these cells, weakening the immune system and making the individual more susceptible to opportunistic infections and diseases. If left untreated, HIV can progress to Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS), a condition characterized by a severely compromised immune system and increased risk of life-threatening illnesses.
The importance of understanding HIV cannot be overstated. With over 38 million people living with HIV worldwide, the disease has become a major public health concern. The impact of HIV extends beyond the individual, affecting families, communities, and societies as a whole. By educating ourselves about HIV, we can work towards reducing stigma, promoting prevention, and supporting those affected by the disease.
What is HIV Transmission?

Understanding how HIV is transmitted is essential for preventing new infections. By knowing the risks and taking steps to protect ourselves, we can significantly reduce the spread of the disease.
How Does HIV Affect the Body?
HIV infection can cause a range of symptoms, from mild to severe, depending on the stage of the disease. During the initial stages, people may experience flu-like symptoms, such as fever, fatigue, and swollen lymph nodes. As the disease progresses, the immune system becomes increasingly compromised, making the individual more susceptible to opportunistic infections, such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, and toxoplasmosis.The impact of HIV on the body can be significant, affecting not only physical health but also mental and emotional well-being. People living with HIV may experience anxiety, depression, and social isolation, which can further exacerbate the disease.
HIV Diagnosis and Testing
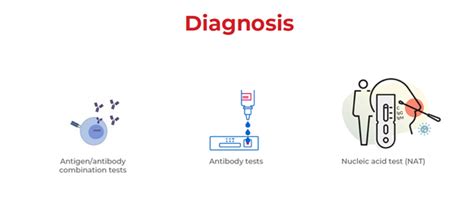
Early detection and diagnosis are critical for effective treatment and prevention of HIV transmission. Regular testing is essential for individuals who engage in high-risk behaviors or have been exposed to the virus.
HIV Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for HIV, antiretroviral therapy (ART) has revolutionized the treatment and management of the disease. ART involves a combination of medications that suppress the virus, allowing the immune system to recover and reducing the risk of transmission. The goals of ART include: * Suppressing the virus to undetectable levels * Restoring immune function * Preventing opportunistic infections and diseases * Reducing the risk of transmission to othersAdherence to ART is crucial for effective treatment and management of HIV. By taking medications as prescribed, individuals can maintain a healthy immune system and reduce the risk of complications.
HIV Prevention Methods

By understanding the importance of prevention and taking steps to protect ourselves, we can significantly reduce the spread of HIV and promote a healthier, more informed community.
HIV Stigma and Discrimination
Unfortunately, HIV is often surrounded by stigma and discrimination, which can have devastating consequences for individuals living with the disease. Stigma can lead to social isolation, depression, and reduced access to healthcare and support services. It is essential to address and challenge these misconceptions, promoting a culture of acceptance, understanding, and compassion.By working together to reduce stigma and promote education, we can create a more supportive and inclusive environment for individuals affected by HIV.
HIV Research and Developments
By investing in research and development, we can accelerate progress towards a world where HIV is no longer a major public health concern.
HIV Support and Resources
For individuals living with HIV, access to support and resources is essential for managing the disease and maintaining a high quality of life. Some of the available resources include: * HIV support groups and counseling services * Online forums and communities * Hotlines and helplines * Healthcare providers and clinics specializing in HIV careBy connecting individuals with the necessary resources and support, we can empower them to take control of their health and well-being.
HIV Awareness and Education

By working together to promote awareness and education, we can create a more informed and compassionate community.
HIV and Mental Health
The impact of HIV on mental health should not be underestimated. Individuals living with HIV may experience anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), among other mental health issues. It is essential to address these concerns, providing access to mental health services and support.By prioritizing mental health and well-being, we can help individuals living with HIV to cope with the emotional and psychological challenges of the disease.
HIV and Social Determinants

By working to address the social determinants of health, we can create a more just and equitable society, where everyone has access to the resources and support they need to thrive.
HIV and Human Rights
The relationship between HIV and human rights is complex and multifaceted. Individuals living with HIV often face discrimination, stigma, and violence, which can have devastating consequences for their health and well-being. It is essential to promote and protect the human rights of individuals affected by HIV, ensuring access to healthcare, education, and social services.By upholding human rights and promoting social justice, we can create a more compassionate and inclusive world, where everyone has the opportunity to live a healthy and fulfilling life.
HIV and Global Health

By working together to address the global health challenges posed by HIV, we can create a more equitable and just world, where everyone has access to the healthcare and resources they need to thrive.
HIV and Future Directions
As we look to the future, it is essential to consider the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. Some of the key areas of focus include: * Developing more effective prevention and treatment strategies * Addressing the social determinants of health and promoting health equity * Supporting research and development in the field of HIV * Promoting awareness and education about HIVBy working together to address these challenges and opportunities, we can create a brighter future for individuals affected by HIV and promote a world where the disease is no longer a major public health concern.
What is HIV?
+HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a type of retrovirus that attacks the body's immune system, specifically targeting CD4 cells (T cells), which play a vital role in fighting off infections.
How is HIV transmitted?
+HIV transmission occurs when the virus is passed from one person to another through bodily fluids, such as blood, semen, vaginal fluids, and breast milk.
What are the symptoms of HIV?
+The symptoms of HIV can vary depending on the stage of the disease, but may include flu-like symptoms, such as fever, fatigue, and swollen lymph nodes, as well as more severe symptoms, such as opportunistic infections and diseases.
How is HIV diagnosed?
+HIV diagnosis involves a series of tests, including antibody tests, antigen tests, and nucleic acid tests (NATs), which detect the presence of the virus or the body's response to it.
What is the treatment for HIV?
+The treatment for HIV involves antiretroviral therapy (ART), which suppresses the virus and allows the immune system to recover, as well as other medications and therapies to manage related health issues.
In conclusion, HIV is a complex and multifaceted disease that requires a comprehensive and nuanced approach. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention methods, we can work towards reducing the spread of the disease and promoting a healthier, more informed community. We invite you to share your thoughts, questions, and experiences in the comments below, and to join us in promoting awareness and education about HIV. Together, we can create a world where HIV is no longer a major public health concern, and where everyone has access to the resources and support they need to thrive.
