Intro
Discover what insulin is, its role in glucose regulation, and how it affects diabetes management, blood sugar levels, and hormone balance, understanding insulin resistance and sensitivity.
Insulin is a vital hormone produced by the pancreas, an organ located behind the stomach. It plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels in the body. When we eat, our body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. Insulin helps to facilitate the entry of glucose into cells, where it can be used for energy production, growth, and repair. Without insulin, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to a range of health problems, including diabetes.
The importance of insulin cannot be overstated. It is essential for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels, which is critical for preventing complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. Insulin also helps to regulate the metabolism of fats and proteins, ensuring that the body uses these nutrients efficiently. Furthermore, insulin has anti-inflammatory properties, which can help to protect against chronic diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer's disease.
In addition to its role in regulating blood sugar levels, insulin has been shown to have a range of other benefits. For example, it can help to improve cognitive function, reduce the risk of certain infections, and even promote wound healing. Insulin has also been used therapeutically to treat a range of conditions, including type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). With its wide range of functions and benefits, it is clear that insulin is a hormone that plays a vital role in maintaining overall health and well-being.
How Insulin Works

Insulin works by binding to insulin receptors on the surface of cells, which triggers a signaling cascade that ultimately leads to the uptake of glucose into the cell. This process is facilitated by a range of proteins, including glucose transporter proteins, which help to transport glucose across the cell membrane. Once inside the cell, glucose can be used to produce energy, synthesize glycogen, or be stored for later use.
The insulin signaling pathway is complex and involves multiple steps. First, insulin binds to its receptor, which activates a tyrosine kinase enzyme. This enzyme then phosphorylates and activates a range of downstream targets, including the insulin receptor substrate (IRS) and the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway. These targets then activate a range of cellular processes, including glucose uptake, glycogen synthesis, and protein synthesis.
Insulin Resistance and Diabetes
Insulin resistance is a condition in which the body's cells become less responsive to insulin, making it harder for glucose to enter the cells. This can lead to high blood sugar levels, which can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Insulin resistance is often associated with obesity, physical inactivity, and a diet high in sugar and saturated fat.Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels, which can lead to a range of complications, including heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. While type 2 diabetes is often associated with insulin resistance, it can also be caused by a range of other factors, including genetics, lifestyle, and certain medical conditions.
Types of Insulin
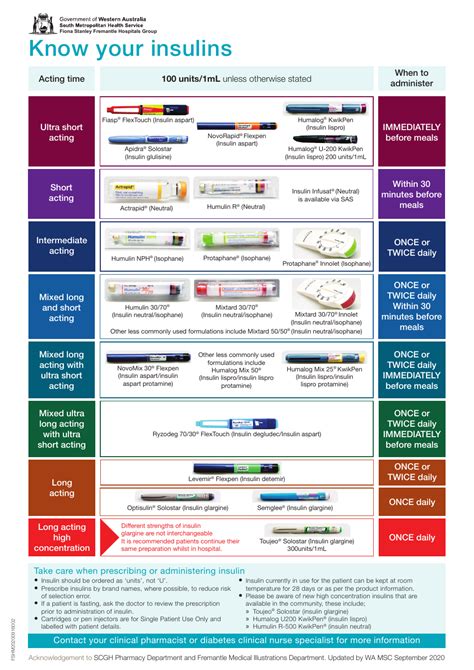
There are several types of insulin, each with its own unique characteristics and uses. These include:
- Rapid-acting insulin: This type of insulin starts to work within 15 minutes of injection and peaks within 1-3 hours. It is often used to control blood sugar levels after meals.
- Short-acting insulin: This type of insulin starts to work within 30 minutes of injection and peaks within 2-4 hours. It is often used to control blood sugar levels between meals.
- Intermediate-acting insulin: This type of insulin starts to work within 1-2 hours of injection and peaks within 4-12 hours. It is often used to control blood sugar levels overnight.
- Long-acting insulin: This type of insulin starts to work within 2-4 hours of injection and lasts for 24 hours or more. It is often used to control blood sugar levels throughout the day.
Insulin Therapy
Insulin therapy is a common treatment for type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. It involves injecting insulin into the body to help regulate blood sugar levels. There are several types of insulin therapy, including:- Basal insulin therapy: This type of therapy involves injecting a long-acting insulin once or twice a day to provide background insulin coverage.
- Bolus insulin therapy: This type of therapy involves injecting a rapid-acting or short-acting insulin before meals to control blood sugar levels.
- Premixed insulin therapy: This type of therapy involves injecting a combination of intermediate-acting and short-acting insulin before meals.
Benefits of Insulin Therapy
Insulin therapy has a range of benefits, including:
- Improved blood sugar control: Insulin therapy can help to regulate blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of complications such as heart disease and kidney damage.
- Increased energy: Insulin therapy can help to improve energy levels, reducing fatigue and improving overall quality of life.
- Weight management: Insulin therapy can help to regulate appetite and metabolism, making it easier to manage weight.
- Reduced risk of complications: Insulin therapy can help to reduce the risk of complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
Insulin Pumps and Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems are advanced technologies that can help to improve blood sugar control and reduce the risk of complications. Insulin pumps involve wearing a small device that delivers insulin continuously throughout the day, while CGM systems involve wearing a small sensor that tracks blood sugar levels continuously.These technologies have a range of benefits, including:
- Improved blood sugar control: Insulin pumps and CGM systems can help to regulate blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of complications.
- Increased flexibility: Insulin pumps and CGM systems can be programmed to deliver insulin and track blood sugar levels at specific times of the day, making it easier to manage blood sugar levels.
- Reduced risk of hypoglycemia: Insulin pumps and CGM systems can help to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), which can be a serious complication of diabetes.
Insulin and Weight Loss
Insulin has a range of effects on weight loss, including:
- Regulating appetite: Insulin can help to regulate appetite, reducing the desire to eat and making it easier to stick to a weight loss diet.
- Improving metabolism: Insulin can help to improve metabolism, increasing the body's ability to burn fat and lose weight.
- Reducing inflammation: Insulin has anti-inflammatory properties, which can help to reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
However, insulin can also have negative effects on weight loss, including:
- Increasing fat storage: Insulin can help to store fat, making it harder to lose weight.
- Reducing fat burning: Insulin can reduce the body's ability to burn fat, making it harder to lose weight.
Insulin and Exercise
Exercise is an important part of any weight loss plan, and insulin can play a range of roles in exercise, including:- Regulating blood sugar levels: Insulin can help to regulate blood sugar levels during exercise, reducing the risk of hypoglycemia.
- Improving performance: Insulin can help to improve exercise performance, increasing strength and endurance.
- Reducing inflammation: Insulin has anti-inflammatory properties, which can help to reduce inflammation and improve recovery after exercise.
Insulin and Nutrition
Nutrition plays a critical role in insulin function, and a healthy diet can help to regulate blood sugar levels and improve overall health. Some of the key nutrients that can help to regulate insulin function include:
- Fiber: Fiber can help to slow the absorption of glucose, reducing the risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
- Protein: Protein can help to regulate blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of hypoglycemia and improving overall health.
- Healthy fats: Healthy fats, such as omega-3 fatty acids, can help to reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
However, some nutrients can also have negative effects on insulin function, including:
- Sugar: Consuming high amounts of sugar can increase the risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
- Saturated fat: Consuming high amounts of saturated fat can increase the risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
- Refined carbohydrates: Consuming high amounts of refined carbohydrates can increase the risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
Insulin and Mental Health
Insulin can also have a range of effects on mental health, including:- Reducing stress: Insulin can help to reduce stress and anxiety, improving overall mental health.
- Improving mood: Insulin can help to improve mood, reducing the risk of depression and anxiety.
- Improving cognitive function: Insulin can help to improve cognitive function, reducing the risk of dementia and Alzheimer's disease.
However, insulin can also have negative effects on mental health, including:
- Increasing anxiety: Insulin can increase anxiety and stress, particularly in people with diabetes.
- Reducing self-esteem: Insulin can reduce self-esteem, particularly in people with diabetes.
Conclusion and Future Directions
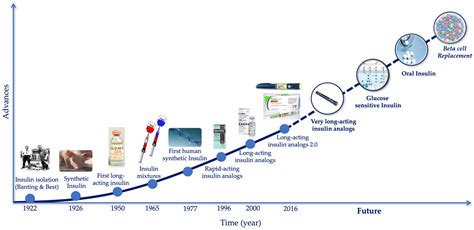
In conclusion, insulin is a vital hormone that plays a critical role in regulating blood sugar levels and overall health. Insulin therapy is a common treatment for type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes, and can have a range of benefits, including improved blood sugar control, increased energy, and reduced risk of complications. However, insulin can also have negative effects, including increased fat storage and reduced fat burning.
Future directions for insulin research include:
- Developing new insulin therapies, such as inhaled insulin and oral insulin.
- Improving insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitoring systems.
- Developing new treatments for insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
We hope that this article has provided a comprehensive overview of insulin and its role in regulating blood sugar levels and overall health. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with insulin in the comments below.
What is insulin?
+Insulin is a vital hormone produced by the pancreas that plays a critical role in regulating blood sugar levels and overall health.
What are the benefits of insulin therapy?
+Insulin therapy can have a range of benefits, including improved blood sugar control, increased energy, and reduced risk of complications.
What are the different types of insulin?
+There are several types of insulin, including rapid-acting insulin, short-acting insulin, intermediate-acting insulin, and long-acting insulin.
How does insulin affect weight loss?
+Insulin can have both positive and negative effects on weight loss, including regulating appetite, improving metabolism, and reducing inflammation, but also increasing fat storage and reducing fat burning.
What is the relationship between insulin and exercise?
+Insulin can play a range of roles in exercise, including regulating blood sugar levels, improving performance, and reducing inflammation.
