Intro
Discover Value-Based Care, a healthcare model focusing on patient outcomes, quality metrics, and cost-effective solutions, emphasizing population health, care coordination, and preventive medicine.
The concept of value-based care has been gaining significant attention in the healthcare industry over the past few years. As the healthcare system continues to evolve, there is a growing need to shift the focus from traditional fee-for-service models to more patient-centered and cost-effective approaches. Value-based care is a healthcare delivery model that prioritizes quality and value over volume, aiming to improve patient outcomes while reducing costs. In this article, we will delve into the world of value-based care, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, and key aspects that are transforming the healthcare landscape.
The traditional fee-for-service model has been criticized for promoting unnecessary treatments, tests, and procedures, which can lead to increased healthcare costs without necessarily improving patient outcomes. In contrast, value-based care focuses on providing high-quality, patient-centered care that addresses the unique needs and preferences of each individual. This approach encourages healthcare providers to work together as a team, sharing data and best practices to deliver coordinated and effective care. By prioritizing value over volume, healthcare providers can reduce waste, improve efficiency, and enhance patient satisfaction.
As the healthcare industry continues to shift towards value-based care, it is essential to understand the underlying principles and mechanisms that drive this approach. Value-based care is built on several key elements, including patient engagement, population health management, and data-driven decision making. By empowering patients to take an active role in their care, healthcare providers can tailor their services to meet individual needs and preferences. Population health management involves analyzing data and trends to identify high-risk patients and develop targeted interventions to improve outcomes. Data-driven decision making enables healthcare providers to track performance, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions about care delivery.
What is Value-Based Care?
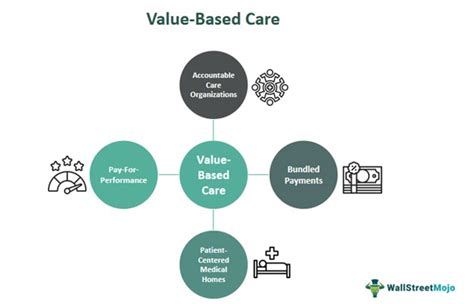
Key Elements of Value-Based Care
The key elements of value-based care include: * Patient engagement: Empowering patients to take an active role in their care, making informed decisions, and setting personalized goals. * Population health management: Analyzing data and trends to identify high-risk patients, developing targeted interventions, and improving outcomes. * Data-driven decision making: Tracking performance, identifying areas for improvement, and making informed decisions about care delivery. * Care coordination: Collaborating with healthcare providers, specialists, and community resources to deliver comprehensive and coordinated care. * Quality metrics: Establishing and tracking quality metrics to measure performance, identify areas for improvement, and drive quality improvement initiatives.Benefits of Value-Based Care
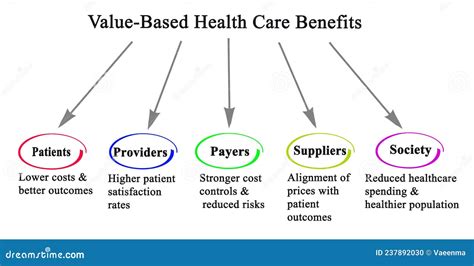
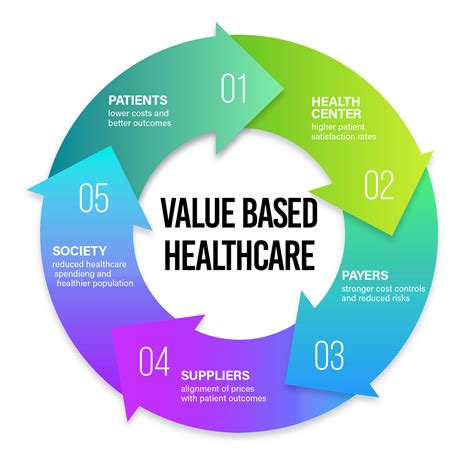
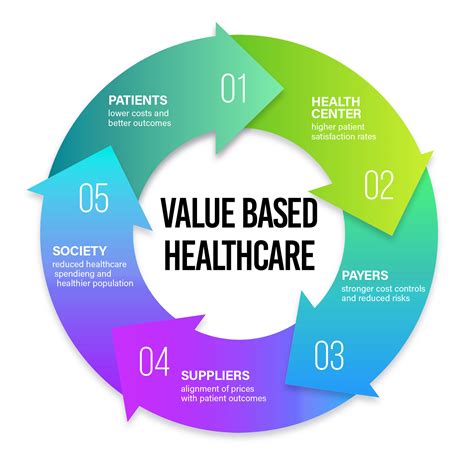
Value-Based Care Models
There are several value-based care models, including: * Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs): ACOs are networks of healthcare providers that work together to deliver coordinated care and share financial risks and rewards. * Patient-Centered Medical Homes (PCMHs): PCMHs are primary care practices that prioritize patient-centered care, care coordination, and population health management. * Bundled Payments: Bundled payments involve paying a single fee for a bundle of services, such as a surgical procedure or a hospital stay. * Value-Based Payment (VBP) Models: VBP models involve paying healthcare providers based on performance, quality, and patient outcomes, rather than volume or fee-for-service.Implementing Value-Based Care

Challenges and Opportunities
The transition to value-based care is not without challenges. Healthcare providers must navigate complex regulatory requirements, invest in new technologies and workflows, and develop new skills and competencies. However, the opportunities are significant, including: * Improved patient outcomes and satisfaction * Reduced costs and improved affordability * Enhanced care coordination and population health management * Increased reimbursement and financial incentives for high-quality careValue-Based Care and Technology
Artificial Intelligence and Value-Based Care
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are being increasingly used to support value-based care. AI and ML can help analyze large datasets, identify high-risk patients, and develop personalized care plans. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can also enhance patient engagement, improve care coordination, and reduce costs.Value-Based Care and Population Health
Social Determinants of Health
Social determinants of health, such as housing, education, and employment, play a critical role in shaping health outcomes. Value-based care recognizes the importance of addressing social determinants of health and involves: * Assessing patient needs and developing care plans to address social determinants of health * Collaborating with community resources and social services to support patient care * Developing interventions to address health disparities and inequitiesConclusion and Future Directions
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with value-based care. How do you think value-based care can be improved or expanded? What challenges or opportunities do you see in implementing value-based care? Join the conversation and help shape the future of healthcare.
What is value-based care?
+Value-based care is a healthcare delivery model that prioritizes quality and value over volume, aiming to improve patient outcomes while reducing costs.
What are the key elements of value-based care?
+The key elements of value-based care include patient engagement, population health management, data-driven decision making, care coordination, and quality metrics.
How can value-based care improve patient outcomes?
+Value-based care can improve patient outcomes by prioritizing patient-centered care, reducing waste, and promoting preventive care.
