Intro
Discover the Norethindrone Medication Guide, covering uses, side effects, and interactions of this synthetic progestin hormone, including birth control, menopause symptoms, and menstrual regulation, to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Norethindrone is a synthetic form of progestin, a hormone that plays a crucial role in the female reproductive system. It is commonly used in various medications, including birth control pills, to regulate menstrual cycles, treat endometriosis, and manage other conditions related to hormonal imbalances. Understanding the importance of norethindrone and its effects on the body is essential for individuals considering or already using medications containing this hormone.
The use of norethindrone has become increasingly prevalent due to its effectiveness in addressing a range of health issues. From regulating irregular periods to alleviating symptoms of menopause, norethindrone has proven to be a versatile and valuable component of many treatment plans. However, like any medication, it is crucial to approach its use with a comprehensive understanding of its benefits, potential side effects, and interactions with other substances. This knowledge enables individuals to make informed decisions about their health and ensures the safe and effective use of norethindrone-containing medications.
As the role of norethindrone in healthcare continues to expand, so does the need for detailed information about its mechanism of action, dosages, and potential risks. Whether used for contraceptive purposes, to manage hormonal deficiencies, or as part of hormone replacement therapy, understanding the specifics of norethindrone is vital for maximizing its benefits while minimizing its risks. This guide aims to provide a thorough overview of norethindrone, covering its uses, side effects, and essential considerations for those using or considering medications that contain this hormone.
Norethindrone Uses and Benefits

Menstrual Regulation and Endometriosis Treatment
Norethindrone's ability to regulate menstrual cycles makes it an effective treatment for conditions like dysmenorrhea (painful menstruation) and menorrhagia (heavy menstrual bleeding). By inducing a state of pseudo-pregnancy, it can reduce the frequency and severity of menstrual periods, offering relief to individuals suffering from these conditions. For endometriosis, norethindrone can be used continuously or cyclically to suppress the growth of endometrial implants, thereby reducing pain and inflammation associated with the condition.How Norethindrone Works
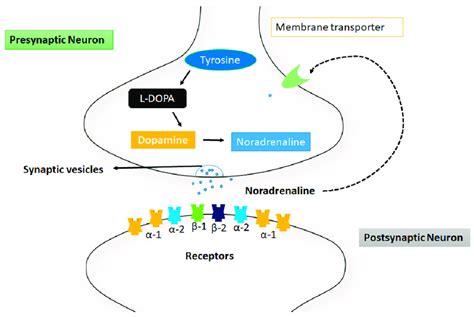
Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism
Understanding the pharmacokinetics of norethindrone, including its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, is crucial for optimizing its therapeutic effects and minimizing potential side effects. Norethindrone is absorbed quickly after oral administration, reaching peak levels within a few hours. It is then metabolized by the liver and excreted in the urine. The metabolism of norethindrone involves various pathways, including hydroxylation and reduction, resulting in several metabolites that contribute to its overall pharmacological effect.Potential Side Effects and Risks
Contraindications and Interactions
Norethindrone is contraindicated in certain conditions, including known or suspected pregnancy, severe liver disease, and a history of breast cancer. It may also interact with other medications, such as anticonvulsants, rifampin, and certain anti-HIV drugs, which can affect its efficacy or increase the risk of side effects. Individuals should inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking before starting norethindrone.Dosage and Administration

Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular monitoring is crucial for individuals taking norethindrone, especially during the initial phases of treatment. This includes tracking menstrual cycles, monitoring for side effects, and adjusting the dosage as necessary. Annual check-ups with a healthcare provider are recommended to assess the continued efficacy and safety of norethindrone treatment.Practical Considerations and Lifestyle Advice

Nutritional and Dietary Considerations
A well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help support hormonal balance and overall health. Certain nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and calcium, may also play a role in mitigating side effects or enhancing the therapeutic effects of norethindrone. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider before making any significant dietary changes.Conclusion and Future Directions

Final Thoughts and Recommendations
For those considering or currently using norethindrone, it is crucial to maintain open communication with healthcare providers, report any side effects promptly, and adhere to prescribed treatment plans. By doing so, individuals can maximize the benefits of norethindrone while ensuring their safety and well-being. As the field of women's health continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest developments and advancements in norethindrone therapy will be essential for making informed decisions about one's health.What is norethindrone used for?
+Norethindrone is used for birth control, to treat endometriosis, and for managing other conditions related to hormonal imbalances.
How does norethindrone work?
+Norethindrone works by binding to progesterone receptors, mimicking the effects of natural progesterone, and affecting various physiological processes.
What are the potential side effects of norethindrone?
+Potential side effects include nausea, breast tenderness, headache, and mood changes. Rare but more severe side effects can include blood clots, stroke, or liver tumors.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about norethindrone in the comments below. Your engagement and feedback are invaluable in creating a comprehensive and supportive community focused on women's health and wellness. If you found this guide informative and helpful, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information. Together, we can promote a deeper understanding of norethindrone and its role in maintaining and improving health outcomes for individuals around the world.
