Intro
Discover the LEEP procedure, a minimally invasive treatment for cervical dysplasia, using loop electrosurgical excision to remove abnormal cells, preventing cervical cancer and promoting womens health through diagnostic and therapeutic methods.
The Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure, commonly referred to as LEEP, is a widely used medical technique for treating abnormal cell growth on the cervix. This procedure is crucial for preventing the development of cervical cancer, which is often caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). The importance of understanding and addressing cervical abnormalities cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts women's health and well-being. The LEEP procedure has become a cornerstone in gynecological care due to its effectiveness and relatively low risk of complications.
Cervical health is a significant concern for women, especially those of childbearing age. Regular Pap tests and HPV screenings are essential for early detection of abnormalities. When abnormal cells are found, healthcare providers often recommend a LEEP procedure to remove the affected tissue. This not only helps in preventing the progression of these cells into cancer but also provides a sample for further pathological examination to ensure all abnormal cells have been removed. The procedure is typically performed in a doctor's office and requires minimal recovery time, making it a convenient option for many women.
Understanding the LEEP procedure and its implications is vital for women's health awareness. It's a subject that combines medical knowledge with personal health care, emphasizing the importance of regular screenings and proactive approaches to health. By delving into the details of the LEEP procedure, including its benefits, the process itself, and post-procedure care, individuals can better navigate their health options and make informed decisions. This knowledge empowers women to take control of their cervical health, fostering a proactive approach to preventing cervical cancer.
What is the LEEP Procedure?
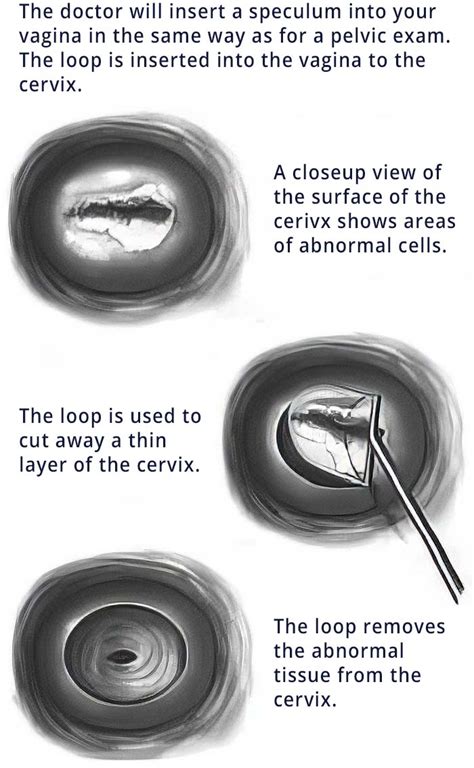
The LEEP procedure is a minor surgical intervention that uses a specialized tool to remove abnormal tissue from the cervix. The tool, known as a loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) device, consists of a wire loop through which an electric current is passed. This current heats the wire, allowing it to cut and coagulate the tissue simultaneously. The procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia to minimize discomfort and is typically completed within 10 to 15 minutes.
Benefits of the LEEP Procedure
The primary benefit of the LEEP procedure is its effectiveness in removing precancerous cells from the cervix, thereby reducing the risk of these cells developing into cervical cancer. Other benefits include: - **Minimally Invasive:** The procedure is relatively simple and does not require a hospital stay. - **Quick Recovery:** Most women can return to their normal activities within a day or two. - **High Success Rate:** The LEEP procedure has a high success rate in removing all abnormal cells. - **Diagnostic and Therapeutic:** It serves both as a diagnostic tool by providing tissue for further examination and as a treatment by removing the abnormal cells.How is the LEEP Procedure Performed?

The performance of the LEEP procedure involves several steps:
- Preparation: The patient is positioned in a speculum exam position, similar to a Pap test.
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is applied to the cervix to minimize discomfort during the procedure.
- Visualization: The healthcare provider uses a colposcope to visualize the abnormal areas on the cervix.
- Excision: The LEEP device is then used to remove the abnormal tissue. The loop is inserted through the speculum and placed around the affected area. An electric current is passed through the loop, which cuts and removes the tissue.
- Cauterization: After the tissue is removed, the area may be cauterized to stop any bleeding.
- Follow-Up: The patient is advised on post-procedure care and scheduled for a follow-up appointment to check on healing and remove any stitches if they were used.
Post-Procedure Care and Follow-Up
After the LEEP procedure, it's essential to follow the healthcare provider's instructions for post-procedure care. This typically includes: - **Rest:** Avoiding strenuous activities for a few days. - **Bleeding:** Expecting some vaginal bleeding or discharge, which should be light. - **Hygiene:** Avoiding tampons, douching, and sexual intercourse for a specified period. - **Follow-Up Appointments:** Attending scheduled follow-up appointments to monitor healing and check for any residual abnormal cells.Risks and Complications of the LEEP Procedure

While the LEEP procedure is generally safe, there are potential risks and complications to be aware of:
- Bleeding: Heavy bleeding is a possible complication, though it's rare.
- Infection: As with any surgical procedure, there's a risk of infection.
- Cervical Stenosis: The cervix may become narrower, potentially causing problems with future pregnancies or menstrual flow.
- Preterm Labor: Women who have had a LEEP procedure may have a slightly increased risk of preterm labor in future pregnancies.
LEEP Procedure and Pregnancy
The LEEP procedure can have implications for future pregnancies. While it's generally considered safe, there is a potential increased risk of preterm labor and cervical insufficiency. However, the benefits of removing precancerous cells usually outweigh these risks. Women who have undergone a LEEP procedure should discuss their pregnancy plans with their healthcare provider to understand any necessary precautions or special care during pregnancy.Alternatives to the LEEP Procedure

For some patients, alternatives to the LEEP procedure may be considered, including:
- Cryotherapy: Freezing the abnormal cells, which then fall off.
- Laser Therapy: Using a laser to destroy the abnormal cells.
- Cold Knife Cone Biopsy: A surgical procedure that removes a larger cone-shaped sample of tissue.
- Observation: In some cases, especially if the abnormal cells are mild, a healthcare provider might recommend close observation with regular Pap tests and HPV screenings instead of immediate treatment.
Choosing the Right Option
The choice between the LEEP procedure and its alternatives depends on several factors, including the severity of the abnormal cell growth, the patient's overall health, and their reproductive plans. It's crucial for patients to discuss all options thoroughly with their healthcare provider to make an informed decision that best suits their needs and health status.LEEP Procedure and Emotional Well-being

Undergoing a LEEP procedure can have emotional implications for women. Receiving a diagnosis of abnormal cell growth can be stressful and may evoke fears about cancer. The procedure itself and the anticipation of results can also cause anxiety. It's essential for patients to seek support from their healthcare providers, family, and friends. Discussing feelings and concerns can help alleviate some of the emotional burden associated with the procedure.
Coping Mechanisms
Coping with the emotional aspects of the LEEP procedure involves: - **Education:** Understanding the procedure and its outcomes can reduce anxiety. - **Support Networks:** Talking to loved ones, support groups, or counselors can provide emotional relief. - **Self-Care:** Engaging in activities that promote relaxation and well-being, such as exercise, meditation, or hobbies, can help manage stress.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, the LEEP procedure is a vital tool in the prevention and treatment of cervical cancer. By understanding the procedure, its benefits, and its potential risks, women can make informed decisions about their health. It's crucial to maintain open communication with healthcare providers and to follow recommended screenings and treatments. Empowering oneself with knowledge about cervical health and the LEEP procedure is a significant step towards proactive health care and cancer prevention.
We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, or questions about the LEEP procedure in the comments below. Your engagement can help others feel more informed and supported. If you found this article helpful, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this information.
What is the purpose of the LEEP procedure?
+The primary purpose of the LEEP procedure is to remove abnormal cell growth from the cervix to prevent the development of cervical cancer.
Is the LEEP procedure painful?
+Most women do not find the LEEP procedure to be painful, as it is typically performed under local anesthesia. However, some women may experience mild discomfort or cramping during or after the procedure.
Can I get pregnant after having a LEEP procedure?
+Yes, most women can get pregnant after having a LEEP procedure. However, there might be a slight increase in the risk of preterm labor or cervical insufficiency in future pregnancies.
