Intro
Discover 5 essential angioplasty tips to improve heart health, including balloon angioplasty, stent placement, and post-procedure care, for a successful coronary artery disease treatment and recovery, with expert advice on cardiac catheterization and vascular health management.
Angioplasty is a medical procedure used to widen narrowed or obstructed arteries or veins, typically to treat arterial atherosclerosis. This procedure is crucial for patients suffering from heart disease, as it can help restore blood flow and reduce the risk of heart attacks. Understanding the ins and outs of angioplasty can be daunting, but with the right information, patients can make informed decisions about their care. In this article, we will delve into the world of angioplasty, exploring its importance, benefits, and what patients can expect from the procedure.
The importance of angioplasty cannot be overstated. By widening narrowed arteries, this procedure can help reduce the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events. Additionally, angioplasty can help alleviate symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue, significantly improving a patient's quality of life. With the advancements in medical technology, angioplasty has become a relatively safe and effective procedure, with a high success rate. However, as with any medical procedure, there are risks and potential complications that patients should be aware of.
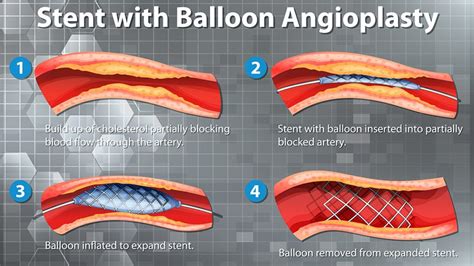
For patients undergoing angioplasty, it is essential to understand the procedure and what to expect. The procedure typically involves the insertion of a catheter into an artery in the leg or arm, which is then guided to the affected area using X-ray imaging. A balloon on the catheter is then inflated to widen the artery, and a stent may be placed to keep the artery open. While the procedure can be intimidating, patients can take comfort in knowing that it is relatively quick, usually taking around 30 minutes to an hour to complete. Furthermore, with the right preparation and aftercare, patients can minimize the risk of complications and ensure a smooth recovery.
Understanding Angioplasty
Benefits of Angioplasty
The benefits of angioplasty are numerous. By widening narrowed arteries, angioplasty can help restore blood flow and reduce the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events. Additionally, angioplasty can help alleviate symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue, significantly improving a patient's quality of life. Angioplasty can also help patients avoid more invasive procedures, such as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG). Furthermore, angioplasty is a relatively quick procedure, usually taking around 30 minutes to an hour to complete, and patients can typically return home the same day.Preparing for Angioplasty
What to Expect During Angioplasty
During angioplasty, patients can expect to feel some discomfort, but the procedure is usually not painful. The doctor will insert a catheter into an artery in the leg or arm and guide it to the affected area using X-ray imaging. Once the catheter is in place, a balloon on the catheter is inflated to widen the artery, and a stent may be placed to keep the artery open. The procedure usually takes around 30 minutes to an hour to complete, and patients can typically return home the same day. After the procedure, patients may experience some bruising or swelling at the catheter site, but this should resolve on its own within a few days.Recovering from Angioplasty
Tips for a Smooth Recovery
Here are some tips for a smooth recovery from angioplasty: * Follow the doctor's instructions carefully * Avoid heavy lifting, bending, or strenuous activities for a few days after the procedure * Take any medications as directed * Monitor the catheter site for any signs of infection * Seek medical attention immediately if symptoms occur * Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water * Get plenty of rest to help the body recoverRisks and Complications of Angioplasty
Minimizing the Risk of Complications
To minimize the risk of complications, patients should: * Follow the doctor's instructions carefully * Inform their doctor about any allergies or medical conditions * Take any medications as directed * Monitor the catheter site for any signs of infection * Seek medical attention immediately if symptoms occurAngioplasty and Stents
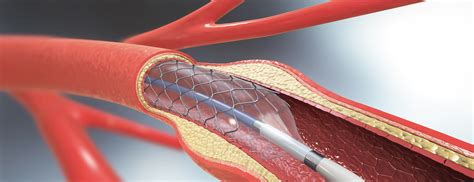
Benefits of Stents
The benefits of stents include: * Keeping the artery open after angioplasty * Reducing the risk of restenosis (re-narrowing of the artery) * Improving blood flow to the heart * Reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes * Improving symptoms such as chest pain and shortness of breathAngioplasty and Lifestyle Changes

Importance of Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes are essential for patients who have undergone angioplasty. By making healthy lifestyle changes, patients can reduce the risk of further cardiovascular events and improve their overall health. Additionally, lifestyle changes can help improve symptoms such as chest pain and shortness of breath, and improve overall quality of life.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with angioplasty in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please share it with your friends and family who may be considering angioplasty.
What is angioplasty?
+Angioplasty is a medical procedure used to widen narrowed or obstructed arteries or veins, typically to treat arterial atherosclerosis.
What are the benefits of angioplasty?
+The benefits of angioplasty include restoring blood flow, reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes, and improving symptoms such as chest pain and shortness of breath.
What are the risks and complications of angioplasty?
+The risks and complications of angioplasty include bleeding or hematoma at the catheter site, infection, allergic reaction to the contrast dye, kidney damage, stroke or heart attack, restenosis, and death.
