Intro
Discover oxybutynin uses and benefits for overactive bladder treatment, including symptom relief and improved bladder control, with related medications and therapies.
Oxybutynin is a medication that has been widely used for several decades to treat various medical conditions, primarily those related to the urinary system. Its effectiveness in managing symptoms of overactive bladder, urinary incontinence, and other related issues has made it a staple in the field of urology. Understanding the uses and benefits of oxybutynin is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike, as it can significantly improve the quality of life for those suffering from these conditions.
The importance of oxybutynin lies in its ability to address the uncomfortable and often embarrassing symptoms associated with overactive bladder and urinary incontinence. These conditions can affect individuals of all ages, though they are more common among the elderly. The impact on daily life can be substantial, affecting not only physical health but also psychological well-being and social interactions. Therefore, finding effective treatments is paramount, and oxybutynin has emerged as a valuable option.
Oxybutynin works by relaxing the muscles in the bladder, thereby increasing its capacity to hold urine and reducing the urgency to urinate. This mechanism of action helps in controlling the symptoms of overactive bladder, such as frequent urination, urgent need to urinate, and leakage of urine. By managing these symptoms, oxybutynin improves the patient's ability to engage in daily activities without the constant worry of urinary leakage or the need for frequent bathroom visits.
Oxybutynin Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of oxybutynin involves its anticholinergic and antispasmodic properties. As an anticholinergic agent, oxybutynin blocks the action of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that stimulates the bladder muscle, leading to contractions and the sensation of needing to urinate. By blocking these receptors, oxybutynin reduces the frequency and urgency of urination. Additionally, its antispasmodic properties help in relaxing the smooth muscle of the bladder, further contributing to its therapeutic effects.
Benefits of Oxybutynin

The benefits of oxybutynin are multifaceted, offering relief from the bothersome symptoms of overactive bladder and urinary incontinence. Some of the key benefits include:
- Improved bladder control: By reducing the urgency and frequency of urination, oxybutynin helps patients regain control over their bladder.
- Enhanced quality of life: With reduced symptoms of urinary incontinence, patients can engage more freely in social and physical activities without the fear of leakage.
- Reduced risk of accidents: The medication decreases the likelihood of urinary accidents, which can be embarrassing and distressing.
- Better sleep: By minimizing nighttime urination, oxybutynin can help improve sleep quality, which is essential for overall health and well-being.
Common Uses of Oxybutynin
Oxybutynin is commonly used for: - Overactive bladder (OAB) with symptoms of urge incontinence, urgency, and frequency. - Neurogenic bladder, which is a condition where a person has trouble with bladder control due to a brain, spinal cord, or nerve problem. - Enuresis, or bedwetting, in children.Oxybutynin Side Effects and Precautions

While oxybutynin is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects. Common side effects include dry mouth, constipation, and drowsiness. Less common but more serious side effects can include confusion, especially in the elderly, and heat intolerance. It is essential for patients to discuss any concerns or side effects with their healthcare provider, as adjustments in dosage or switching to a different medication may be necessary.
Precautions and Interactions
Before starting oxybutynin, patients should inform their healthcare provider about any other medications they are taking, including over-the-counter drugs, as oxybutynin can interact with various medications. Additionally, patients with certain medical conditions, such as narrow-angle glaucoma, gastrointestinal obstruction, or ulcerative colitis, should use oxybutynin with caution.Oxybutynin Dosage and Administration
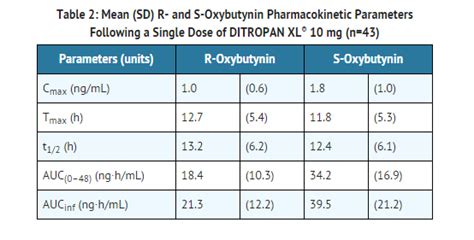
The dosage of oxybutynin varies depending on the patient's age, medical condition, and response to treatment. It is available in various formulations, including tablets, syrup, and extended-release tablets. The typical dose for adults with overactive bladder is 5 mg two to three times a day. The dosage can be adjusted based on the patient's response and tolerance to the medication.
Extended-Release Formulation
The extended-release formulation of oxybutynin is designed to release the medication slowly over time, allowing for once-daily dosing. This formulation can offer improved patient compliance and may reduce side effects associated with peak drug levels.Oxybutynin for Children
Oxybutynin is also used in the treatment of enuresis (bedwetting) in children. The medication helps by increasing bladder capacity and reducing the contractions of the bladder muscle that can lead to bedwetting. The dosage for children is typically lower than for adults and is adjusted based on the child's weight and response to the medication.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Children on oxybutynin for enuresis should be monitored regularly for effectiveness and potential side effects. The goal of treatment is not only to reduce or eliminate bedwetting but also to improve the child's self-esteem and overall well-being.Oxybutynin and Pregnancy

The use of oxybutynin during pregnancy should be approached with caution. While there is limited data on the safety of oxybutynin in pregnant women, animal studies have shown potential risks. Oxybutynin should only be used during pregnancy if the benefits to the mother outweigh the potential risks to the fetus.
Alternatives and Future Directions
For pregnant women or those planning to become pregnant, alternative treatments for overactive bladder and urinary incontinence may be considered. These can include behavioral therapies, pelvic floor exercises, and other medications with safer profiles during pregnancy.Oxybutynin vs. Other Medications
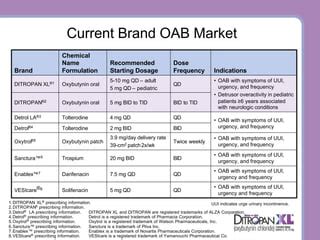
Oxybutynin is one of several medications available for the treatment of overactive bladder and urinary incontinence. Other medications in its class, such as tolterodine and solifenacin, offer similar benefits but may have different side effect profiles. The choice of medication depends on the patient's specific needs, medical history, and how they respond to treatment.
Comparison of Efficacy and Safety
Studies comparing oxybutynin with other antimuscarinic agents have shown that while efficacy may be similar, the side effect profiles can vary. For example, oxybutynin may cause more dry mouth compared to some other medications, but it can be as effective in controlling symptoms of overactive bladder.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In conclusion, oxybutynin is a valuable medication for the management of overactive bladder, urinary incontinence, and other related conditions. Its benefits in improving bladder control, enhancing quality of life, and reducing the risk of urinary accidents make it a preferred treatment option for many patients. However, like all medications, it should be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider, with careful consideration of its potential side effects and interactions.
As research continues to advance, new treatments and formulations of oxybutynin may become available, offering improved efficacy and safety profiles. For now, oxybutynin remains a cornerstone in the management of urinary disorders, providing relief and improving the lives of countless individuals worldwide.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with oxybutynin in the comments below. Your insights can help others understand the benefits and challenges of this medication, fostering a supportive community for those managing urinary health issues.
What is oxybutynin used for?
+Oxybutynin is used to treat overactive bladder and its symptoms, including frequent urination, urgent need to urinate, and leakage of urine.
How does oxybutynin work?
+Oxybutynin works by relaxing the muscles in the bladder, increasing its capacity to hold urine and reducing the urgency to urinate.
What are the common side effects of oxybutynin?
+Common side effects of oxybutynin include dry mouth, constipation, and drowsiness. Less common but more serious side effects can include confusion and heat intolerance.
