Intro
Discover low-fiber diet menu examples, including gentle foods, soft diets, and bowel rest plans, to manage digestive issues with easy-to-digest meals and snacks.
A low-fiber diet is often recommended for individuals who have certain medical conditions, such as gastrointestinal disorders, or those who are recovering from surgery. The primary goal of a low-fiber diet is to reduce the amount of undigested food that reaches the colon, thereby minimizing the risk of discomfort, bloating, and other digestive issues. In this article, we will delve into the world of low-fiber diets, exploring their benefits, working mechanisms, and providing practical examples of low-fiber diet menu plans.
The importance of a low-fiber diet cannot be overstated, particularly for those who experience digestive problems. By limiting the intake of high-fiber foods, individuals can reduce the risk of irritating their digestive system, which can lead to a range of unpleasant symptoms, including abdominal pain, diarrhea, and constipation. Moreover, a low-fiber diet can be beneficial for those who are undergoing certain medical procedures, such as colonoscopy, as it can help to clear the bowel and reduce the risk of complications.
A low-fiber diet is not just about restricting certain food groups; it's also about making informed choices about the types of foods that are consumed. By focusing on low-fiber foods, individuals can ensure that they are getting the nutrients they need while minimizing the risk of digestive discomfort. In the following sections, we will explore the benefits and working mechanisms of a low-fiber diet, as well as provide practical examples of low-fiber diet menu plans.
Understanding Low-Fiber Diets
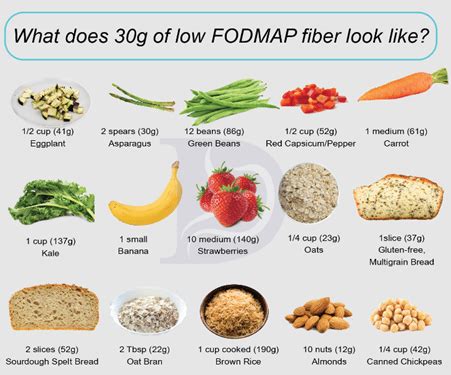
A low-fiber diet is a type of diet that restricts the intake of high-fiber foods, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. The goal of a low-fiber diet is to reduce the amount of undigested food that reaches the colon, thereby minimizing the risk of digestive discomfort. Low-fiber diets are often recommended for individuals who have certain medical conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), or those who are recovering from surgery.
Benefits of a Low-Fiber Diet
The benefits of a low-fiber diet are numerous, particularly for those who experience digestive problems. Some of the key benefits of a low-fiber diet include: * Reduced risk of digestive discomfort, such as bloating, gas, and abdominal pain * Minimized risk of irritating the digestive system, which can lead to diarrhea, constipation, and other symptoms * Improved management of certain medical conditions, such as IBS and IBD * Reduced risk of complications during certain medical procedures, such as colonoscopyWorking Mechanisms of a Low-Fiber Diet

A low-fiber diet works by restricting the intake of high-fiber foods, which can be difficult for the body to digest. By limiting the amount of undigested food that reaches the colon, a low-fiber diet can help to reduce the risk of digestive discomfort and minimize the risk of irritating the digestive system. Some of the key working mechanisms of a low-fiber diet include:
- Reducing the amount of undigested food that reaches the colon
- Minimizing the risk of irritating the digestive system
- Improving the management of certain medical conditions, such as IBS and IBD
- Reducing the risk of complications during certain medical procedures, such as colonoscopy
Steps to Follow a Low-Fiber Diet
Following a low-fiber diet can be challenging, particularly for those who are used to consuming high-fiber foods. However, by following some simple steps, individuals can ensure that they are getting the nutrients they need while minimizing the risk of digestive discomfort. Some of the key steps to follow a low-fiber diet include: * Restricting the intake of high-fiber foods, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables * Focusing on low-fiber foods, such as lean proteins, low-fiber grains, and low-fiber dairy products * Drinking plenty of water to help prevent constipation * Avoiding foods that are high in fat, sugar, and saltLow-Fiber Diet Menu Examples
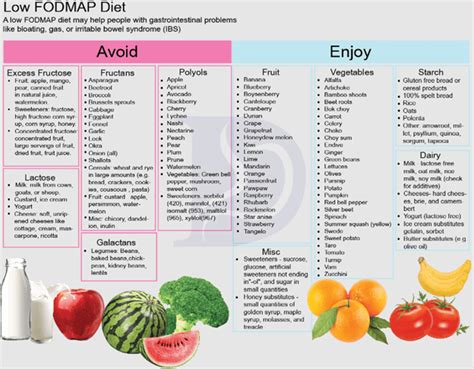
A low-fiber diet menu plan should be tailored to an individual's specific needs and preferences. However, here are some examples of low-fiber diet menu plans:
- Breakfast: scrambled eggs, low-fiber toast, and low-fiber cereal
- Lunch: grilled chicken, low-fiber rice, and low-fiber vegetables
- Dinner: baked fish, low-fiber potatoes, and low-fiber green beans
- Snacks: low-fiber fruits, such as bananas and avocados, and low-fiber dairy products, such as yogurt and cheese
Practical Tips for Following a Low-Fiber Diet
Following a low-fiber diet can be challenging, particularly for those who are used to consuming high-fiber foods. However, by following some practical tips, individuals can ensure that they are getting the nutrients they need while minimizing the risk of digestive discomfort. Some of the key practical tips for following a low-fiber diet include: * Keeping a food diary to track food intake and identify trigger foods * Avoiding foods that are high in fat, sugar, and salt * Drinking plenty of water to help prevent constipation * Eating small, frequent meals to help manage digestive symptomsCommon Foods to Avoid on a Low-Fiber Diet

There are several foods that should be avoided on a low-fiber diet, including:
- High-fiber grains, such as whole wheat bread and brown rice
- High-fiber fruits, such as apples and berries
- High-fiber vegetables, such as broccoli and Brussels sprouts
- Legumes, such as beans and lentils
- Nuts and seeds, such as almonds and sunflower seeds
Common Foods to Eat on a Low-Fiber Diet
There are several foods that are suitable for a low-fiber diet, including: * Lean proteins, such as chicken and fish * Low-fiber grains, such as white bread and white rice * Low-fiber fruits, such as bananas and avocados * Low-fiber vegetables, such as green beans and cucumbers * Low-fiber dairy products, such as yogurt and cheeseManaging Digestive Symptoms on a Low-Fiber Diet

Managing digestive symptoms on a low-fiber diet can be challenging, particularly for those who experience persistent symptoms. However, by following some simple tips, individuals can help to manage their digestive symptoms and improve their overall quality of life. Some of the key tips for managing digestive symptoms on a low-fiber diet include:
- Keeping a food diary to track food intake and identify trigger foods
- Avoiding foods that are high in fat, sugar, and salt
- Drinking plenty of water to help prevent constipation
- Eating small, frequent meals to help manage digestive symptoms
Seeking Medical Attention
If digestive symptoms persist or worsen on a low-fiber diet, it is essential to seek medical attention. A healthcare provider can help to diagnose the underlying cause of digestive symptoms and provide guidance on the best course of treatment. Some of the key signs that medical attention is needed include: * Persistent or severe abdominal pain * Vomiting or diarrhea * Blood in the stool or rectal bleeding * Fever or chillsWhat is a low-fiber diet?
+A low-fiber diet is a type of diet that restricts the intake of high-fiber foods, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, to reduce the amount of undigested food that reaches the colon and minimize the risk of digestive discomfort.
Who should follow a low-fiber diet?
+A low-fiber diet is often recommended for individuals who have certain medical conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), or those who are recovering from surgery.
What are the benefits of a low-fiber diet?
+The benefits of a low-fiber diet include reduced risk of digestive discomfort, minimized risk of irritating the digestive system, and improved management of certain medical conditions, such as IBS and IBD.
How long should I follow a low-fiber diet?
+The length of time that an individual should follow a low-fiber diet will depend on their specific needs and medical condition. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment.
Can I still get enough nutrients on a low-fiber diet?
+Yes, it is possible to get enough nutrients on a low-fiber diet by focusing on low-fiber foods that are rich in nutrients, such as lean proteins, low-fiber grains, and low-fiber dairy products.
In
Final Thoughts

