Intro
Nitroglycerin is a medication that has been used for over a century to treat various health conditions, particularly those related to the heart. It is a powerful vasodilator, which means it helps to widen blood vessels and improve blood flow. This medication is commonly used to treat conditions such as angina pectoris, heart failure, and hypertension. In this article, we will delve into the world of nitroglycerin, exploring its history, benefits, working mechanisms, and potential side effects.
Nitroglycerin has a rich history that dates back to the mid-19th century. It was first synthesized in 1846 by Italian chemist Ascanio Sobrero, who discovered its explosive properties. However, it wasn't until the early 20th century that nitroglycerin began to be used medicinally. The medication was initially used to treat angina pectoris, a condition characterized by chest pain due to reduced blood flow to the heart. Over time, its use has expanded to include other cardiovascular conditions, such as heart failure and hypertension.
The importance of nitroglycerin lies in its ability to rapidly relieve symptoms of angina and other cardiovascular conditions. When taken sublingually (under the tongue), nitroglycerin is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream, where it begins to work its magic. By widening blood vessels and reducing blood pressure, nitroglycerin helps to increase blood flow to the heart, reducing the workload on this vital organ. This, in turn, can help to alleviate symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue.
Nitroglycerin Mechanism of Action
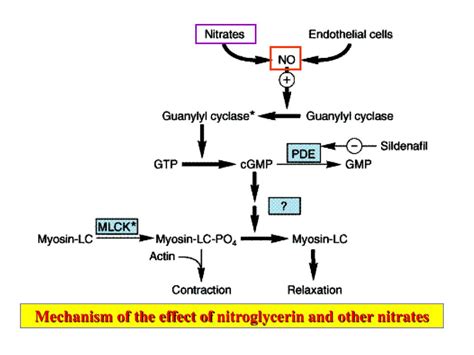
Nitroglycerin works by releasing nitric oxide, a potent vasodilator, into the bloodstream. Nitric oxide then binds to guanylate cyclase, an enzyme found in smooth muscle cells, causing a relaxation of these cells. This relaxation leads to a widening of blood vessels, which in turn reduces blood pressure and increases blood flow to the heart. The increased blood flow helps to reduce the workload on the heart, alleviating symptoms of angina and other cardiovascular conditions.
Benefits of Nitroglycerin

The benefits of nitroglycerin are numerous and well-documented. Some of the most significant advantages of this medication include:
- Rapid relief from angina symptoms: Nitroglycerin can provide quick relief from chest pain, shortness of breath, and other symptoms associated with angina.
- Improved blood flow: By widening blood vessels, nitroglycerin helps to increase blood flow to the heart, reducing the workload on this vital organ.
- Reduced blood pressure: Nitroglycerin can help to lower blood pressure, reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease and stroke.
- Increased exercise tolerance: By improving blood flow and reducing symptoms of angina, nitroglycerin can help individuals with cardiovascular conditions to exercise more comfortably.
Nitroglycerin Administration and Dosage

Nitroglycerin can be administered in various forms, including sublingual tablets, sprays, and patches. The dosage and administration of nitroglycerin will depend on the individual's specific needs and medical condition. Generally, the medication is taken as needed to relieve symptoms of angina, with the typical dosage ranging from 0.3 to 0.6 milligrams. It is essential to follow the doctor's instructions and take the medication exactly as prescribed to ensure optimal benefits and minimize potential side effects.
Potential Side Effects of Nitroglycerin
While nitroglycerin is generally well-tolerated, there are potential side effects to be aware of. Some of the most common side effects include:
- Headache: Nitroglycerin can cause headaches due to its vasodilatory effects.
- Dizziness: The medication can cause dizziness and lightheadedness, particularly when standing up quickly.
- Nausea and vomiting: Some individuals may experience nausea and vomiting when taking nitroglycerin.
- Low blood pressure: Nitroglycerin can cause a sudden drop in blood pressure, leading to dizziness and lightheadedness.
Nitroglycerin Interactions and Contraindications

Nitroglycerin can interact with various medications, including:
- Phosphodiesterase inhibitors: Medications such as sildenafil (Viagra) can interact with nitroglycerin, leading to a sudden drop in blood pressure.
- Beta-blockers: Beta-blockers can increase the risk of hypotension (low blood pressure) when taken with nitroglycerin.
- Calcium channel blockers: Calcium channel blockers can also increase the risk of hypotension when taken with nitroglycerin.
It is essential to inform your doctor about any medications you are taking before starting nitroglycerin therapy.
Nitroglycerin and Pregnancy

Nitroglycerin is generally not recommended during pregnancy, particularly in the first trimester. The medication can cause a sudden drop in blood pressure, which can be detrimental to the developing fetus. However, in some cases, the benefits of nitroglycerin may outweigh the risks, and the medication may be prescribed under close medical supervision.
Nitroglycerin and Breastfeeding

Nitroglycerin is generally considered safe during breastfeeding, as it is not expected to pass into breast milk in significant amounts. However, it is essential to consult with your doctor before taking any medication while breastfeeding, as they can provide personalized advice and guidance.
Nitroglycerin Overdose

A nitroglycerin overdose can occur if an individual takes too much of the medication. Symptoms of an overdose may include:
- Severe headache
- Dizziness and lightheadedness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Low blood pressure
- Confusion and disorientation
If you suspect a nitroglycerin overdose, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately.
Nitroglycerin Storage and Disposal
Nitroglycerin should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture. The medication should be kept out of reach of children and pets, as it can be toxic if ingested. If you need to dispose of nitroglycerin, it is essential to follow the recommended disposal procedures to minimize the risk of environmental contamination.
What is nitroglycerin used for?
+Nitroglycerin is used to treat various cardiovascular conditions, including angina pectoris, heart failure, and hypertension.
How does nitroglycerin work?
+Nitroglycerin works by releasing nitric oxide, a potent vasodilator, into the bloodstream, causing a relaxation of smooth muscle cells and a widening of blood vessels.
What are the potential side effects of nitroglycerin?
+Potential side effects of nitroglycerin include headache, dizziness, nausea, and low blood pressure.
Can I take nitroglycerin during pregnancy?
+Nitroglycerin is generally not recommended during pregnancy, particularly in the first trimester, due to the risk of hypotension and potential harm to the developing fetus.
Can I take nitroglycerin while breastfeeding?
+Nitroglycerin is generally considered safe during breastfeeding, as it is not expected to pass into breast milk in significant amounts.
In conclusion, nitroglycerin is a powerful medication that has been used for over a century to treat various cardiovascular conditions. Its benefits, working mechanisms, and potential side effects make it an essential medication for individuals with angina, heart failure, and hypertension. By understanding how nitroglycerin works and its potential interactions, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment and take steps to minimize the risk of side effects. If you have any questions or concerns about nitroglycerin, be sure to consult with your doctor or healthcare provider. We encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from this information and to comment below with any questions or thoughts you may have.
