Intro
Discover Furosemide ingredients, a diuretic medication, and understand its active components, side effects, and interactions, including loop diuretics and pharmacological effects.
The world of pharmaceuticals is vast and complex, with numerous medications available to treat a wide range of conditions. One such medication is Furosemide, a diuretic used to treat fluid build-up and swelling caused by congestive heart failure, liver cirrhosis, or a kidney disorder. Understanding the ingredients of Furosemide is essential for patients, healthcare professionals, and researchers alike. In this article, we will delve into the world of Furosemide, exploring its ingredients, mechanisms, benefits, and potential side effects.
Furosemide is a prescription medication that belongs to a class of drugs known as loop diuretics. It works by increasing urine production, which helps to remove excess fluid from the body. This, in turn, reduces swelling and alleviates symptoms associated with fluid build-up. Furosemide is available in various forms, including tablets, oral solutions, and injections. The medication is widely used and has been a cornerstone in the treatment of edema and fluid overload for decades.
The importance of understanding Furosemide ingredients cannot be overstated. With the rise of generic medications and the increasing complexity of pharmaceutical formulations, it is essential to know what goes into the medications we take. This knowledge can help patients make informed decisions about their treatment, enable healthcare professionals to provide better care, and facilitate researchers in developing new and improved medications. In the following sections, we will explore the ingredients of Furosemide, its mechanisms of action, and its benefits and potential side effects.
Furosemide Ingredients

Mechanism of Action
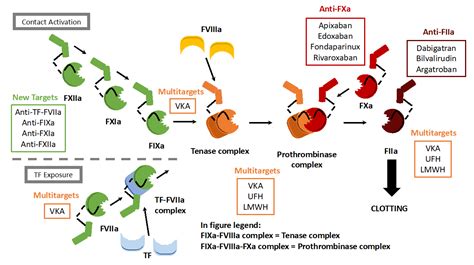
Benefits of Furosemide
The benefits of Furosemide are numerous and well-documented. The medication is effective in treating fluid build-up and swelling caused by congestive heart failure, liver cirrhosis, or a kidney disorder. Furosemide is also used to treat hypertension, although it is not a primary treatment for this condition. The medication is generally well-tolerated, although it can cause side effects such as dizziness, lightheadedness, and increased urination.Side Effects of Furosemide

Interactions with Other Medications
Furosemide can interact with other medications, including ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, and beta blockers. These interactions can increase the risk of side effects or reduce the effectiveness of Furosemide. Patients taking Furosemide should inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking, including prescription and over-the-counter medications, vitamins, and supplements.Dosage and Administration
Special Considerations
Furosemide is not suitable for all patients, particularly those with certain medical conditions or taking specific medications. Patients with kidney or liver disease should use Furosemide with caution, as the medication can worsen these conditions. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should also use Furosemide with caution, as the medication can pass into breast milk and affect the baby.Conclusion and Future Directions

Final Thoughts
As we move forward in the world of pharmaceuticals, it is essential to prioritize patient education and empowerment. By understanding the ingredients and mechanisms of medications like Furosemide, patients can take a more active role in their treatment and make informed decisions about their care. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with Furosemide and to join the conversation about the importance of patient education and empowerment in the comments section below.What is Furosemide used for?
+Furosemide is used to treat fluid build-up and swelling caused by congestive heart failure, liver cirrhosis, or a kidney disorder.
How does Furosemide work?
+Furosemide works by inhibiting the sodium-potassium-chloride cotransporter in the ascending limb of the loop of Henle, leading to increased urine production and removal of excess fluid from the body.
What are the common side effects of Furosemide?
+Common side effects of Furosemide include dizziness, lightheadedness, and increased urination. Less common side effects include hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, and hypomagnesemia.
Can Furosemide interact with other medications?
+Yes, Furosemide can interact with other medications, including ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, and beta blockers. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking.
Is Furosemide suitable for pregnant or breastfeeding women?
+Furosemide should be used with caution in pregnant or breastfeeding women, as the medication can pass into breast milk and affect the baby. Patients should consult their healthcare provider before taking Furosemide.
