Intro
Discover Lisinopril uses and benefits, including blood pressure management, heart failure treatment, and kidney protection, with its ACE inhibitor properties and cardiovascular benefits.
Lisinopril is a medication that has been widely used for several decades to treat various health conditions, particularly those related to the cardiovascular system. It is an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, which means it works by blocking the action of a naturally occurring chemical in the body that constricts blood vessels, allowing blood to flow more smoothly and reducing blood pressure. The importance of managing blood pressure cannot be overstated, as high blood pressure is a major risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. Lisinopril's role in mitigating these risks makes it a crucial medication for many individuals.
The significance of lisinopril extends beyond its ability to lower blood pressure. It has been found to have protective effects on the heart and kidneys, making it a valuable treatment option for patients with heart failure and diabetic nephropathy. Moreover, its use has been associated with a reduced risk of stroke and myocardial infarction (heart attack) in patients with a history of these conditions. The multifaceted benefits of lisinopril underscore its importance in modern medicine, highlighting the need for a comprehensive understanding of its uses, benefits, and potential side effects.
Understanding how lisinopril works is essential for appreciating its benefits. By inhibiting the angiotensin-converting enzyme, lisinopril prevents the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor. This action leads to vasodilation, reducing peripheral resistance and lowering blood pressure. Additionally, lisinopril increases the levels of bradykinin, a peptide that promotes vasodilation and has protective effects on the heart and kidneys. The combination of these effects not only lowers blood pressure but also provides additional cardiovascular benefits, making lisinopril a preferred choice for treating hypertension and related conditions.
Lisinopril Mechanism of Action

Benefits for Hypertension
Lisinopril is primarily used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure) and has been shown to be effective in reducing systolic and diastolic blood pressure in a wide range of patients. Its ability to lower blood pressure makes it an essential medication for preventing the complications of hypertension, including heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. The benefits of lisinopril for hypertension are well-documented, with numerous studies demonstrating its efficacy and safety in various patient populations.Lisinopril Uses

Heart Failure Treatment
The use of lisinopril in heart failure is based on its ability to reduce afterload and improve cardiac function. By decreasing the resistance against which the heart must pump, lisinopril makes it easier for the heart to function, improving symptoms and reducing the risk of further complications. This benefit is particularly significant for patients with reduced ejection fraction, where the heart's ability to pump blood is impaired. Lisinopril's role in managing heart failure underscores its importance in cardiovascular medicine, highlighting the need for careful patient selection and monitoring.Lisinopril Benefits

Protective Effects on the Kidneys
Lisinopril's protective effects on the kidneys are a significant aspect of its benefits. By reducing intraglomerular pressure and proteinuria, lisinopril helps to slow the progression of kidney disease. This effect is particularly beneficial for patients with diabetic nephropathy, where kidney damage is a major concern. The ability of lisinopril to protect the kidneys underscores its value in the management of patients with diabetes and hypertension, highlighting the need for careful monitoring of renal function in these patients.Lisinopril Side Effects
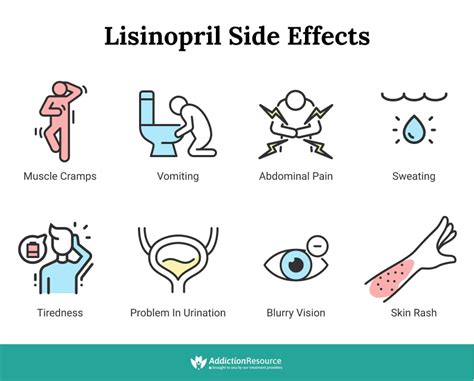
Managing Side Effects
Managing the side effects of lisinopril is crucial for ensuring patient compliance and maximizing its benefits. Healthcare providers should educate patients about the potential side effects of lisinopril and provide guidance on how to manage them. In some cases, adjusting the dosage or switching to a different medication may be necessary. The importance of effective side effect management cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts the patient's quality of life and adherence to treatment.Lisinopril Interactions

Importance of Monitoring
Monitoring patients taking lisinopril is essential for ensuring their safety and maximizing the medication's benefits. Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers allow for the early detection of side effects and potential interactions. Additionally, monitoring blood pressure and renal function helps to assess the efficacy of lisinopril and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan. The importance of monitoring cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts patient outcomes and the effectiveness of treatment.Lisinopril Dosage
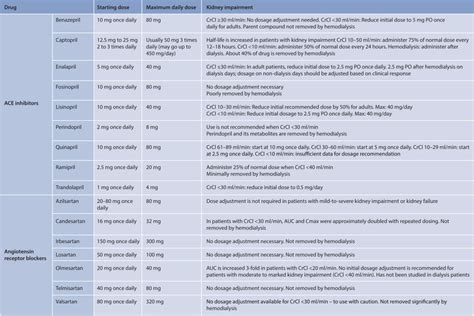
Adjusting the Dosage
Adjusting the dosage of lisinopril may be necessary based on patient response and tolerability. Healthcare providers should carefully monitor patients and adjust the dosage as needed to achieve optimal blood pressure control and minimize side effects. The ability to adjust the dosage highlights the flexibility of lisinopril as a treatment option, making it suitable for a wide range of patients.Lisinopril Contraindications

Special Considerations
Special considerations are necessary when prescribing lisinopril to certain patient populations. For example, pregnant women should avoid using lisinopril due to the risk of fetal harm. Additionally, patients with liver disease may require dose adjustments or closer monitoring. The potential risks and benefits of lisinopril in these patient populations highlight the need for careful evaluation and ongoing monitoring.What is lisinopril used for?
+Lisinopril is used to treat hypertension, heart failure, and diabetic nephropathy. It works by blocking the action of a naturally occurring chemical in the body that constricts blood vessels, allowing blood to flow more smoothly and reducing blood pressure.
What are the benefits of lisinopril?
+The benefits of lisinopril include its ability to lower blood pressure, reduce the risk of stroke and myocardial infarction, and protect the kidneys from damage. It is also effective in treating heart failure and slowing the progression of diabetic nephropathy.
What are the potential side effects of lisinopril?
+The potential side effects of lisinopril include cough, dizziness, and headache. In rare cases, it can cause more serious side effects, such as angioedema and renal impairment. Patients should be carefully monitored for these side effects and report any concerns to their healthcare provider.
In conclusion, lisinopril is a valuable medication that offers numerous benefits for patients with hypertension, heart failure, and diabetic nephropathy. Its ability to lower blood pressure, reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications, and protect the kidneys makes it a preferred choice for many healthcare providers. While it can cause side effects, careful patient monitoring and dose adjustments can minimize these risks. As with any medication, it is essential to weigh the potential benefits and risks of lisinopril and consider individual patient needs and circumstances. By doing so, healthcare providers can optimize treatment outcomes and improve the quality of life for patients taking lisinopril. We invite readers to share their experiences with lisinopril, ask questions, or seek further information on this topic, and we encourage healthcare providers to continue exploring the benefits and potential uses of this versatile medication.
