Intro
Discover 5 key facts about Metronidazole, an antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication, including its uses, side effects, and interactions, to understand its role in treating infections, bacterial vaginosis, and giardiasis.
Metronidazole is a medication that has been widely used for several decades to treat various infections caused by bacteria and protozoa. Its effectiveness and relatively low cost have made it a staple in the treatment of certain conditions. Here are five key facts about metronidazole that highlight its importance, usage, and considerations for patients.
The discovery of metronidazole dates back to the 1950s, and since its introduction into clinical practice, it has become a crucial drug in the management of infections such as trichomoniasis, amoebiasis, and giardiasis, among others. Its mechanism of action involves the interference with the DNA of microbial cells, ultimately leading to their death. This unique mode of action makes metronidazole particularly effective against anaerobic organisms, which are bacteria that thrive in environments lacking oxygen.
Metronidazole's application extends beyond the treatment of protozoal infections to include bacterial vaginosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, and infections of the abdomen, skin, and soft tissues. It is available in various formulations, including oral tablets, capsules, and suspensions, as well as topical creams and gels for the treatment of rosacea and other skin conditions. The versatility of metronidazole in treating a wide range of infections has contributed to its widespread use in clinical settings.
Introduction to Metronidazole

Metronidazole works by entering the cells of microorganisms and damaging their DNA, which prevents them from reproducing and eventually leads to their death. This process is highly effective against anaerobic bacteria and protozoa, making metronidazole a first-line treatment for several types of infections. Its effectiveness, combined with its relatively low cost compared to other antibiotics, has made it a preferred choice for many healthcare providers.
Benefits of Metronidazole
The benefits of metronidazole are numerous, including its broad spectrum of activity, effectiveness against resistant strains of bacteria, and its ability to penetrate into abscesses and other areas where infections reside. Additionally, metronidazole has a relatively long half-life, which allows for less frequent dosing and improves patient compliance. However, like all medications, metronidazole is not without its side effects, which can range from mild gastrointestinal disturbances to more severe reactions such as neurological effects and allergic reactions.Uses of Metronidazole

Metronidazole is used to treat a variety of infections, including:
- Trichomoniasis: A sexually transmitted infection caused by the protozoan Trichomonas vaginalis.
- Amoebiasis: An infection caused by the protozoan Entamoeba histolytica, which can affect the intestines and other parts of the body.
- Giardiasis: An intestinal infection caused by the protozoan Giardia lamblia.
- Bacterial vaginosis: A condition characterized by an imbalance of the normal bacterial flora of the vagina.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): An infection of the female reproductive organs that can be caused by a variety of bacteria.
- Infections of the abdomen, skin, and soft tissues: Metronidazole is often used in combination with other antibiotics to treat these types of infections.
Side Effects and Considerations
While metronidazole is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects, including: - Nausea and vomiting - Diarrhea - Abdominal pain - Headache - Metallic taste - Neurological effects such as numbness, tingling, and seizures (rarely)It is essential for patients to follow the prescribed dosage and duration of treatment to minimize the risk of side effects and ensure the effectiveness of the medication. Additionally, metronidazole should not be used during the first trimester of pregnancy and should be used with caution in patients with liver disease.
Metronidazole Resistance
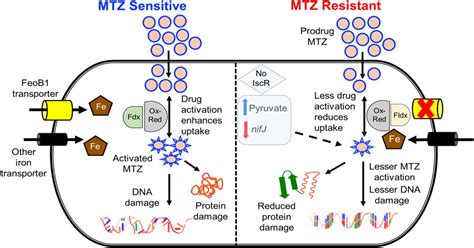
The emergence of resistance to metronidazole is a concern, as it can limit the effectiveness of the medication in treating certain infections. Resistance can develop through various mechanisms, including the inactivation of the drug within the microbial cell and alterations in the target site of the drug. To combat resistance, it is crucial to use metronidazole judiciously and to monitor for signs of resistance during treatment.
Prevention of Resistance
Preventing the development of resistance to metronidazole involves several strategies, including: - Using the medication only when necessary and for the recommended duration. - Combining metronidazole with other antibiotics when treating complex infections. - Monitoring for signs of resistance and adjusting treatment accordingly. - Developing new antibiotics and therapies to treat infections that are resistant to metronidazole.Metronidazole in Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
The use of metronidazole during pregnancy and breastfeeding requires careful consideration. While metronidazole is generally avoided during the first trimester due to potential risks to the fetus, it may be used in the second and third trimesters when the benefits outweigh the risks. In breastfeeding women, metronidazole is usually considered safe, but the infant should be monitored for signs of side effects.
Alternative Treatments
For patients who cannot use metronidazole due to resistance, side effects, or other considerations, alternative treatments are available. These may include other antibiotics, such as clindamycin or tinidazole, or non-antibiotic therapies, depending on the type of infection being treated. The choice of alternative treatment should be based on the specific needs of the patient and the susceptibility of the infecting organism to the medication.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, metronidazole is a valuable medication in the treatment of various infections. Its effectiveness, combined with its relatively low cost, makes it a preferred choice for many healthcare providers. However, the emergence of resistance and the potential for side effects highlight the need for judicious use and ongoing research into new therapies. As the medical community continues to navigate the challenges of antibiotic resistance, metronidazole will likely remain an important tool in the fight against infectious diseases.
Final Thoughts
As we look to the future, it is essential to consider the role of metronidazole in the context of emerging resistance patterns and the development of new antibiotics. By understanding the benefits and limitations of metronidazole, healthcare providers can make informed decisions about its use and contribute to the responsible stewardship of this valuable medication.What is metronidazole used for?
+Metronidazole is used to treat various infections caused by bacteria and protozoa, including trichomoniasis, amoebiasis, giardiasis, bacterial vaginosis, and infections of the abdomen, skin, and soft tissues.
How does metronidazole work?
+Metronidazole works by entering the cells of microorganisms and damaging their DNA, which prevents them from reproducing and eventually leads to their death.
What are the common side effects of metronidazole?
+Common side effects of metronidazole include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, headache, and a metallic taste. Rarely, it can cause neurological effects such as numbness, tingling, and seizures.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with metronidazole in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information. Your engagement and feedback are invaluable in helping us provide the most relevant and useful content.
